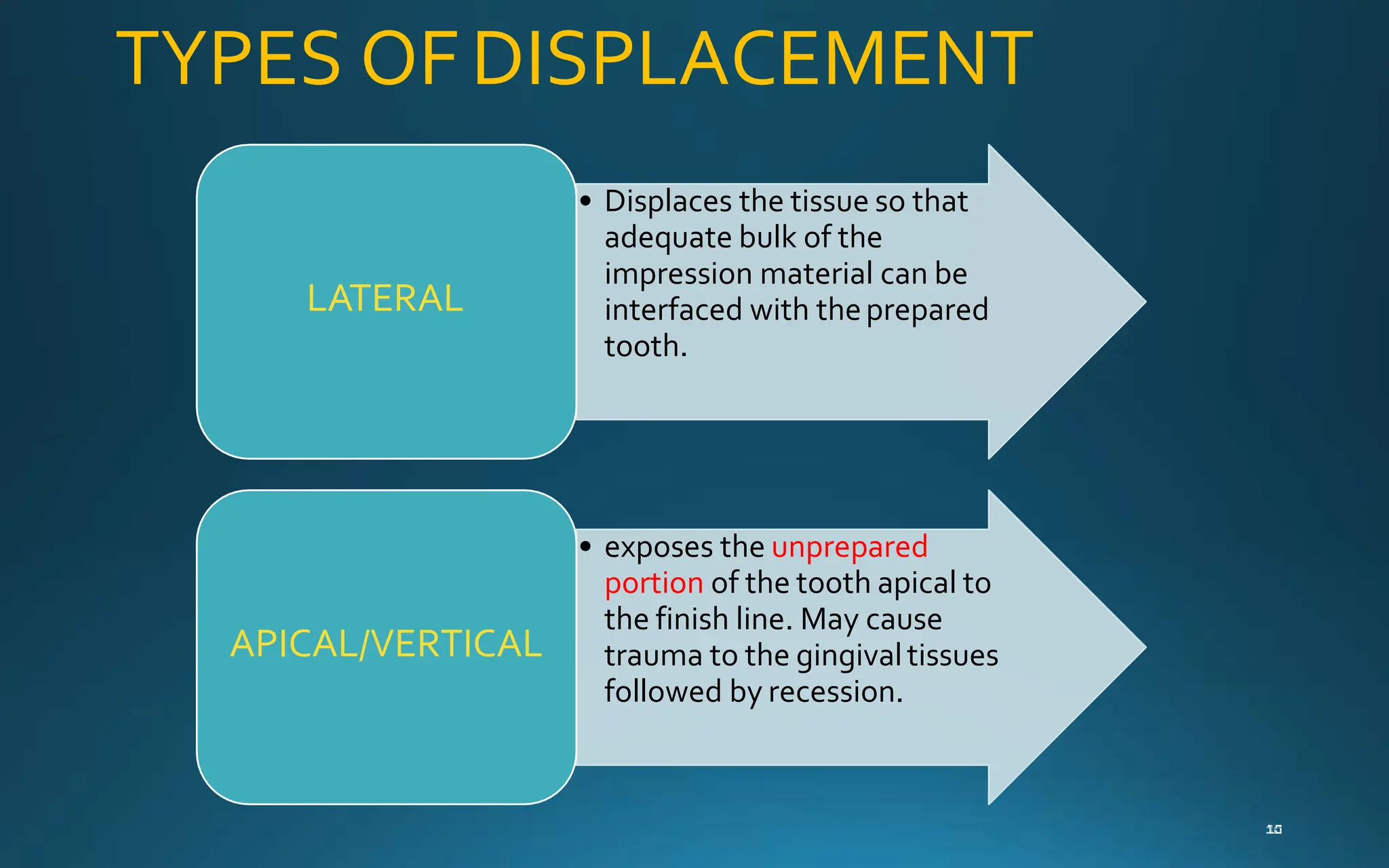
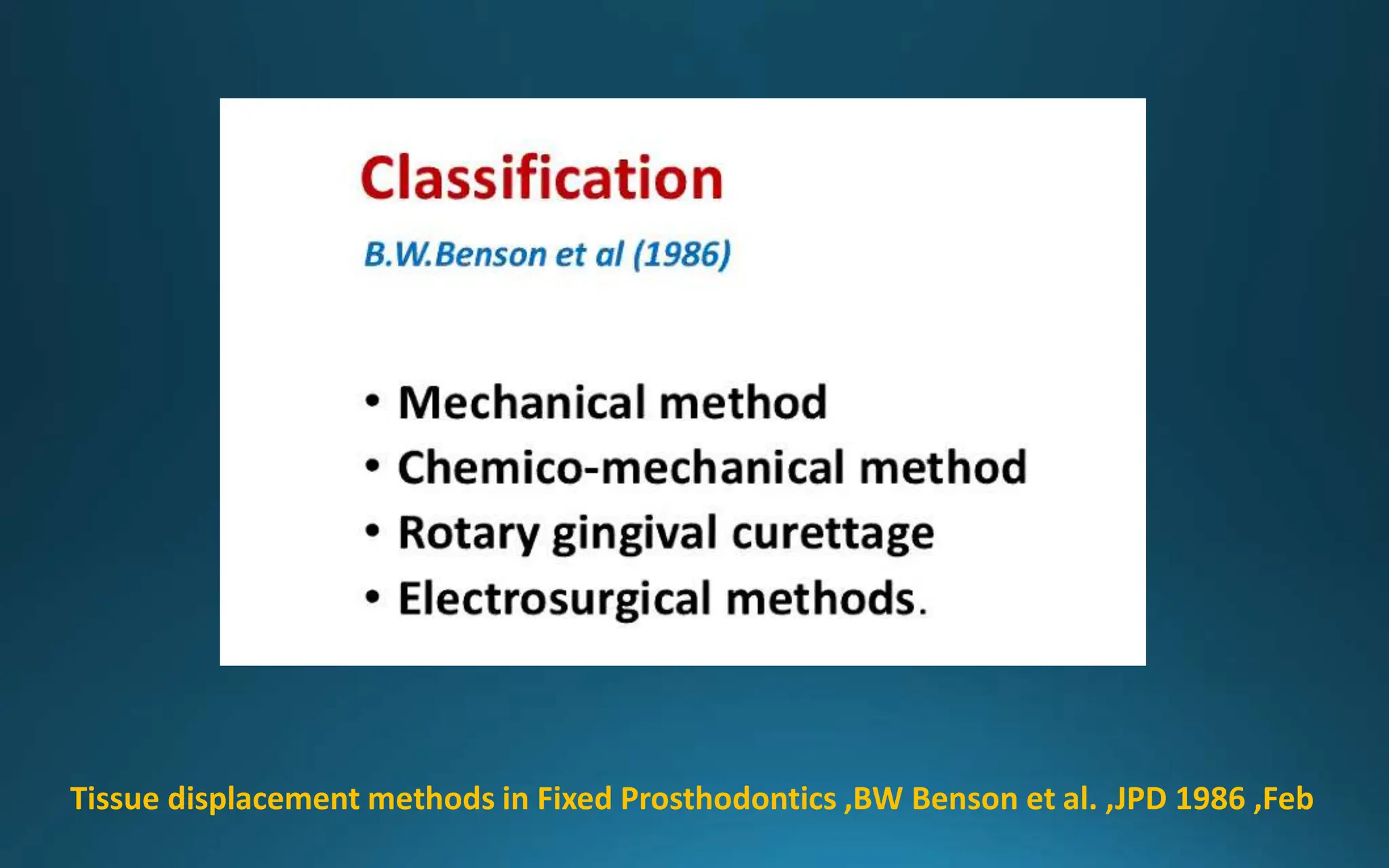
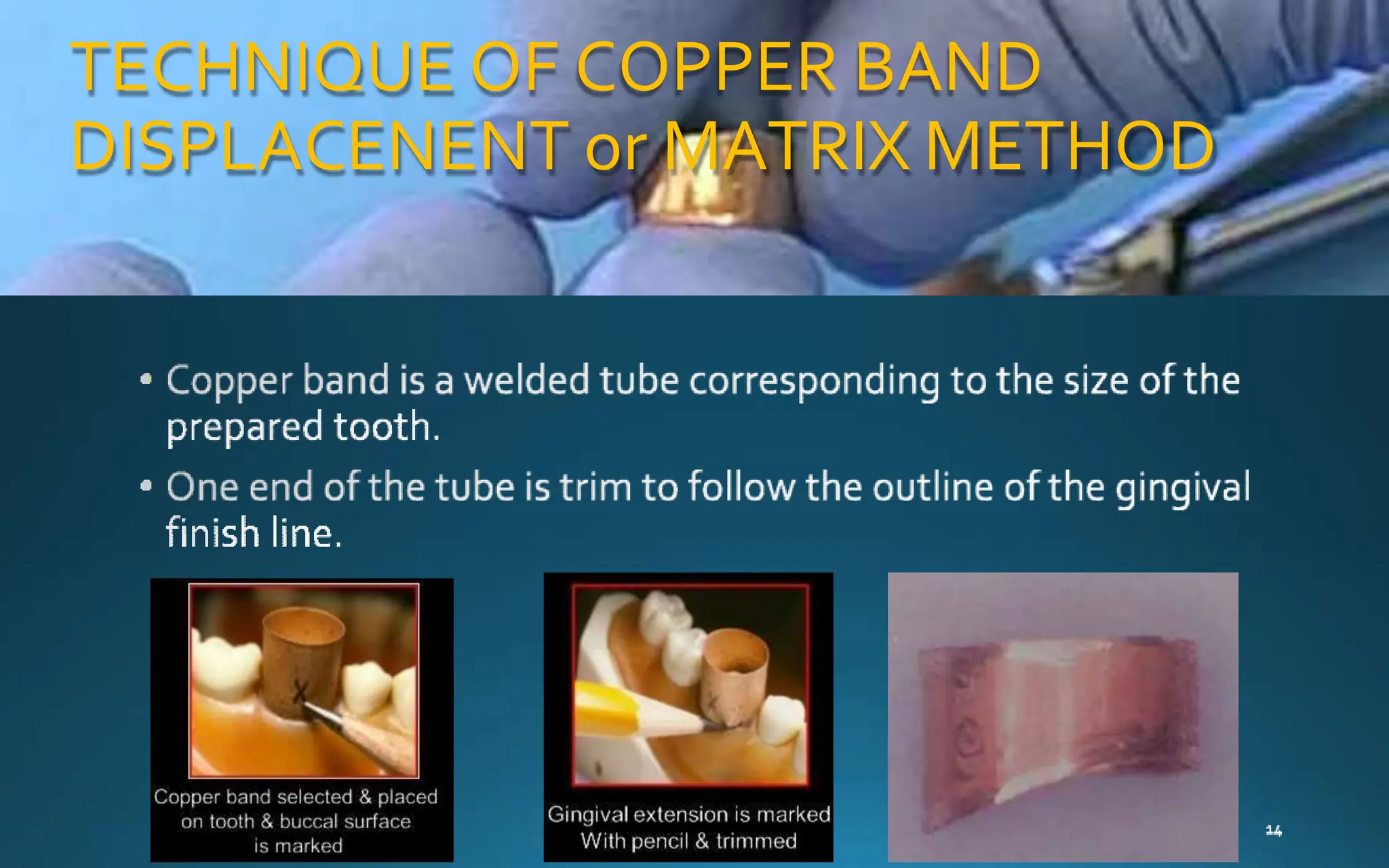
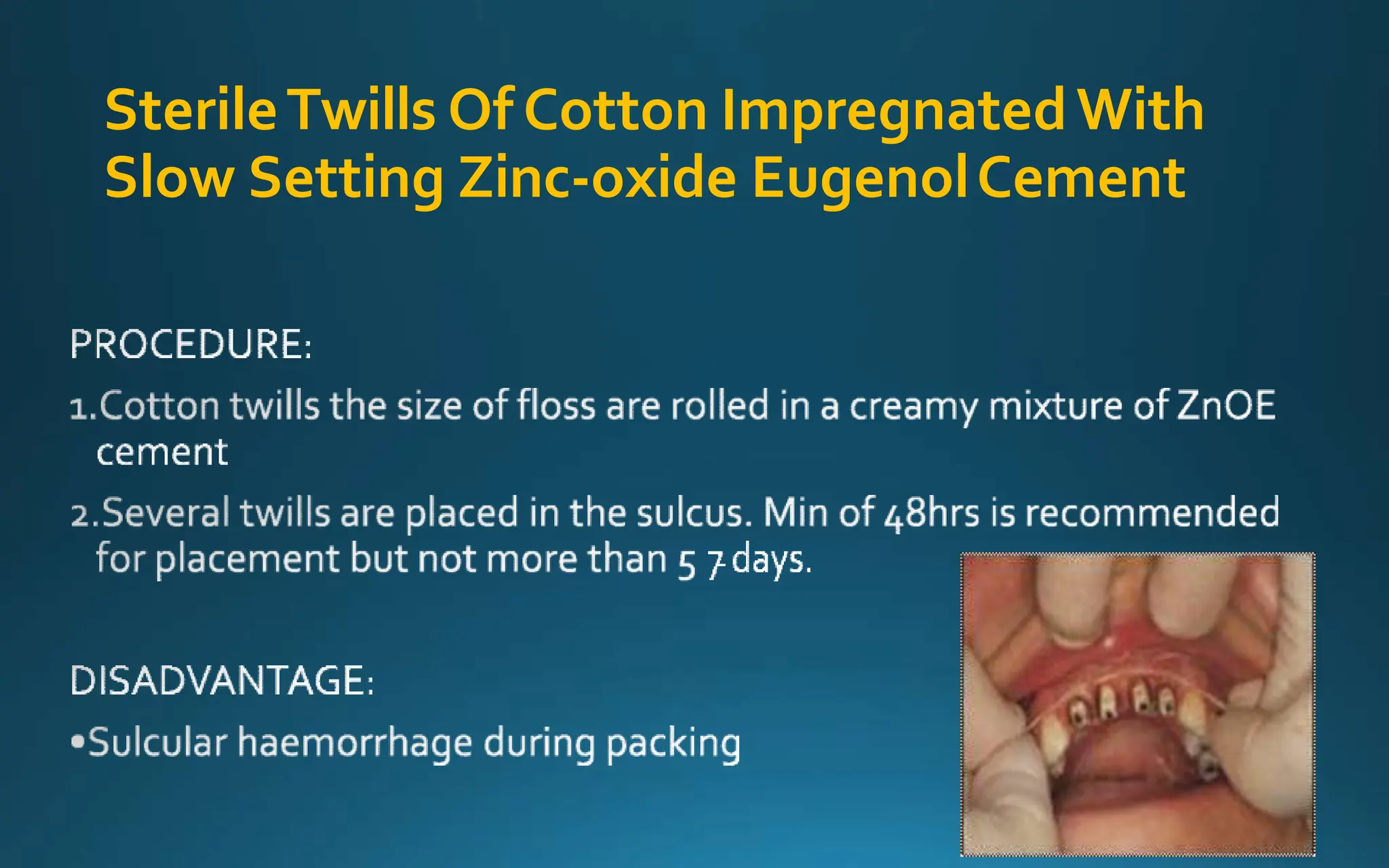
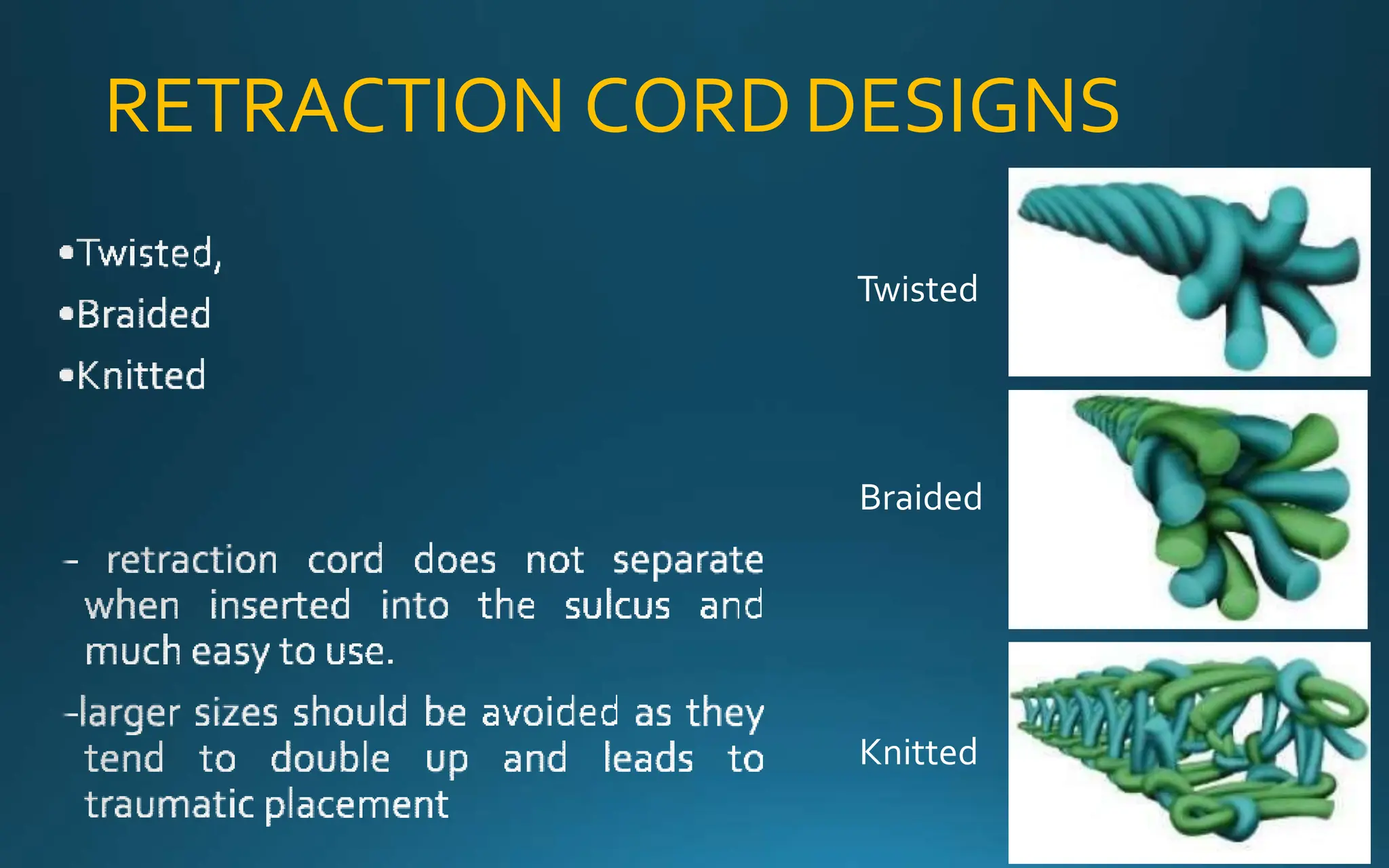
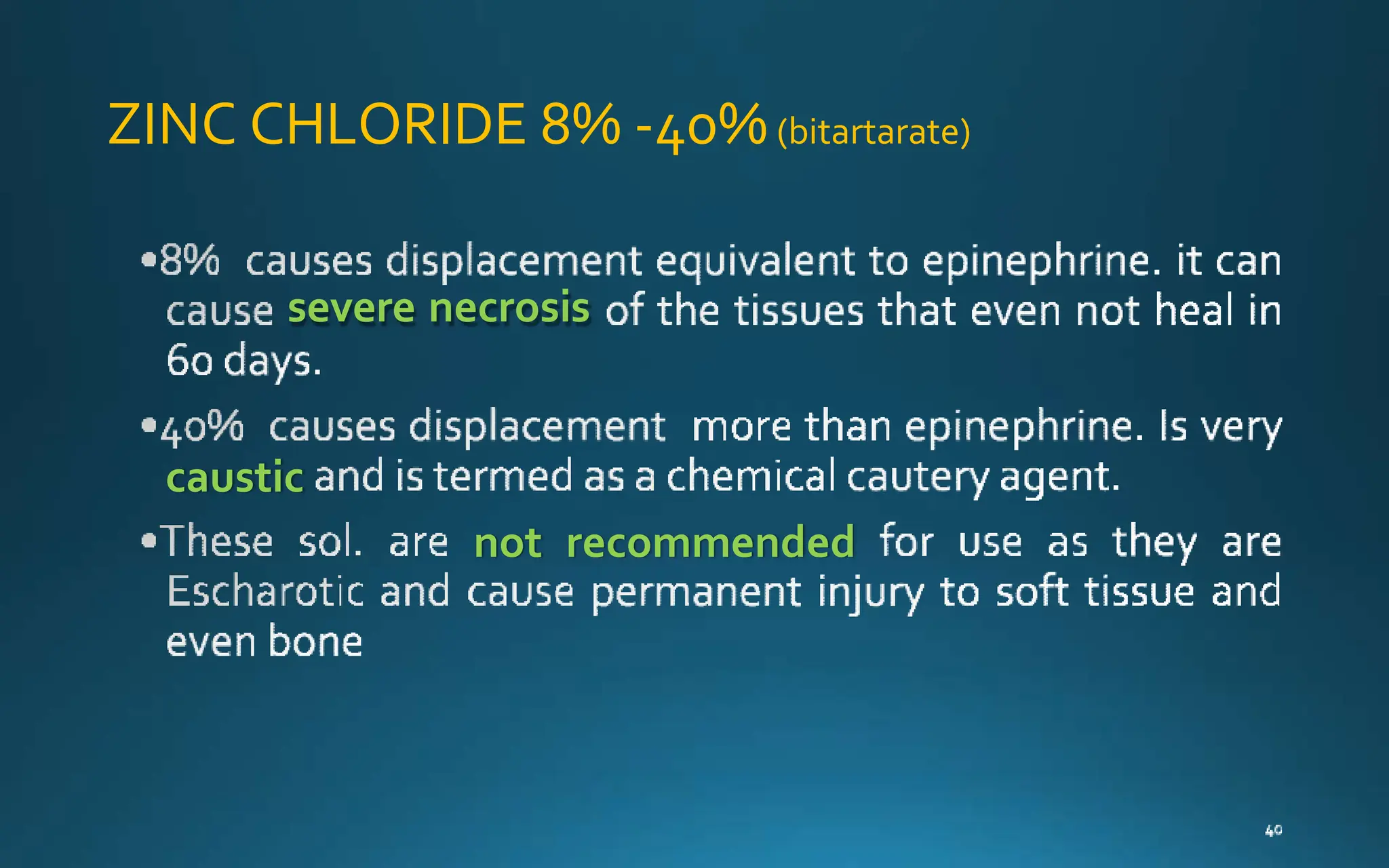
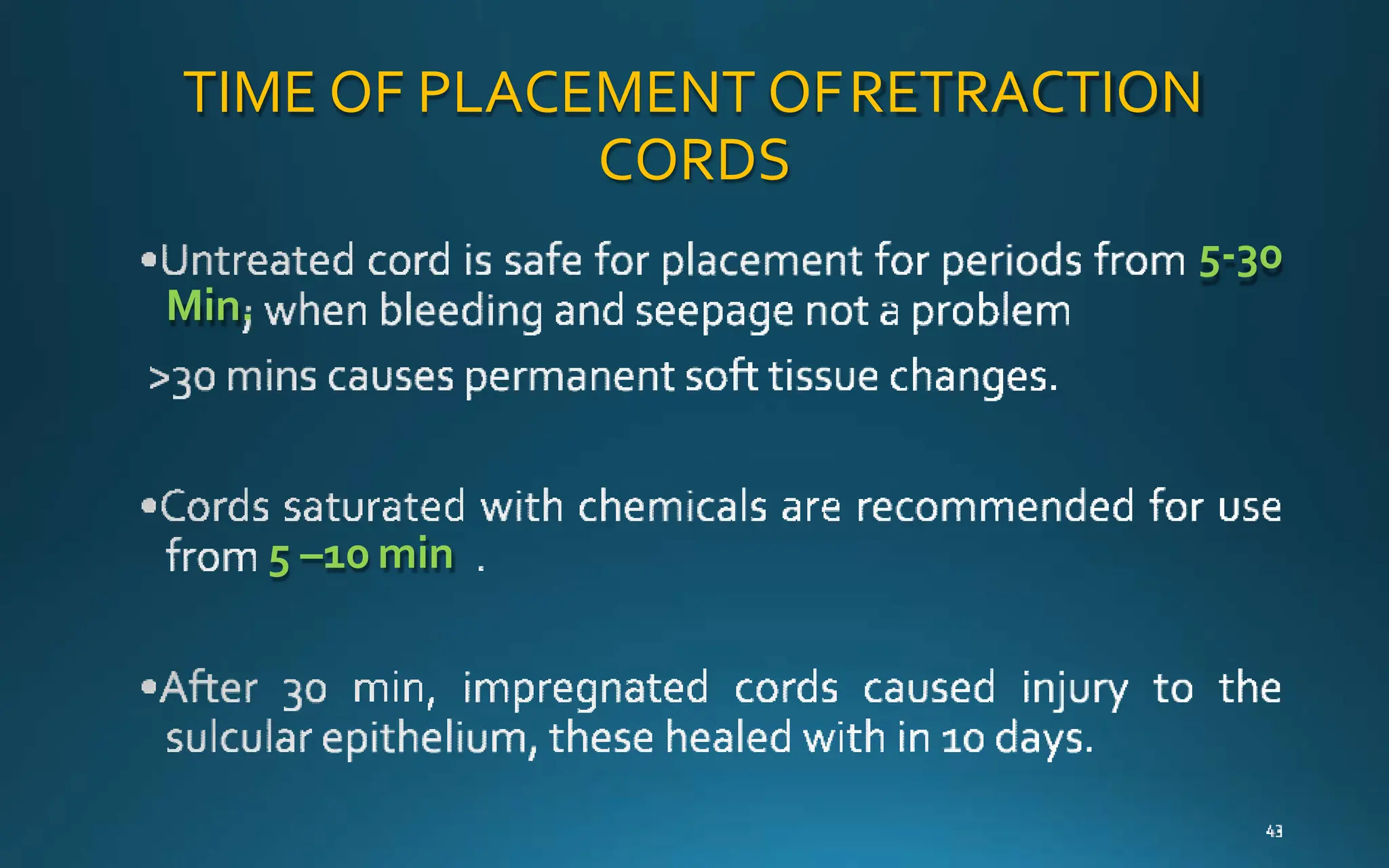
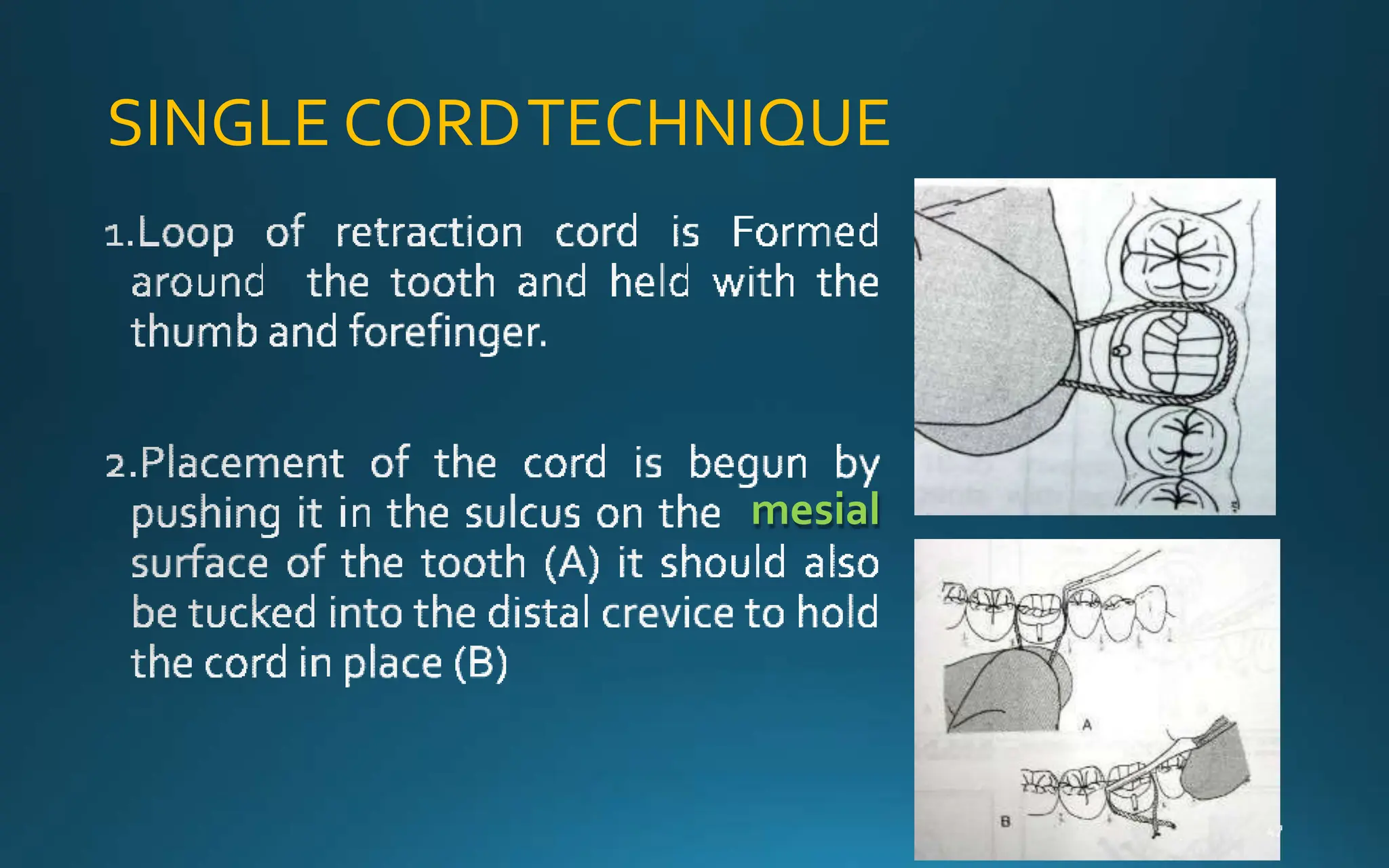
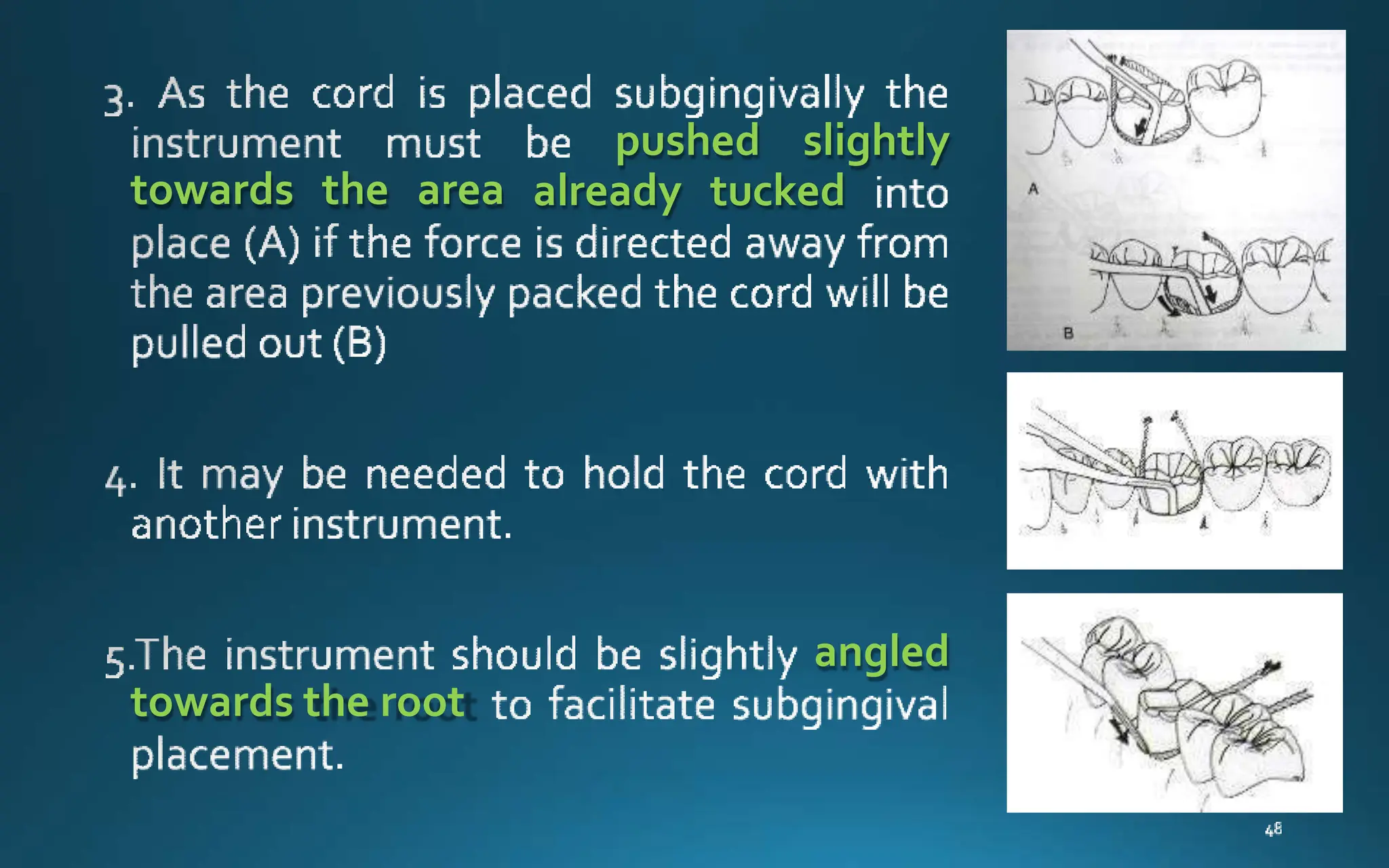
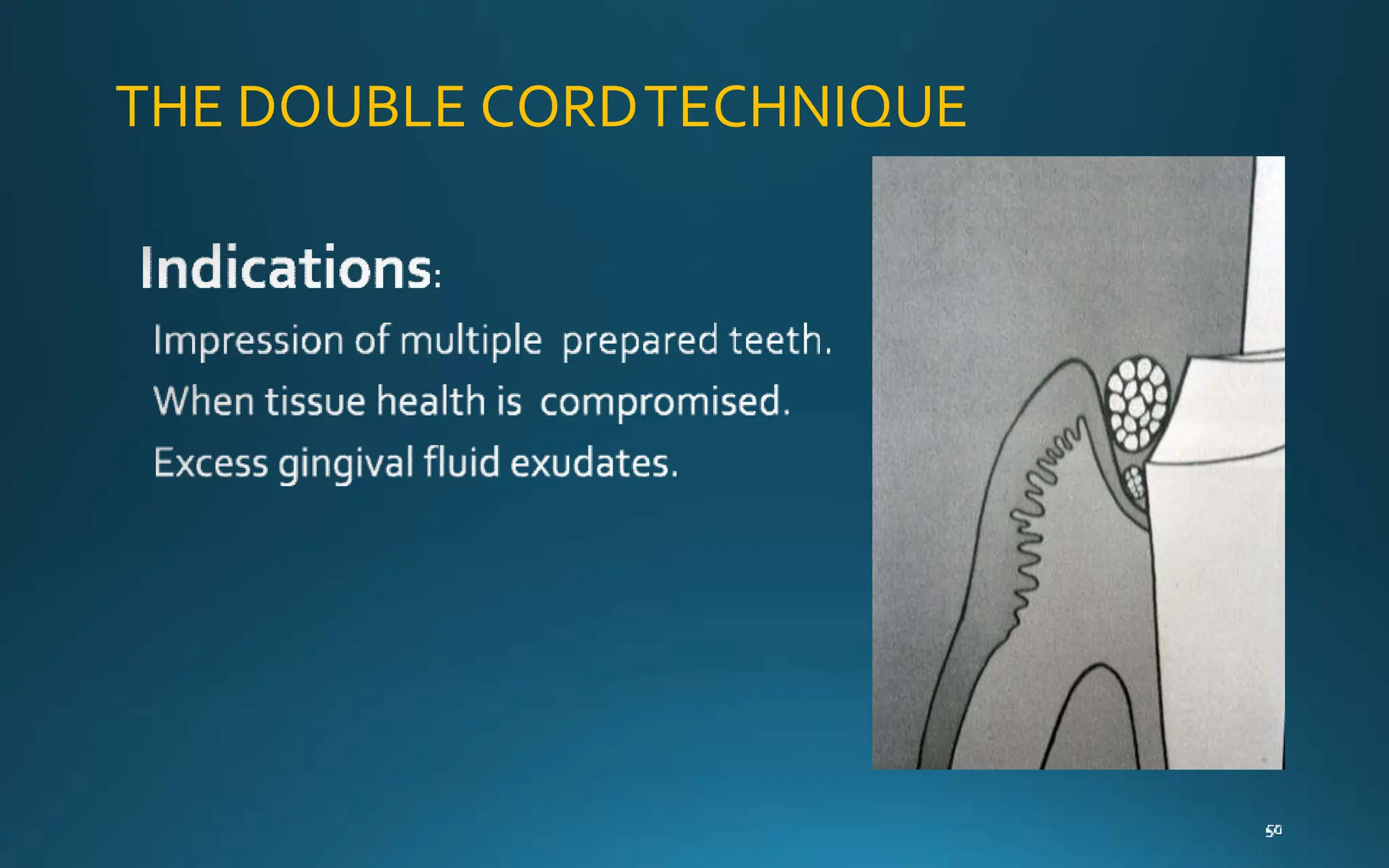
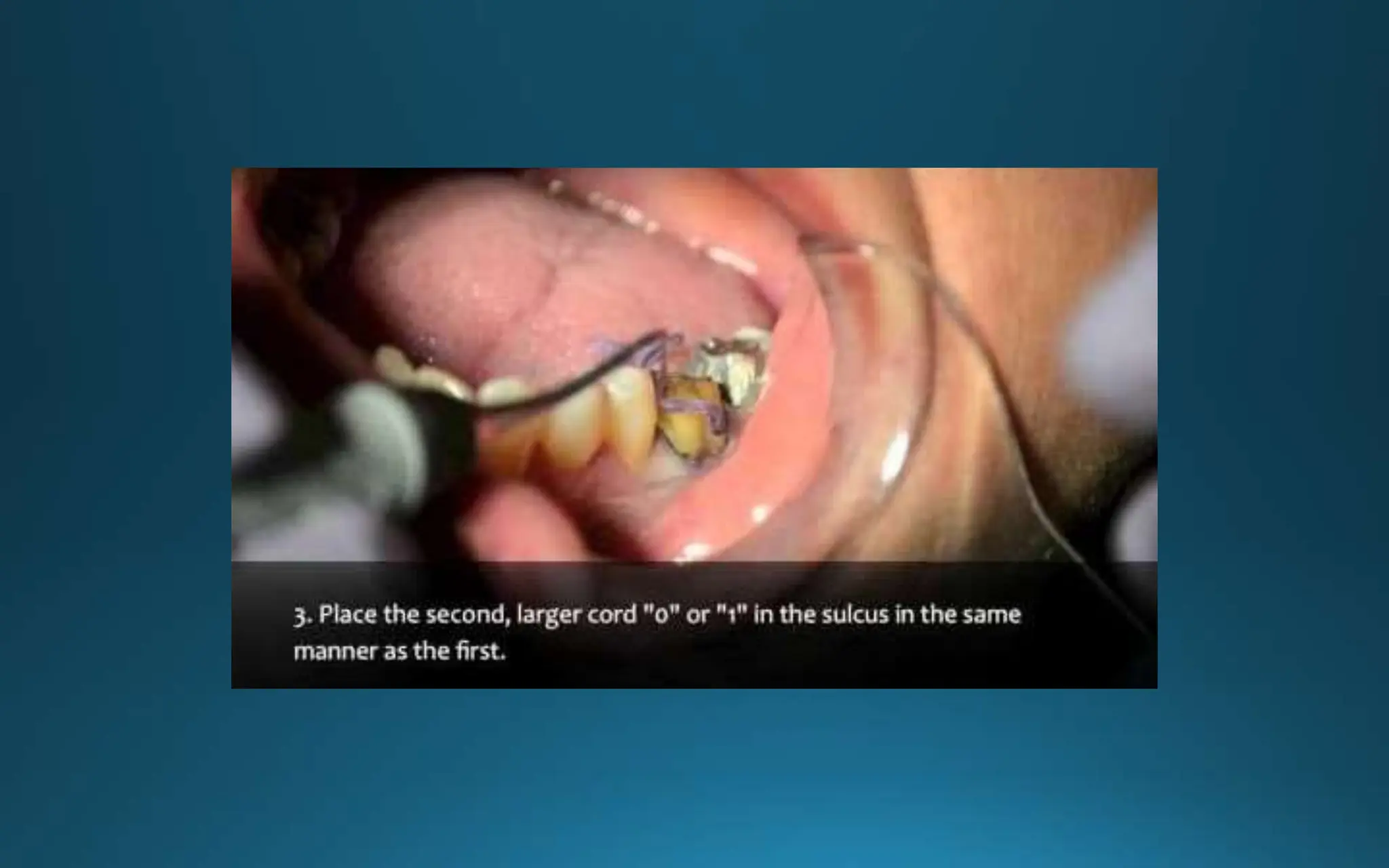
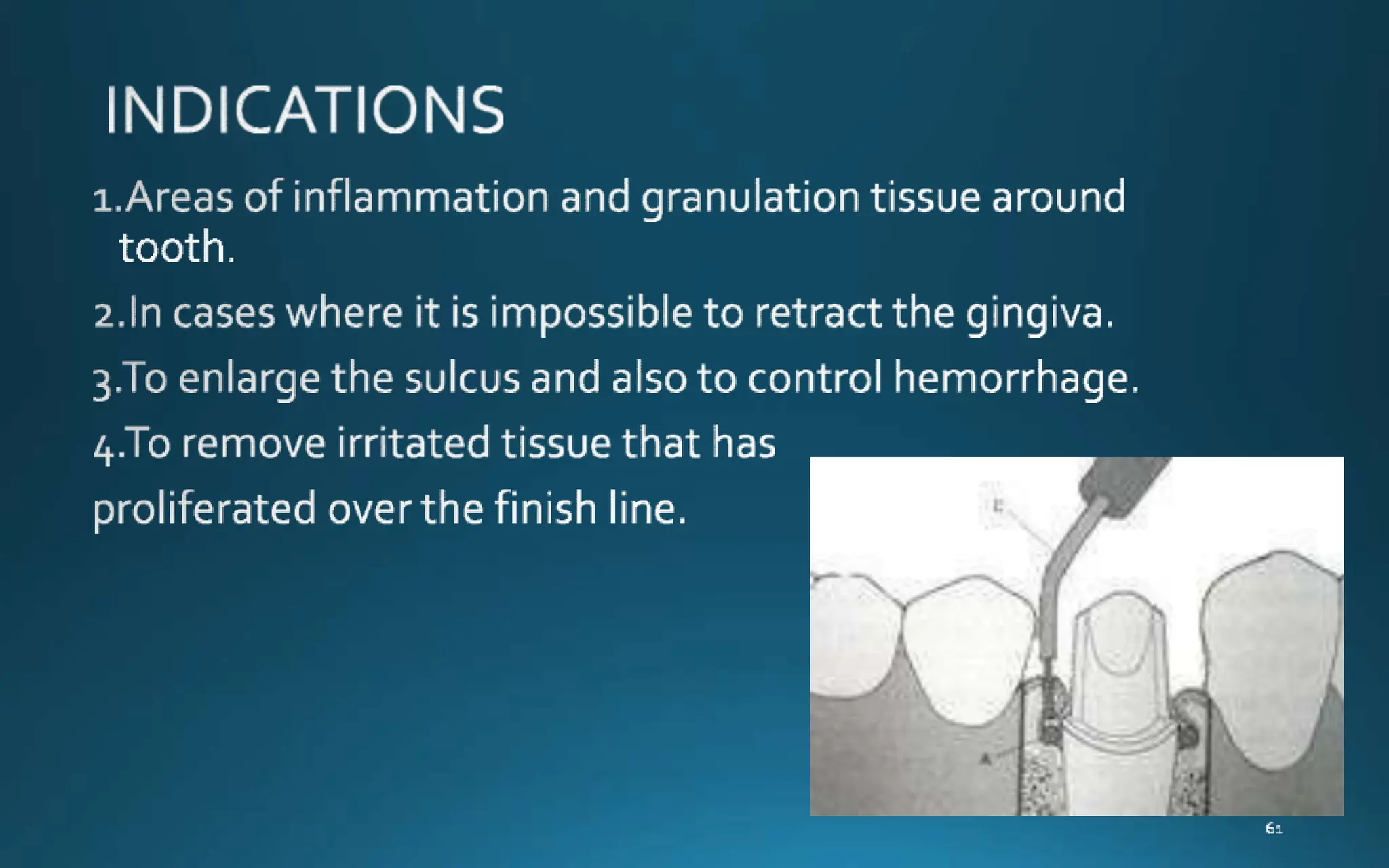
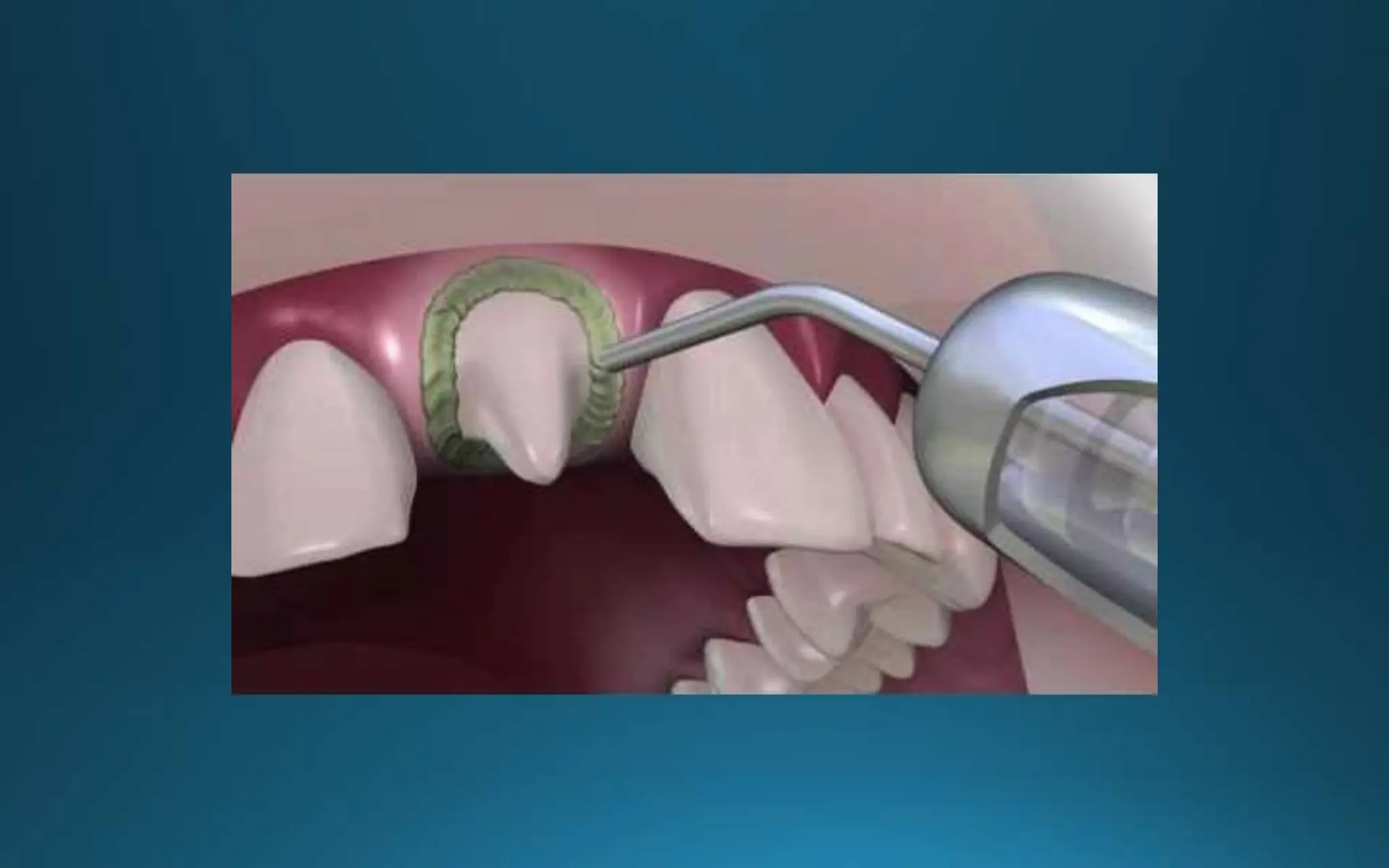
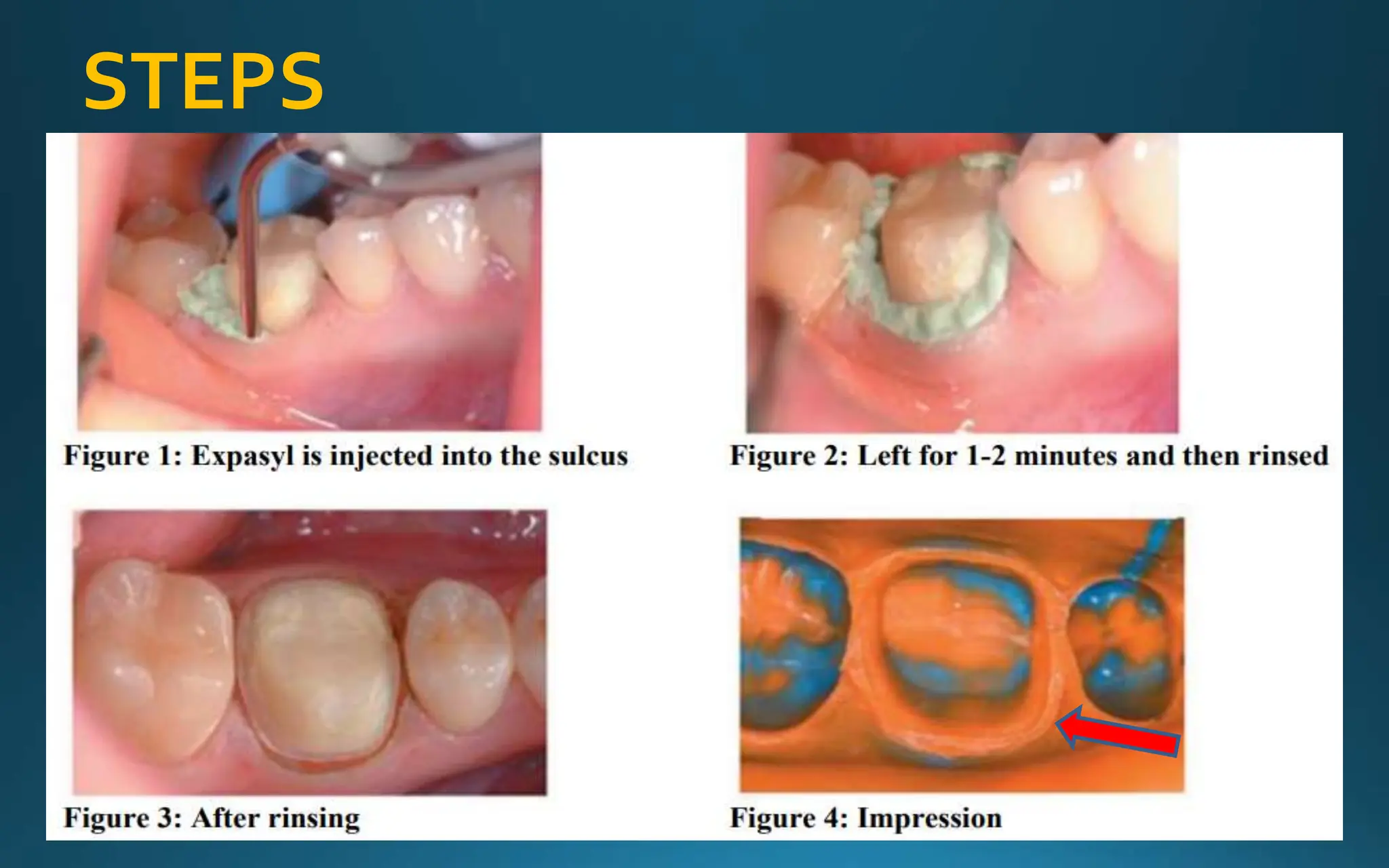
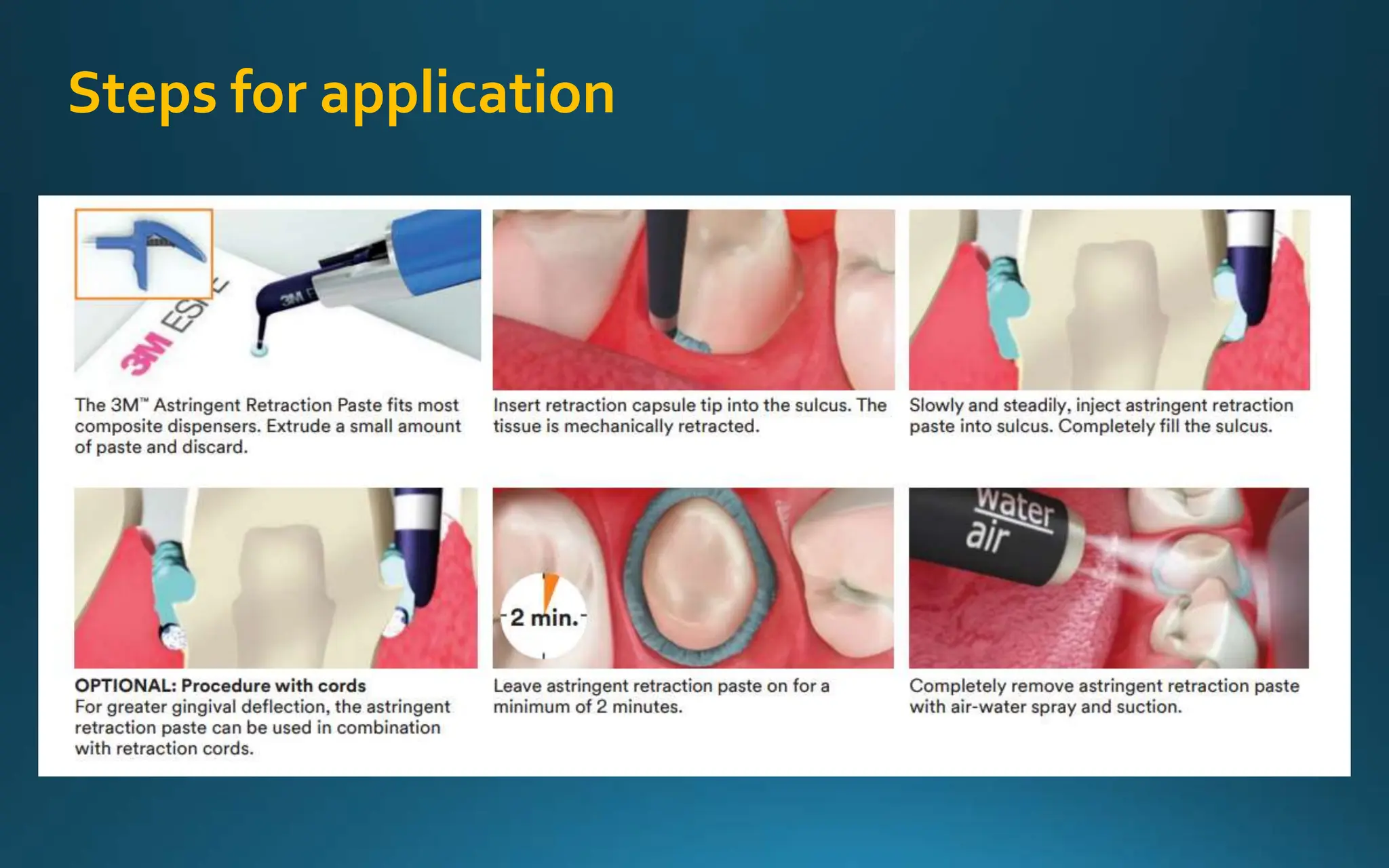
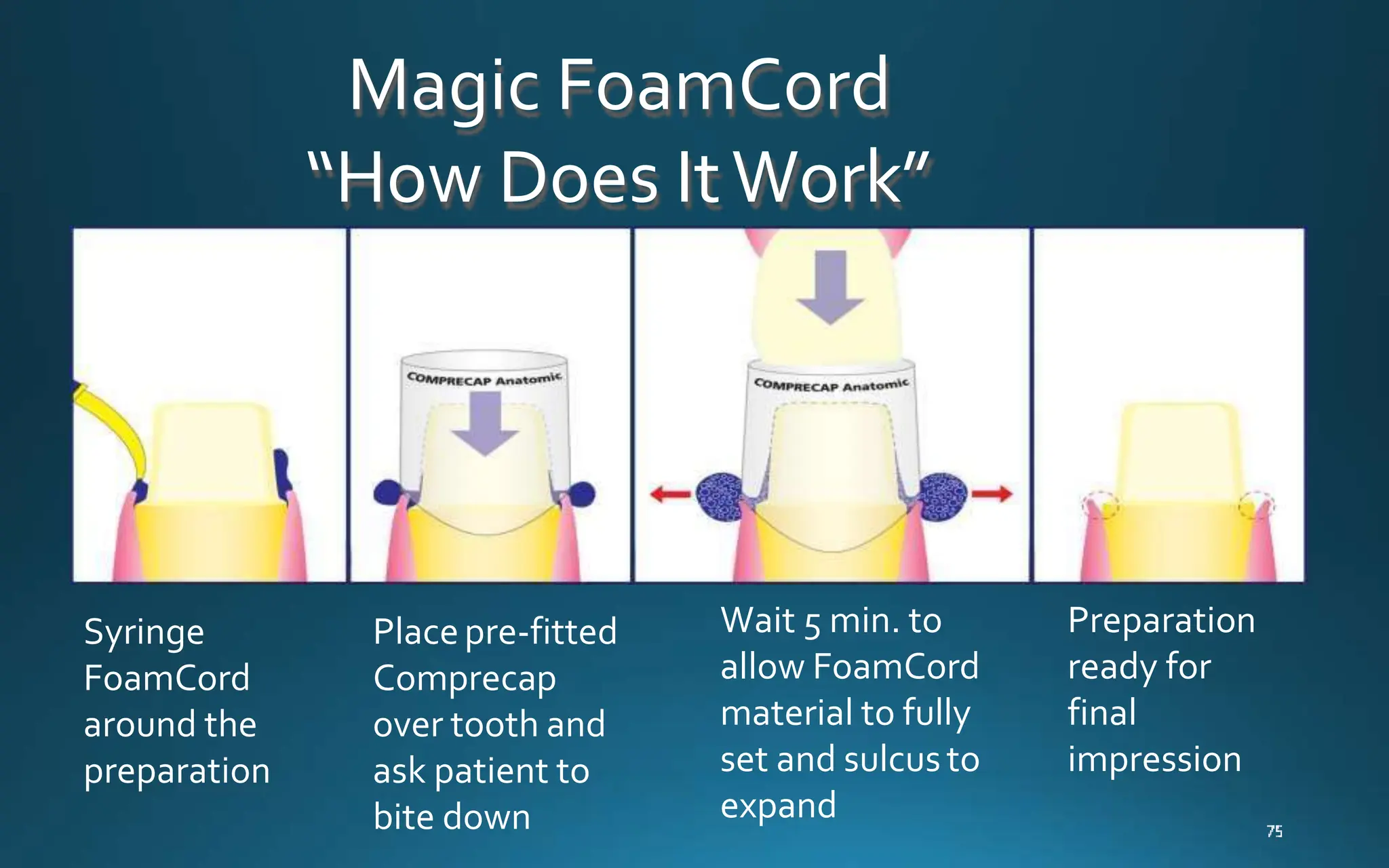
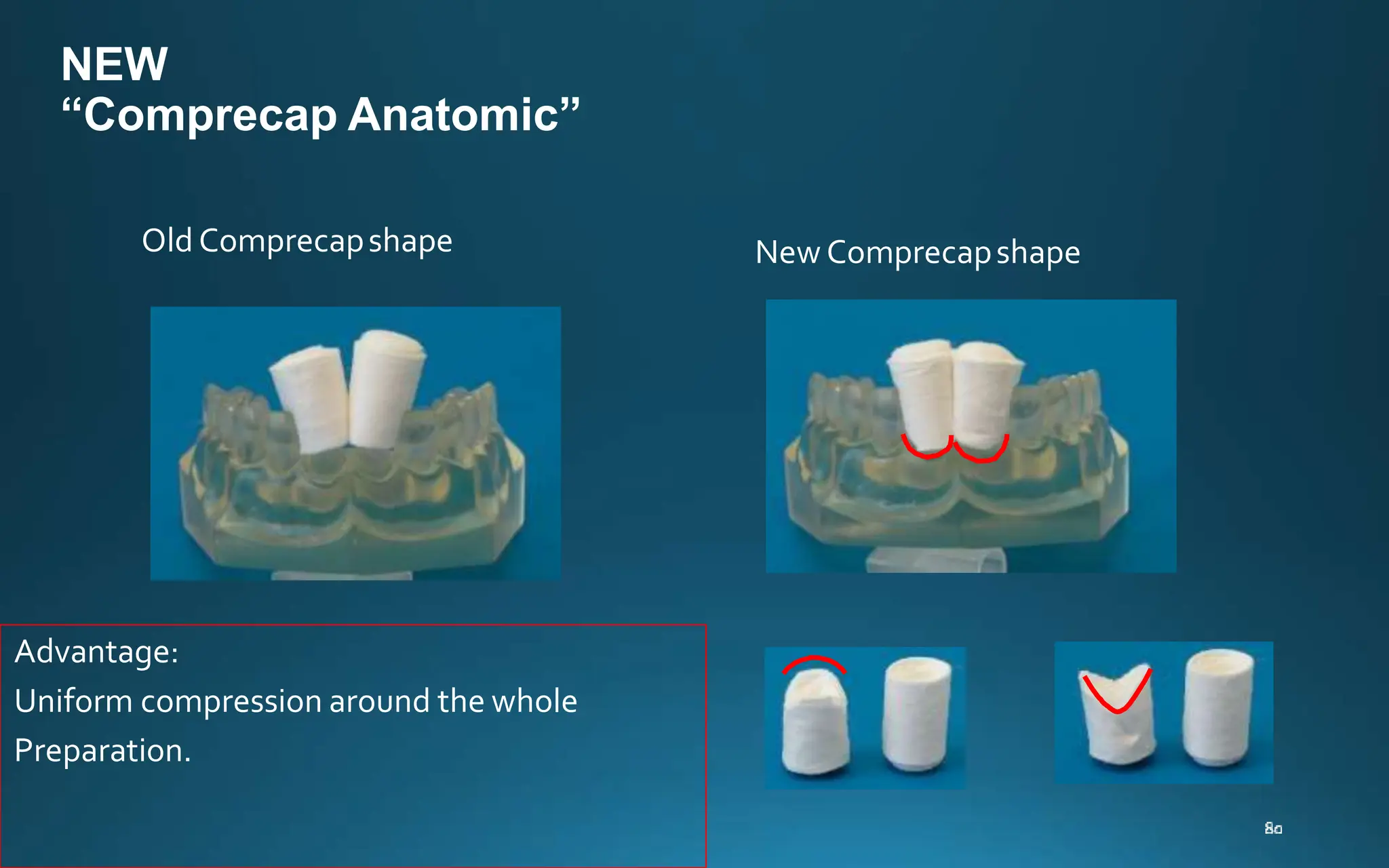
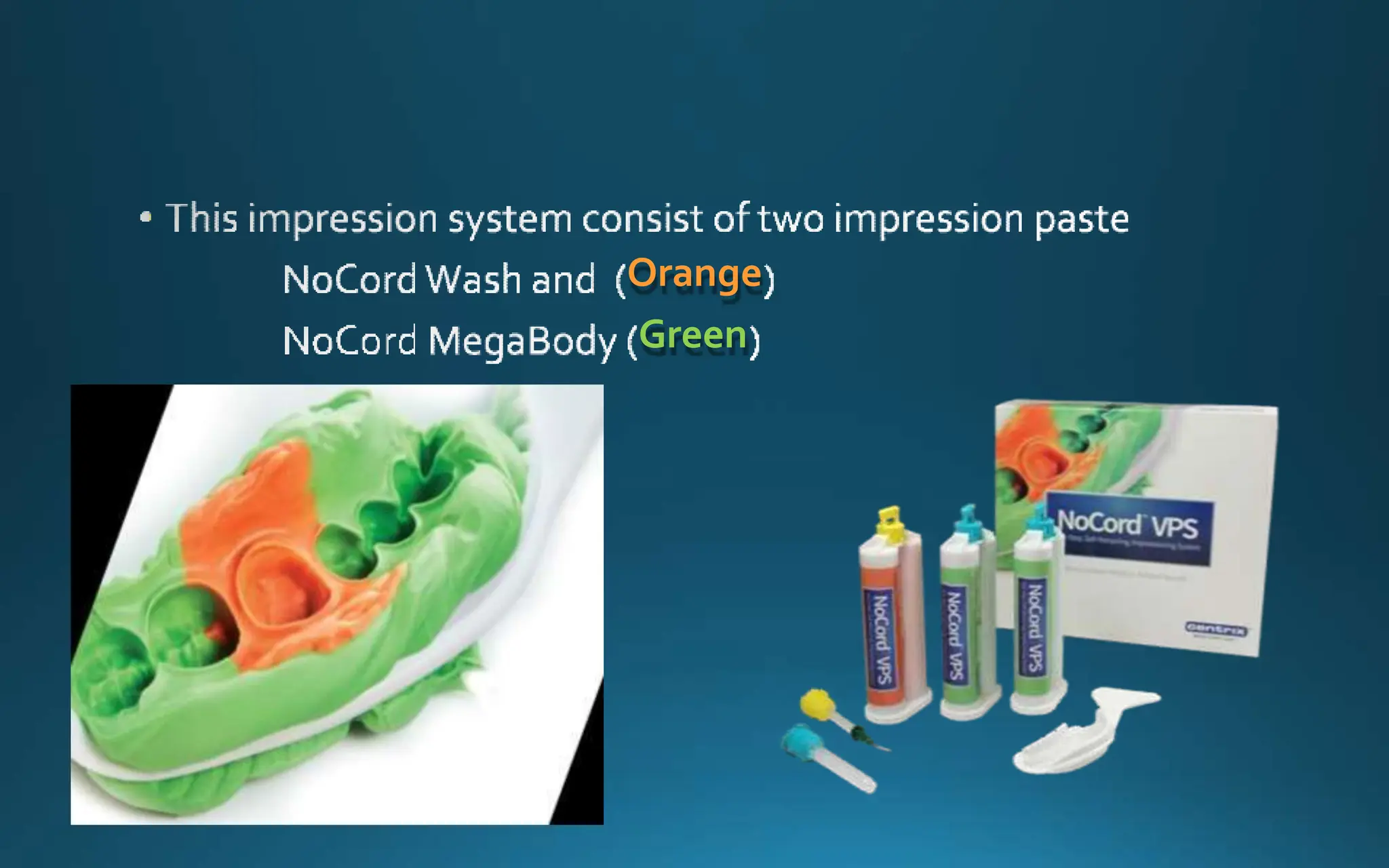
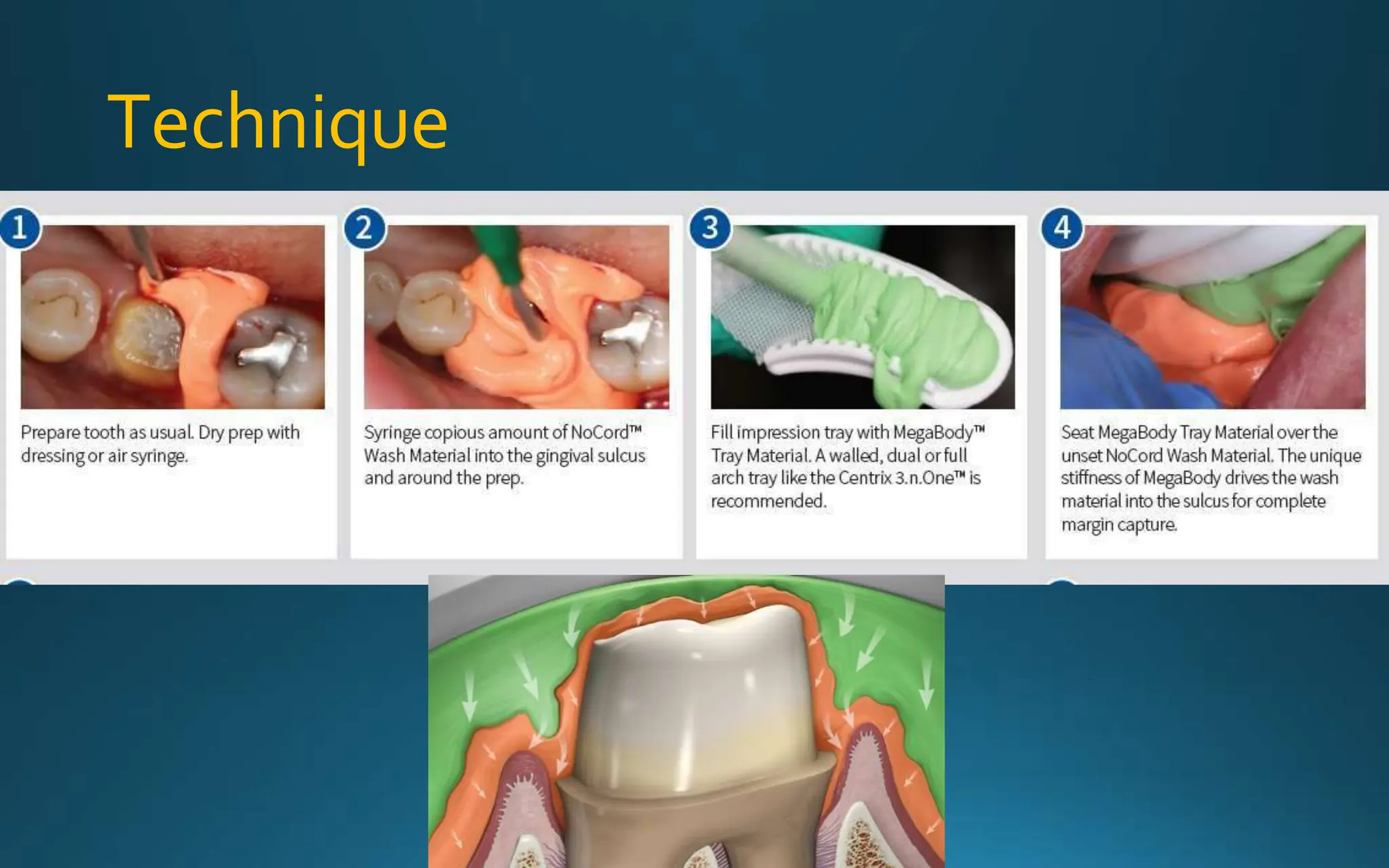
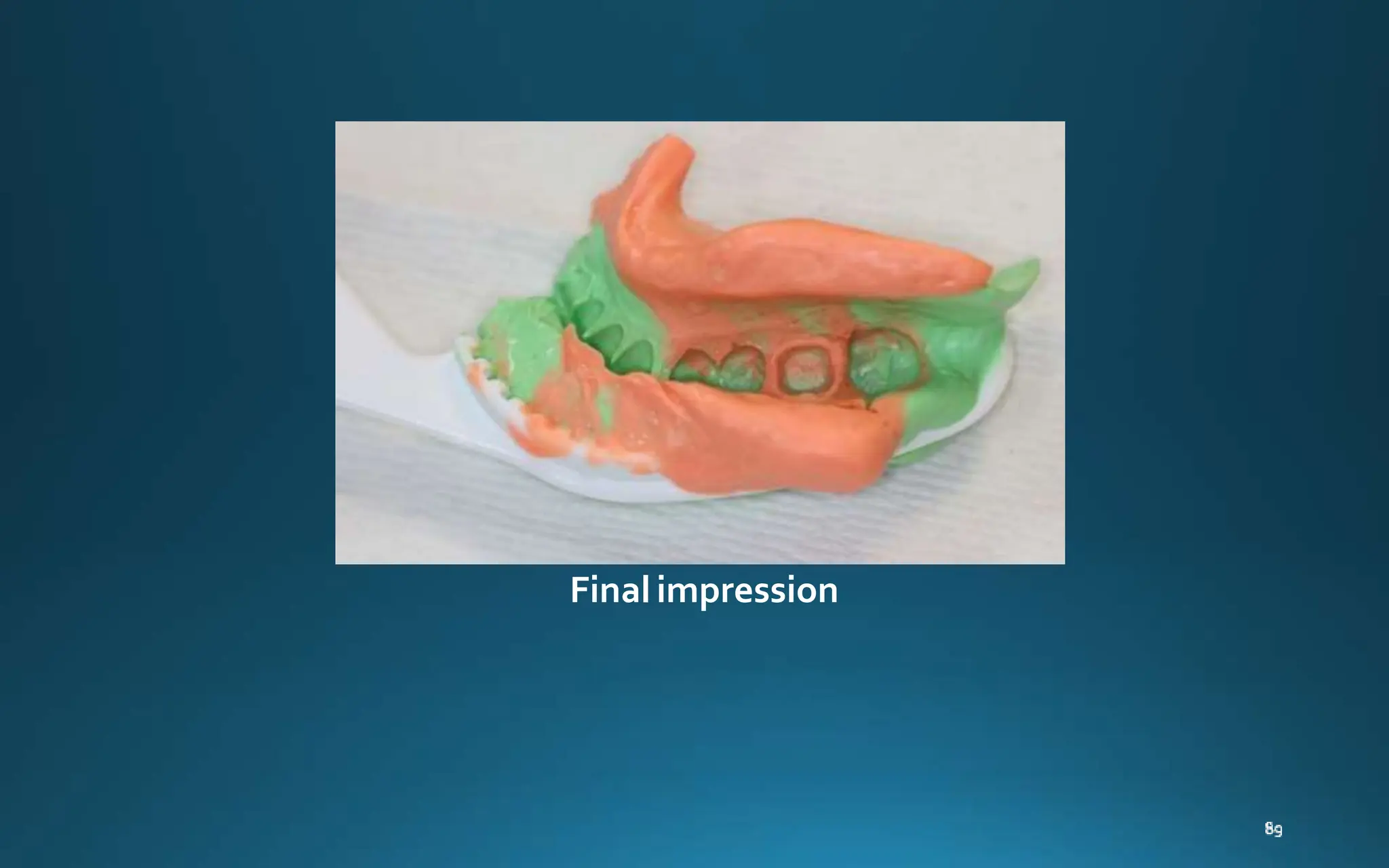
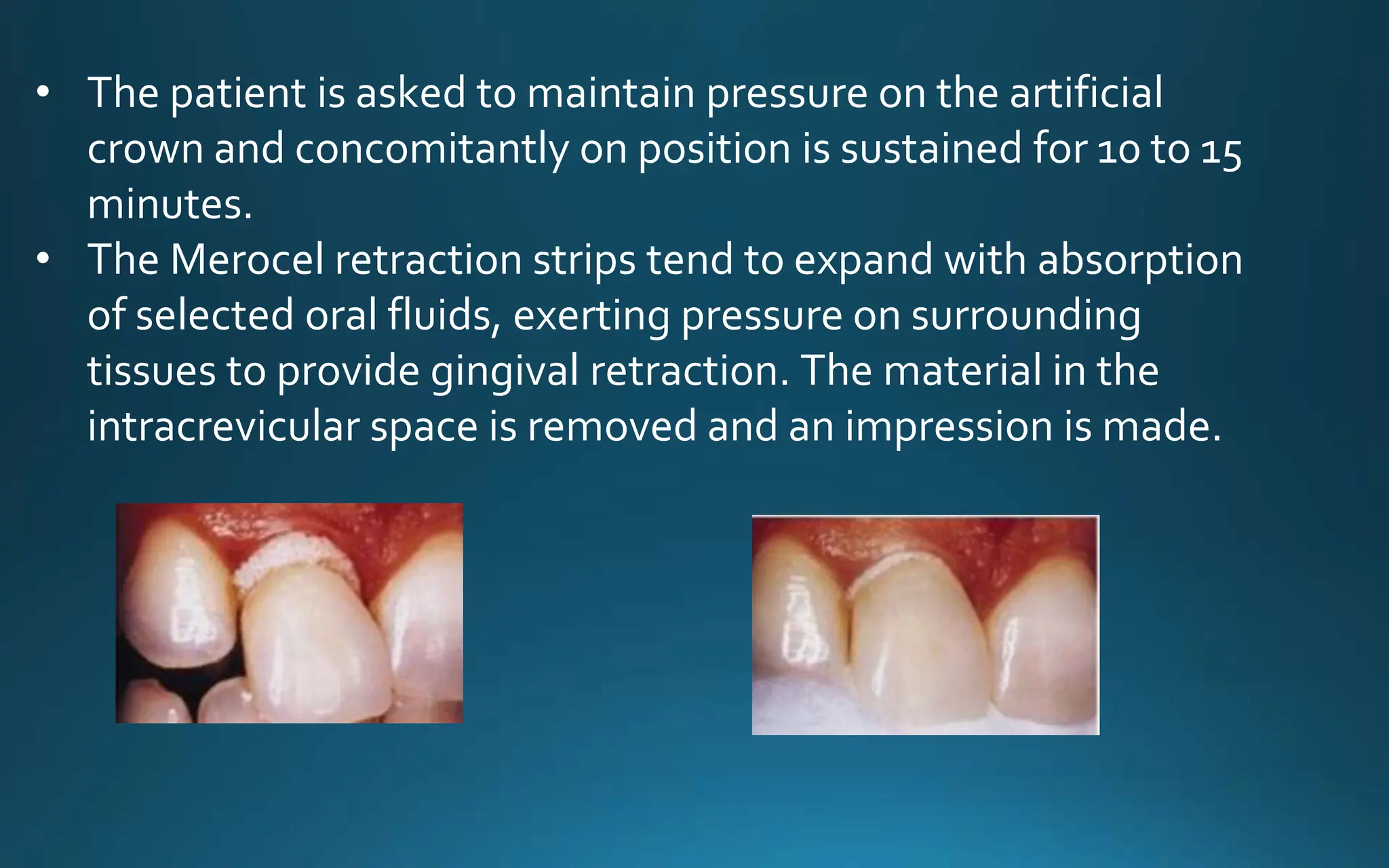
Gingival retraction is a necessary step for accurate impressions in fixed prosthodontics. There are various methods for gingival retraction including mechanical methods using retraction cords, chemicals applied to cords or directly to tissue, electrosurgery, lasers, and new cordless systems. Retraction cords come in different sizes and are placed for 5-30 minutes. Chemicals used include astringents like aluminum chloride that cause hemostasis and tissue displacement. New developments provide retraction without cords or chemicals but additional research is still needed on some techniques and materials. Proper gingival retraction allows for an accurate impression and fit of restorations for optimal function and health of surrounding tissues.