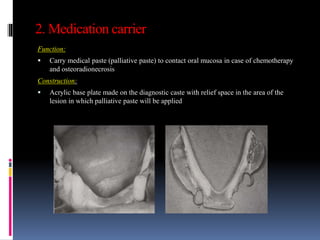
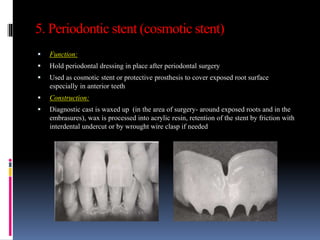
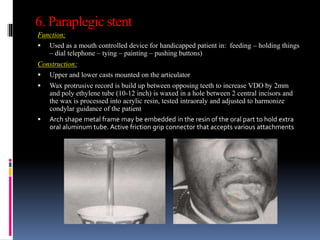
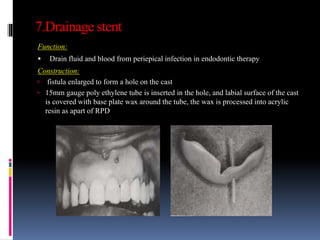
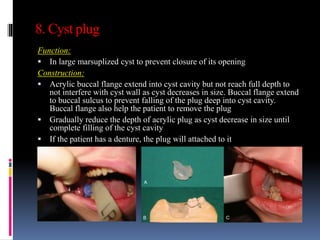
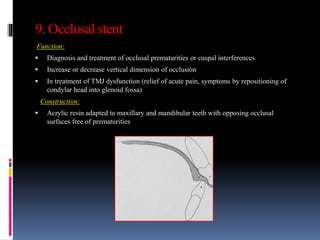
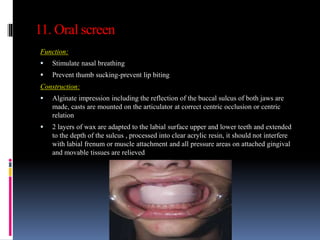
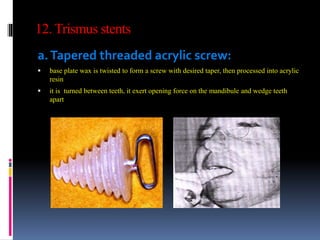
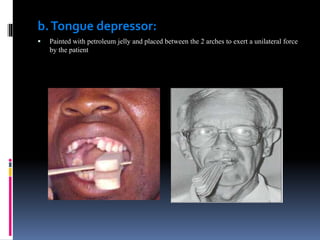
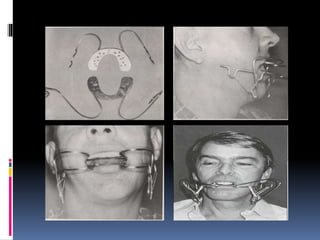
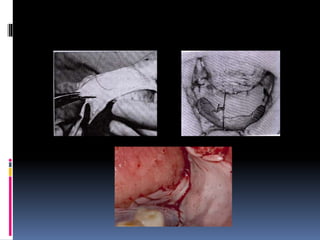
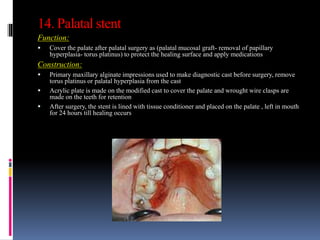
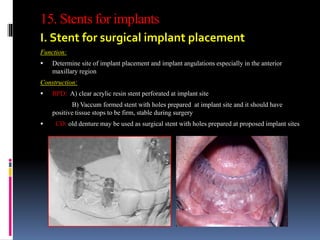
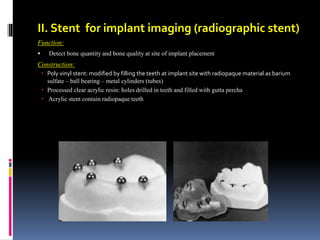
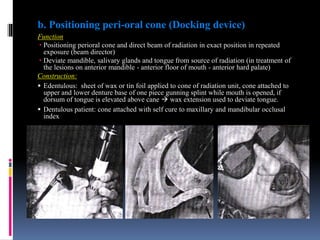
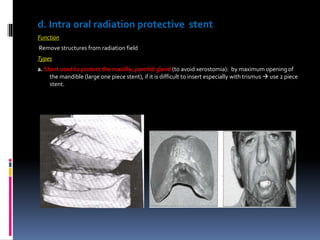
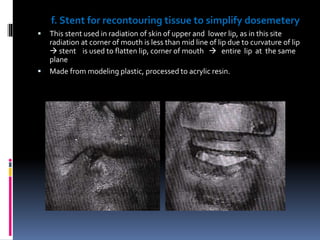
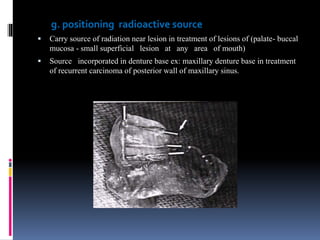
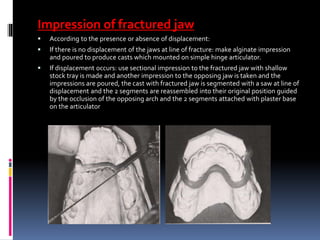
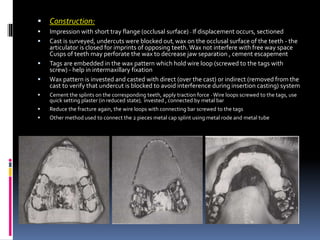
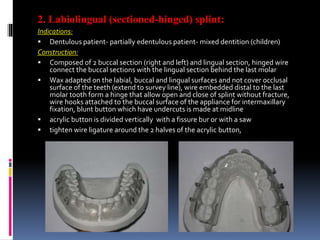
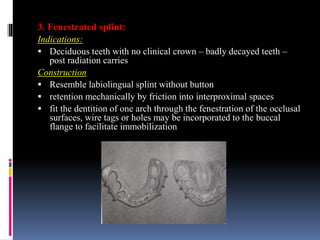
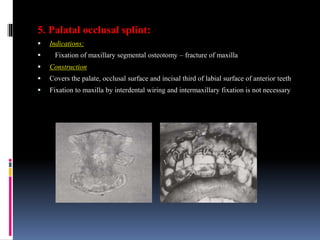
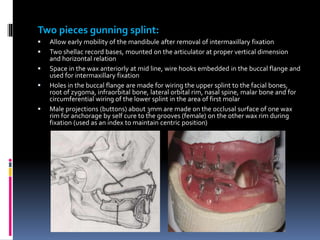
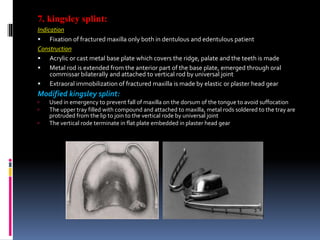
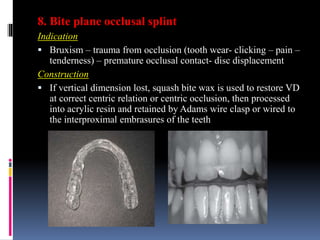
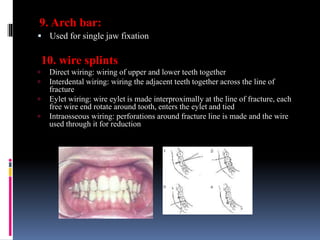
This document discusses different types of stents used in dentistry, including their functions and basic constructions. It describes 18 categories of stents such as anti-hemorrhagic stents used to control bleeding after tooth extractions, medication carrier stents, fluoride carrier stents, various types of stents used for positioning and protecting tissues during radiation therapy, and stents used during implant placement and surgery. Stents are removable dental appliances that serve specific functions, ranging from delivering medications to positioning tissues and radioactive sources. They are typically constructed using materials like acrylic resin, wax, or metal and are customized based on impressions and models of the patient's mouth.