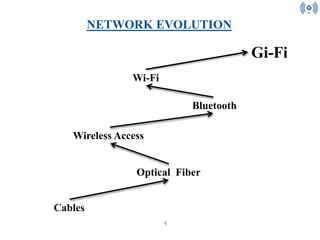
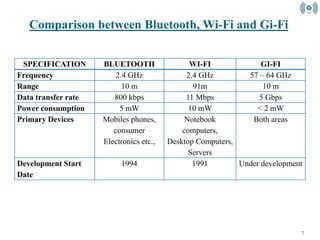
- Gi-Fi allows for wireless transfer of audio and video data at up to 5 GB per second within a 10 meter range using a single-chip 60GHz transceiver. It was developed by NICTA to provide higher data transfer rates and lower power consumption compared to Bluetooth and Wi-Fi. Gi-Fi uses Time Division Duplex to transmit and receive data at 60GHz while avoiding interference through heterodyne down-conversion to 5GHz for transmission. It is expected to enable wireless broadband connectivity in homes and offices in the near future.