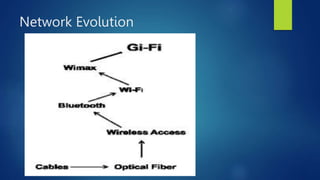
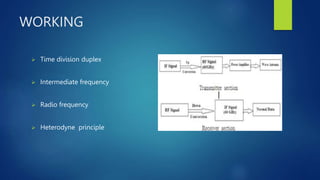
The document discusses Gi-Fi (Gigabit wireless) technology, which allows wireless transfer of data at speeds up to 5 gigabits per second within a 10 meter range. It provides advantages over existing Bluetooth and Wi-Fi technologies by offering higher data rates, lower power consumption, and operating at 60 GHz frequency for better security and interference immunity. The document outlines the network evolution leading to Gi-Fi, its architecture based on IEEE 802.15.3c standard, working principles, advantages, applications in home appliances and vehicle communication, and concludes that Gi-Fi will become the dominant wireless technology for networking within five years.
















![REFERENCES
[1]P.Srikanth, J.R.Thresphine, “Innovative With GI-FI Technology”, In:
International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science &
Technology - Vol. 2 Issue 1 Jan-March 2014.
[2]J. Santhan Kumar Reddy, “Gi-Fi Technology”, In: International Journal of
Advanced Scientific and Technical Research, Issue 3, Volume 1, January-
February 2013.
[3][1]S. Dheeraj and S. Gopichand, 2002,” Gi-Fi: Technology,” IEEE Trans.
Commun., vol. 52, no.5, pp. 1195-1203.
[4]Gowtham S Shetty, 2006,” Gi-Fi: Next Generation Wireless Technology,”
IEEE Trans. Commun., vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 324- 352](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminarppt-230604142302-9f79da50/85/seminar-ppt-pptx-19-320.jpg)
