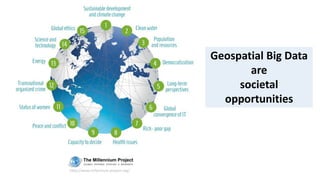
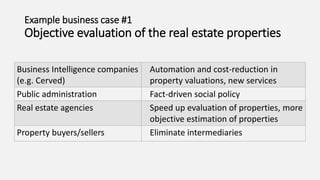
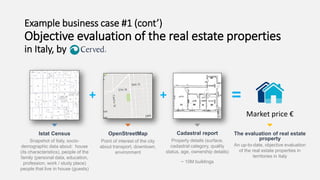
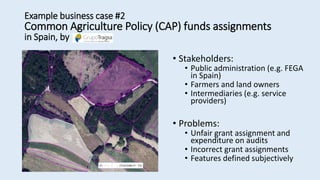
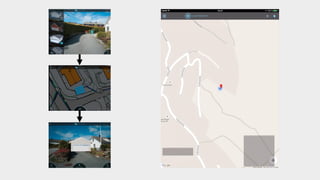
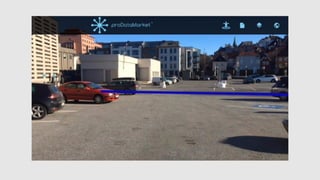
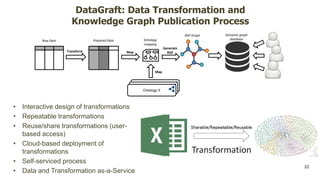
The document discusses the Prodatamarket project, which aims to enhance access and usability of property-related geospatial data by providing a data marketplace and enabling innovation in data usage. It presents various business cases, including the evaluation of real estate properties and the assignment of agricultural policy funds, highlighting the challenges and solutions in processing diverse datasets. Ultimately, the project seeks to improve data integration and quality for stakeholders across private and public sectors.