GEOMETRY.DOCX
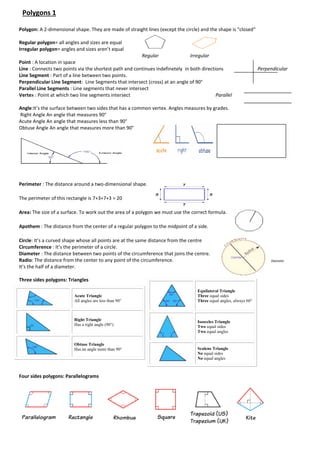
- 1. Polygons 1 Polygon: A 2-dimensional shape. They are made of straight lines (except the circle) and the shape is "closed" Regular polygon= all angles and sizes are equal Irregular polygon= angles and sizes aren’t equal Regular Irregular Point : A location in space Line : Connects two points via the shortest path and continues indefinetely in both directions Perpendicular Line Segment : Part of a line between two points. Perpendicular Line Segment: Line Segments that intersect (cross) at an angle of 90° Parallel Line Segments : Line segments that never intersect Vertex : Point at which two line segments intersect Parallel Angle:It’s the surface between two sides that has a common vertex. Angles measures by grades. Right Angle An angle that measures 90° Acute Angle An angle that measures less than 90° Obtuse Angle An angle that measures more than 90° Perimeter : The distance around a two-dimensional shape. The perimeter of this rectangle is 7+3+7+3 = 20 Area: The size of a surface. To work out the area of a polygon we must use the correct formula. Apothem : The distance from the center of a regular polygon to the midpoint of a side. Circle: It’s a curved shape whose all points are at the same distance from the centre Circumference : It’s the perimeter of a circle. Diameter : The distance between two points of the circumference that joins the centre. Radio: The distance from the center to any point of the circumference. Diameter It’s the half of a diameter. Three sides polygons: Triangles Four sides polygons: Parallelograms Equilateral Triangle Three equal sides Three equal angles, always 60° Isosceles Triangle Two equal sides Two equal angles Scalene Triangle No equal sides No equal angles Acute Triangle All angles are less than 90° Right Triangle Has a right angle (90°) Obtuse Triangle Has an angle more than 90°
- 2. Names of Polygons - 2 Name Sides Shape Area Triangle 3 h b A= (b x a):2 A= (b. h):2 Square 4 a A= l x l= l2 A= a2 Rectangle 4 h a A= b x a A= a . h Trapezoid Trapezium Parallelogram 4 4 a b h h A = (B + b) . a A=(b +a).h 2 2 A= b . a A= b. h Pentagon 5 b A= perimeter.apothem 2 Hexagon 6 Idem all regular polygons Circle A= 2. Π. r2 Circumference L= 2.π.r REMEMBER h = height = alto w= width = ancho d= depth= fondo b= base = base l = side= lado
- 3. POLIEDROS = POLYHEDRAS Polyhedra: A polyhedron is a solid with flat faces which are polygons. It hasn`t got curved surfaces. Faces = Flat surfaces (superficies planas) = caras Edges (bordes) = aristas Vertices = corner of the edges , corner points = vértices 1. Poliedros Regulares = Platonic solids Un poliedro regular es aquel cuyas caras son polígonos regulares iguales y en cada uno de sus vértices concurren el mismo número de caras. Sólo existen cinco tipos de poliedros regulares: Name Area Volumen Tetraedro Tethahedrom Surface Area = √3 × (Edge Length)2 Volume = (√2)/12 × (Edge Length)3 Cubo Cube Surface Area = 6 × (Edge Length)2 Volume = (Edge Length)3 Octaedro Octahedrom Surface Area = 2 × √3 × (Edge Length)2 Volume = (√2)/3 × (Edge Length)3 Dodecaedro Dodecahedrom Surface Area = 3×√(25+10×√5) × (Edge Length)2 Volume = (15+7×√5)/4 × (Edge Length)3 Icosaedro Icosahedrom Surface Area = 5×√3 × (Edge Length)2 Volume = 5×(3+√5)/12 × (Edge Length)3 Platonic Solids = poliedros regulares Prisms = prismas Pyramids = pirámides
- 4. 2. Prismas= Prismas Poliedro limitado por dos polígonos iguales, llamados bases, situados en planos paralelos, y por varios paralelogramos, llamados caras laterales. Un prisma se llama triangular, cuadrangular, pentagonal… según que sus bases sean triángulos, cuadriláteros, pentágonos… A lateral = perímetro de la base · altura A total = área lateral + 2 · área de la base V = área de la base · altura Lateral area= base perimeter . lenght Surface area= lateral area + 2.base area Volume = base area . length 3-. Pirámides= Pyramids apex CUERPOS CILÍNDRICOS = NON - POLYHEDRA CILINDRO-CYLINDER Á. Total = A. Lateral + 2· A. Base Volumen = A. Base · Altura CONO-CONE Area total= A.Lateral + A.Base A Base= Π r2 Volumen = A.Base · Altura ALateral = Π·r·g 3 ESFERA- SPHERE Área= A= 4·Π·r2 Volumen= 4/3 Π ·r3 The Volume of a Pyramid 1/3 × [Base Area] × Height V= (area base . a): 3 The Surface Area of a Pyramid When all side faces are the same: [Base Area] + [Lateral Area] V = Area base + Area lateral .
- 5. 1-. Rectangular Prisms : area and volume V= 576 cm3 V= 80m2 V= 200 m2 V=8 V=24
- 6. 2-. Calculate the volumes volume = 45 cm3 volume = 24000 cm3 V = 565.2 cm3 V = 98,125 cm3 V= 12 cm3
- 7. PROBLEMS 1-. These diagram shows a cylinder of height 4 cm and diameter 4 cm. What is its total surface area? What is its volume? A= 65,36 cm and V= 50,24 cm2 2-. A big building has got four water drums with these measures. If a m3 of water equals a liter . How many liters are there in total? (6160 liters) (YOU MUST READ METRE INSTEAD IN) 3-. A cone diameter 20cm and height 20 cm is filled with ice cream. How many ice cream does it contain? (2094,4 cm3) 4-. A piece of cheese has got these measures. 10 mm 15 18
- 8. €