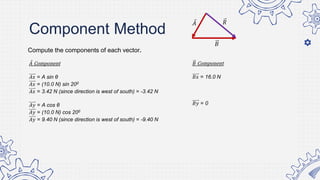
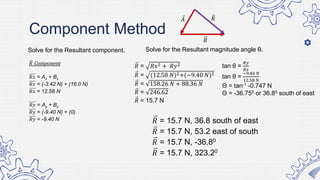
1. Set up the apparatus as shown in the diagram.
2. Attach the 100-g mass to the two spring balances using strong strings.
3. Adjust the angles of the spring balances using the protractor.
4. Record the readings of the two spring balances.
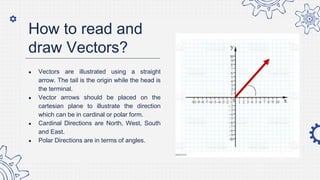
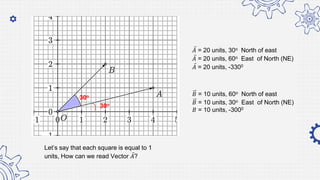
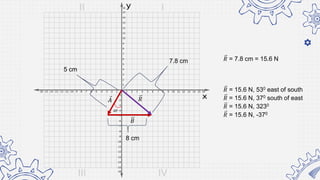
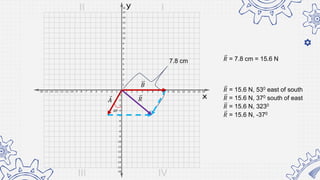
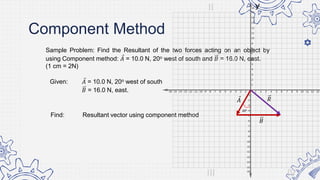
5. Draw the vectors representing the two forces on a graph paper.
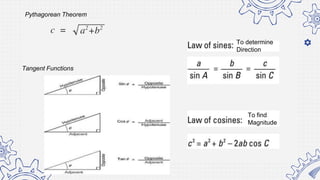
6. Determine the resultant vector using graphical method.
7. Record the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector.
8. Adjust the angles of the spring balances until the reading of one spring balance is zero.
9. Record the angle setting and the reading of the other spring balance.
10. The reading of the one spring balance is the equilibrant