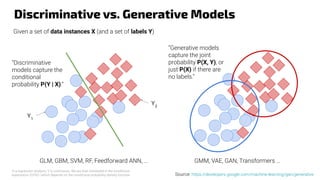
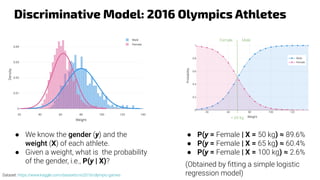
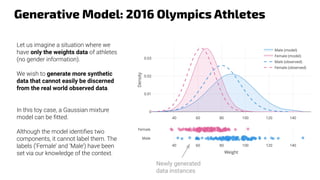
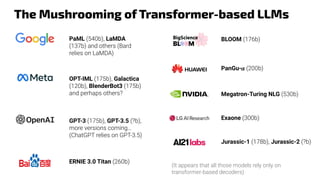
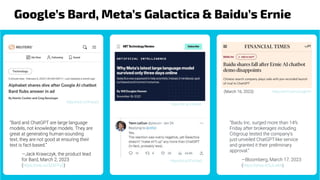
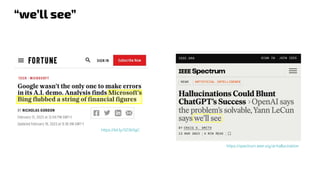
The document discusses generative models, notably focusing on advancements in AI technologies that generate music, images, and text, with examples like Google MusicLM, OpenAI's Jukebox, and ChatGPT. It contrasts generative models, which capture joint probabilities, with discriminative models that depict conditional probabilities through various applications, including athlete data analysis. It also highlights the rise of transformer-based models in language processing, exemplified by ChatGPT's rapid user adoption and the reactions of industry experts regarding its innovativeness.