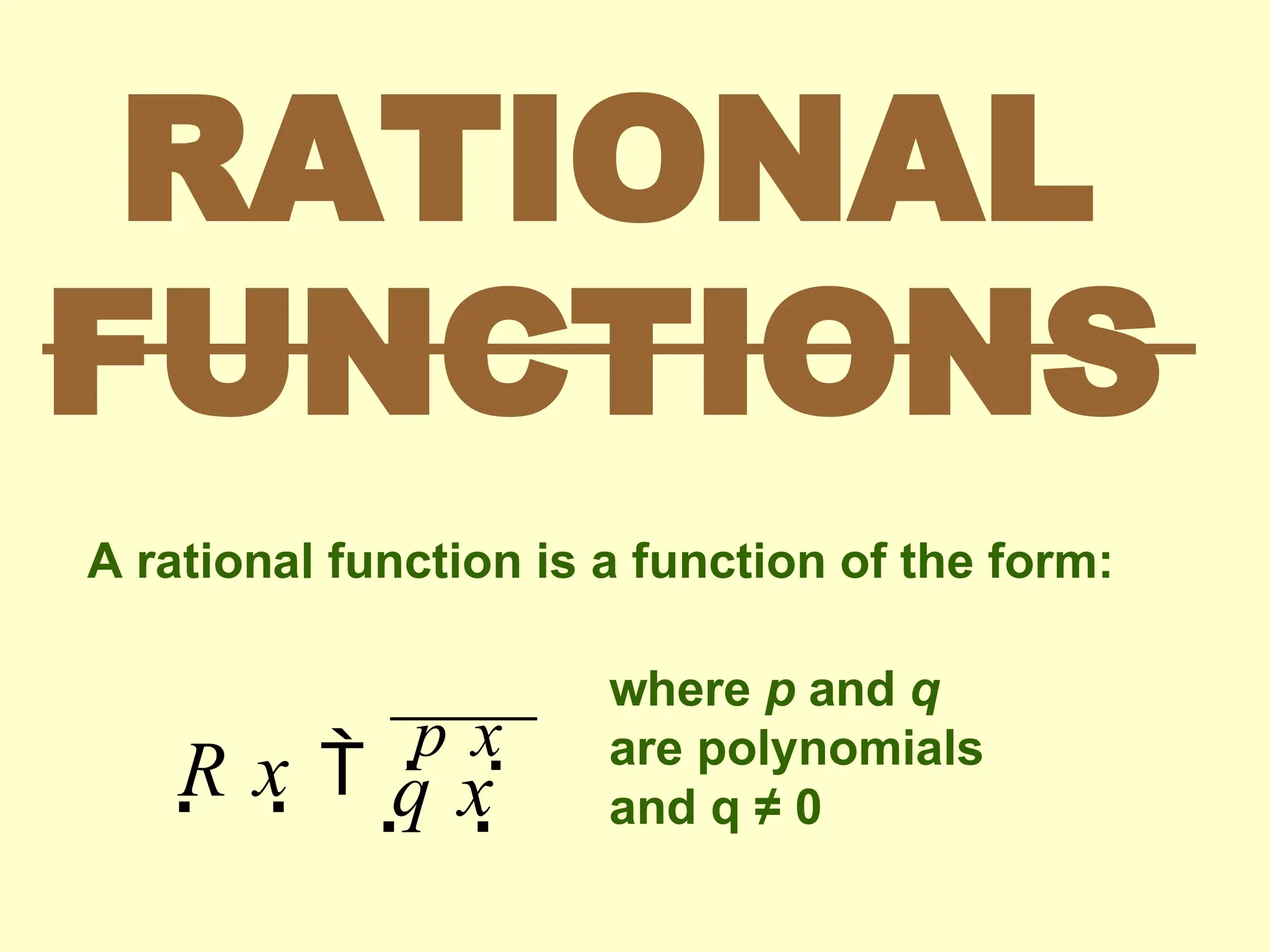
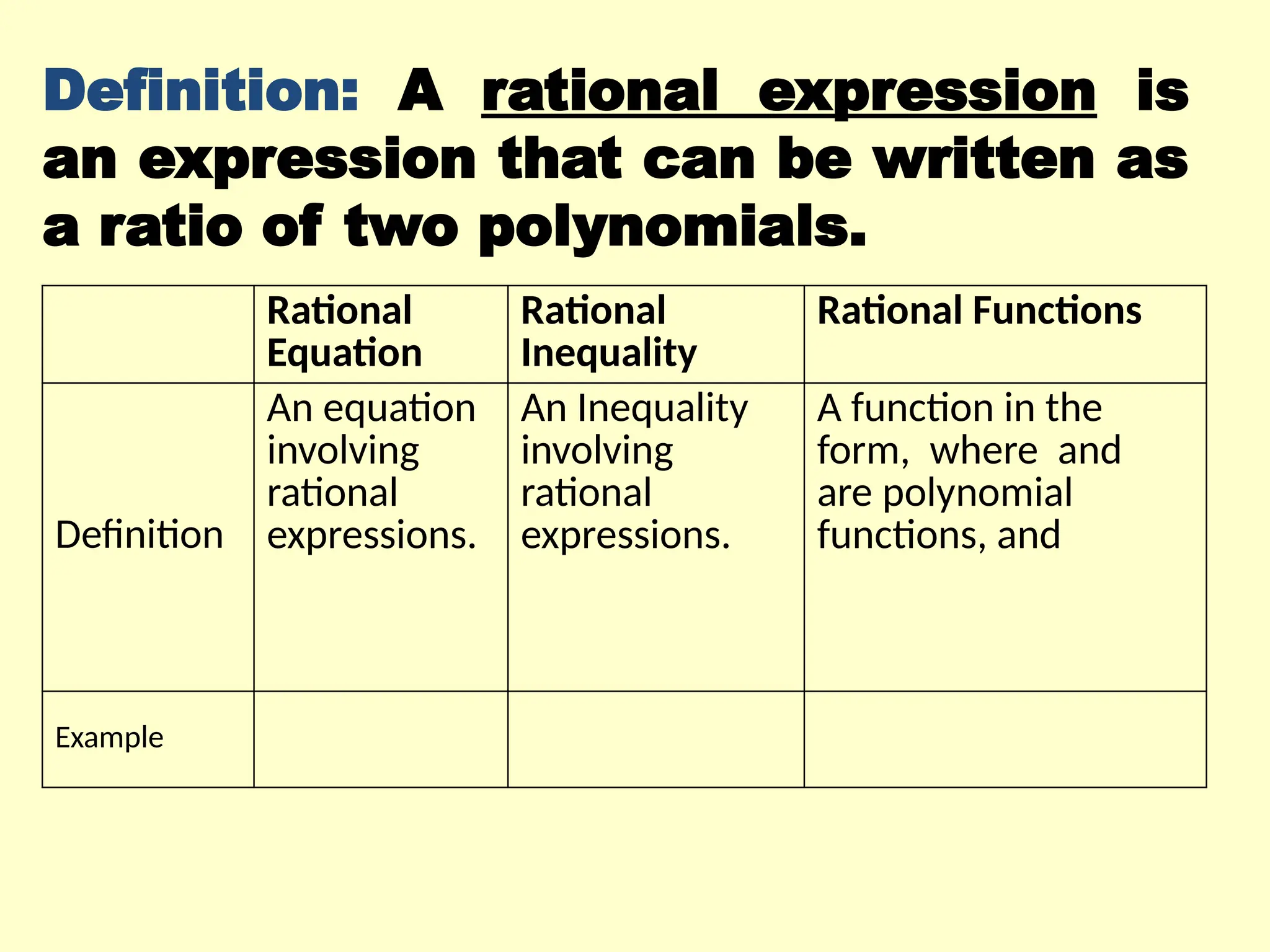
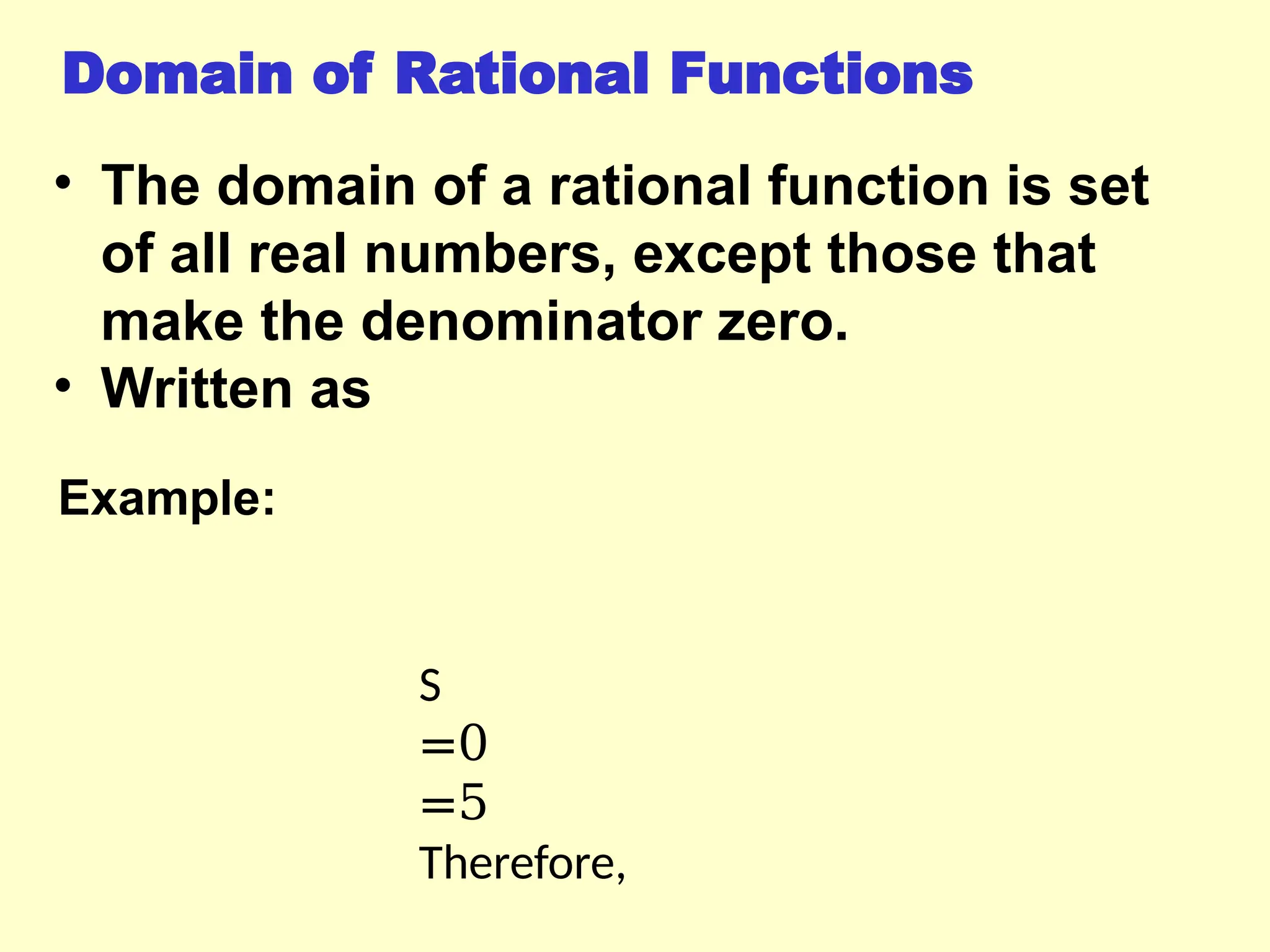
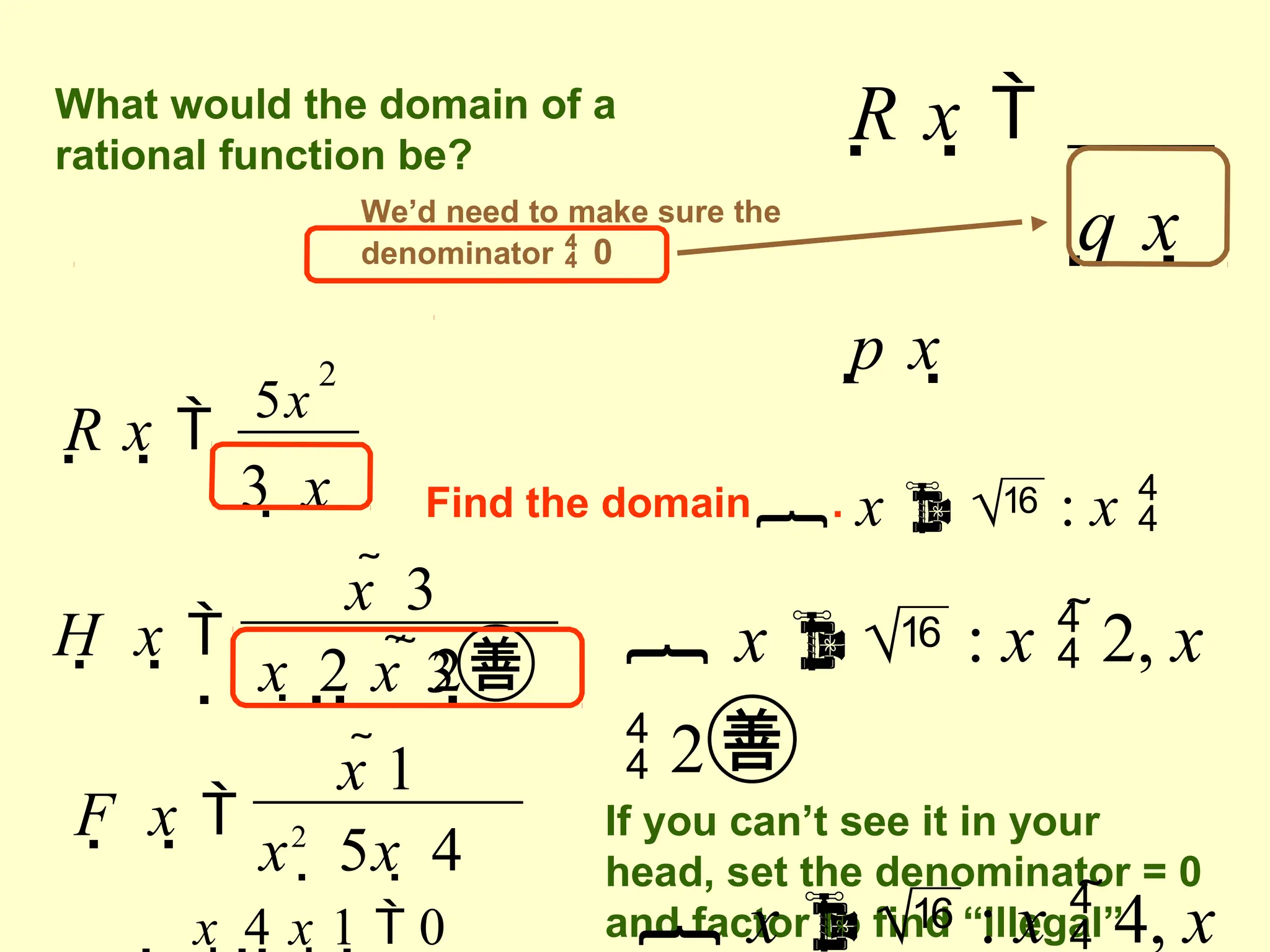
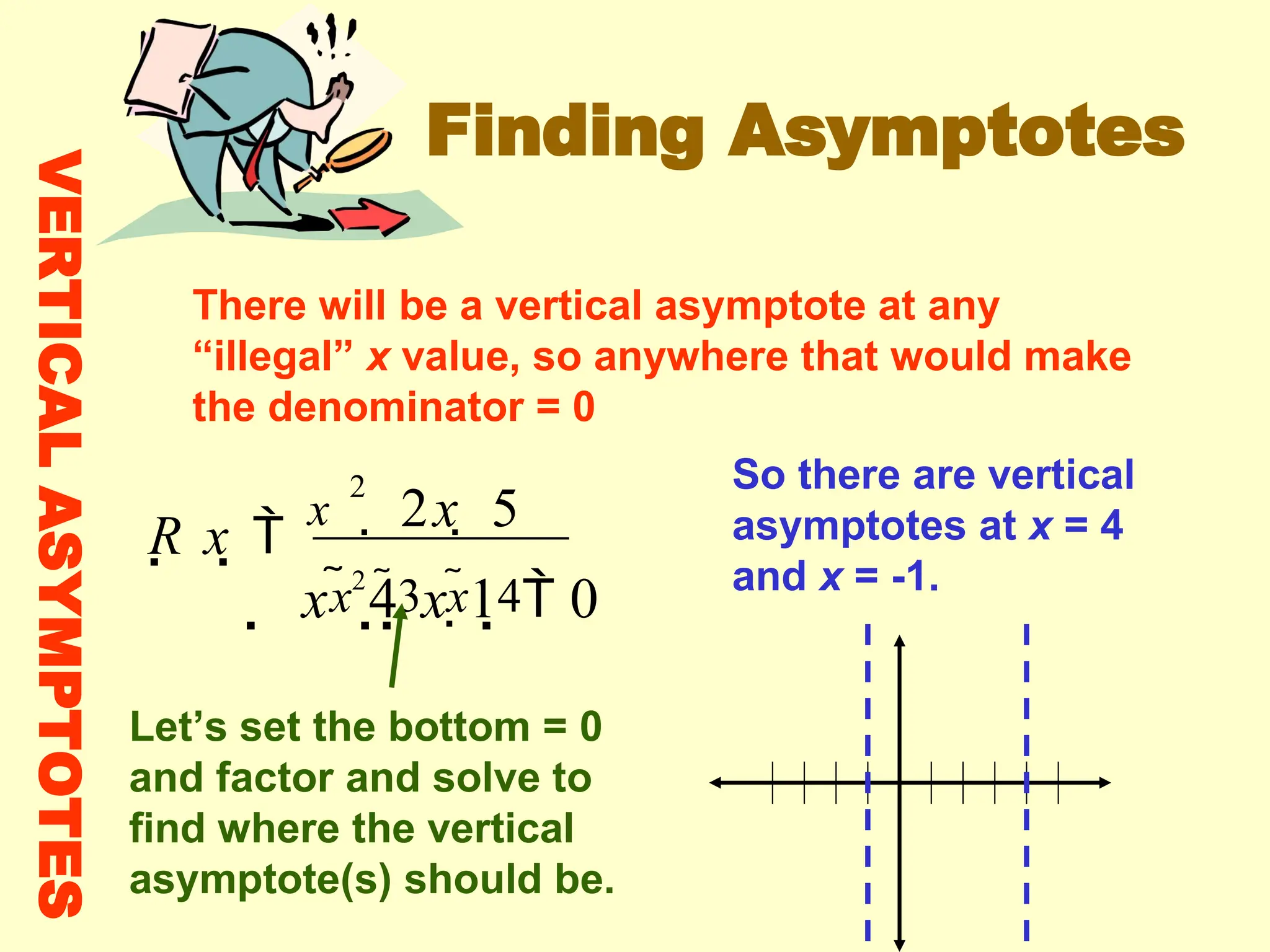
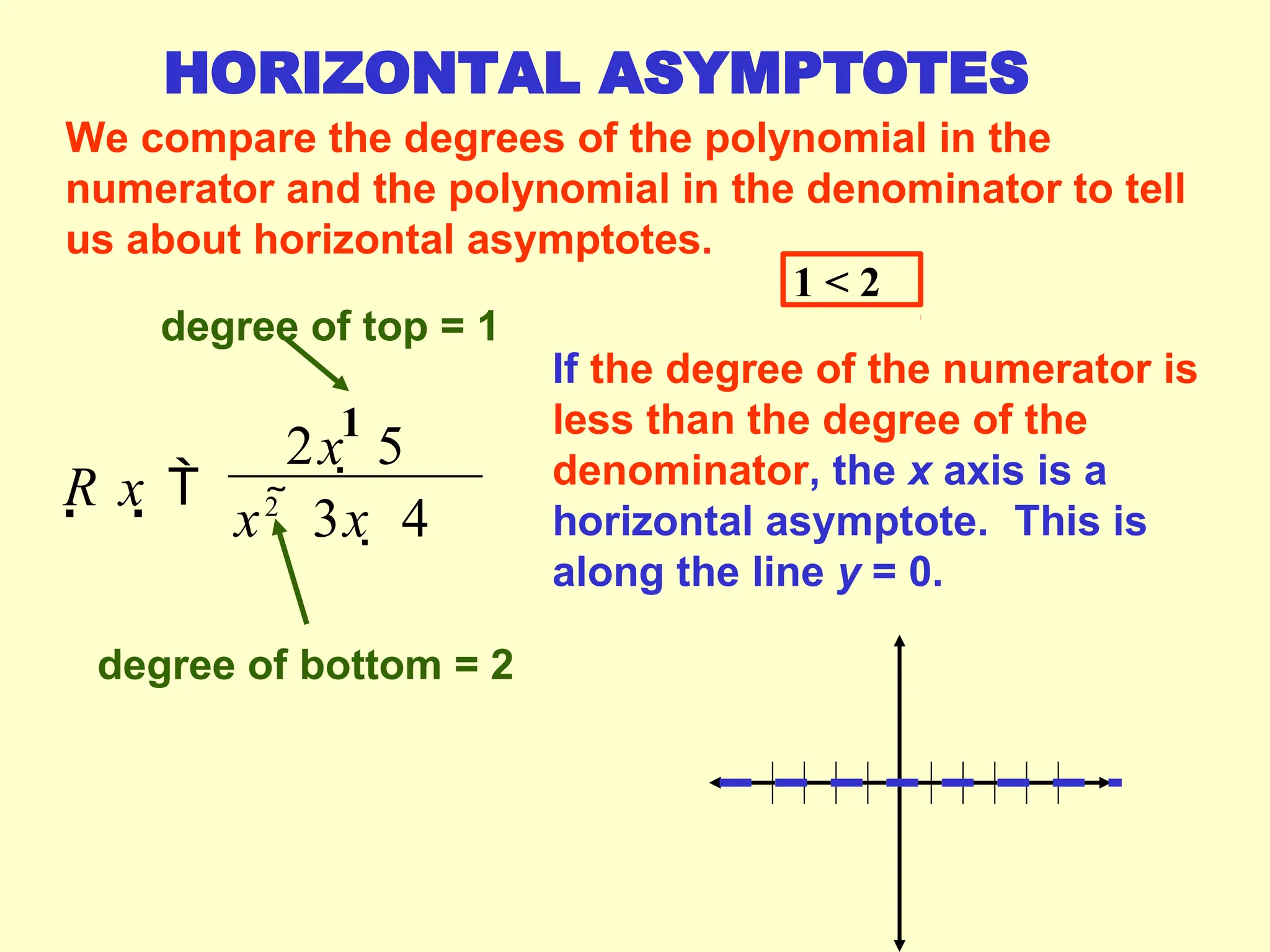
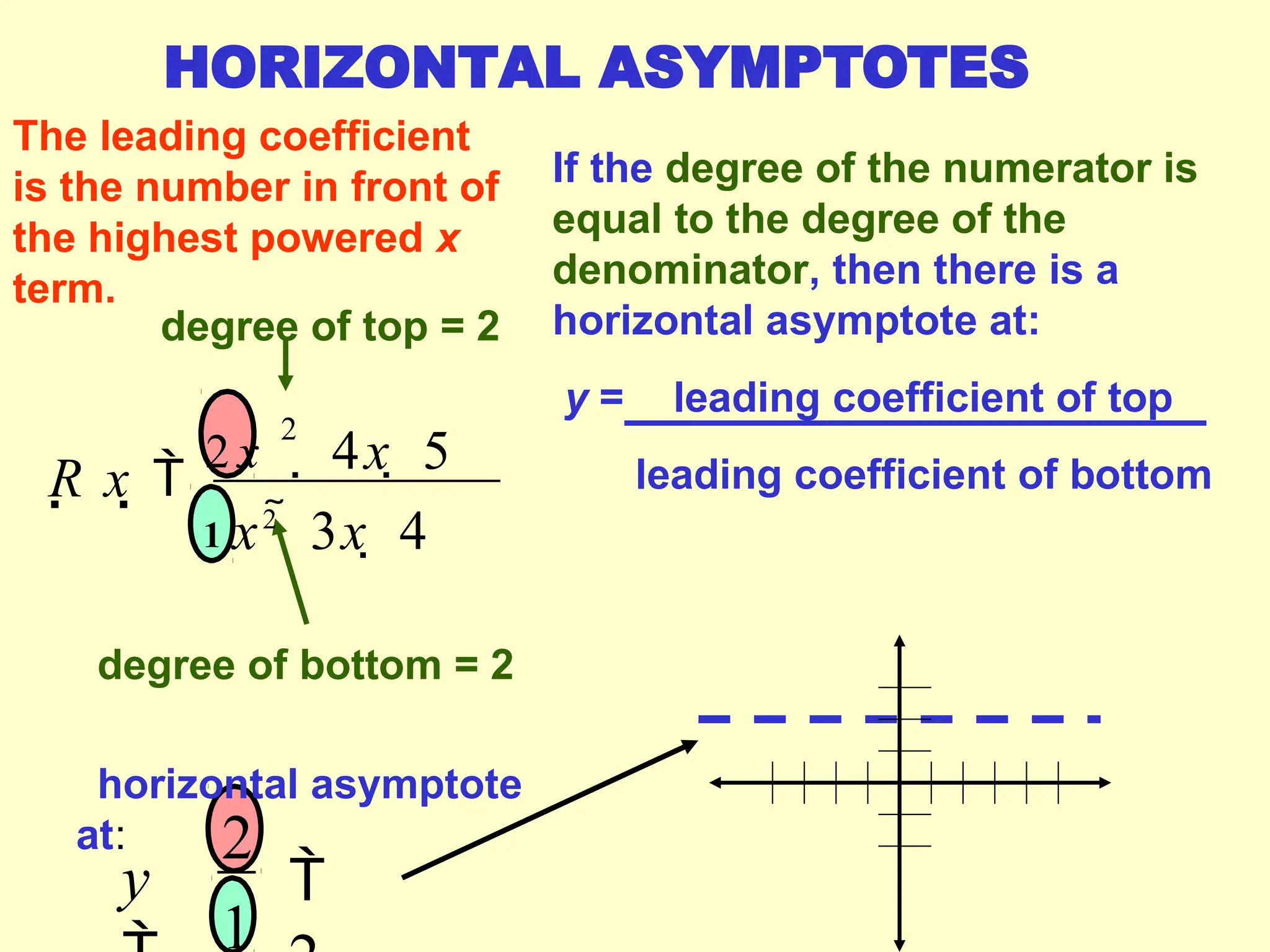
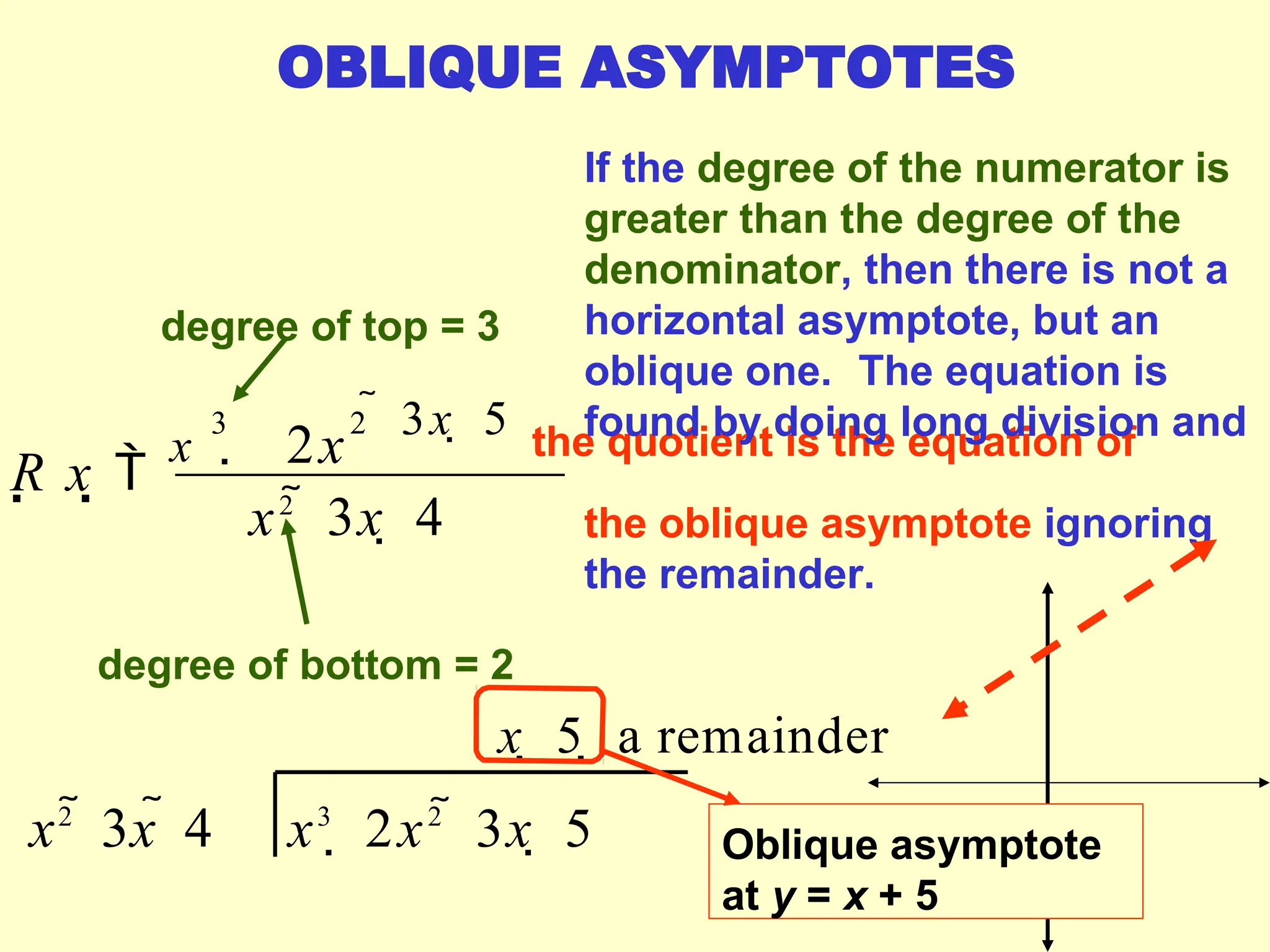
Rational functions are expressed as the ratio of two polynomials, and their domain excludes values that make the denominator zero. Vertical asymptotes occur at 'illegal' x values where the denominator equals zero, while horizontal and oblique asymptotes are determined by comparing the degrees of the numerator and denominator. To find these asymptotes, specific conditions based on the degree relationship must be met, with horizontal asymptotes involving the x-axis or leading coefficients and oblique asymptotes derived from polynomial long division.