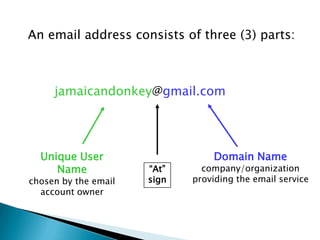
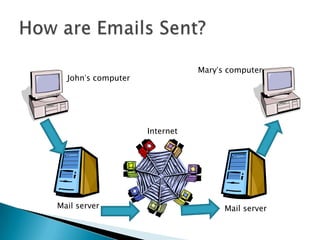
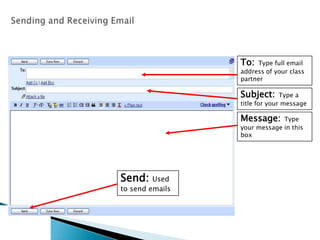
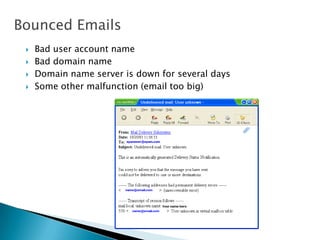
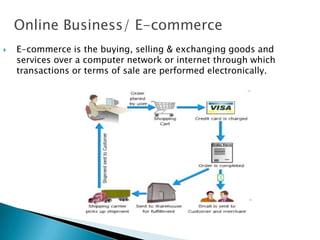
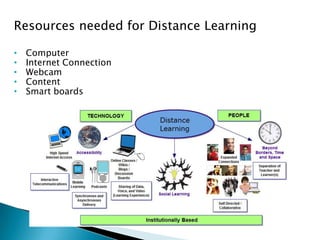
The document provides an overview of email and its functionalities, explaining how it works, the components of an email address, and types of email services. It also discusses the advantages and disadvantages of email, e-commerce, electronic banking, telecommuting, and distance learning, emphasizing the convenience and potential risks associated with online communication. Additionally, the document highlights practical exercises for using email and suggests further reading resources.