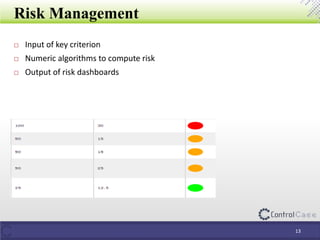
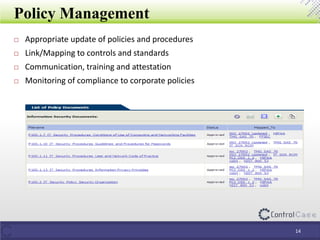
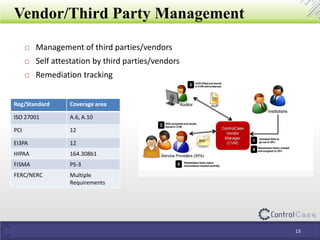
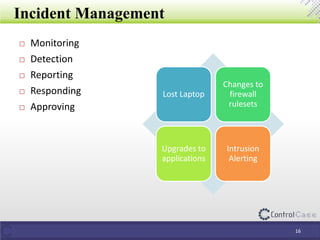
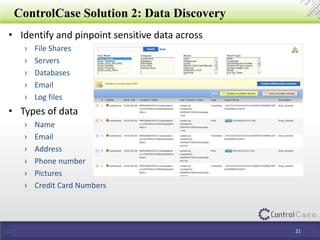
The document outlines the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), detailing compliance requirements, non-compliance consequences, and the roles of data processors and controllers. It emphasizes the necessity of a Data Protection Officer, the importance of a Data Impact Assessment, and the tactical steps for ensuring GDPR compliance, including policies for data security and breach notifications. ControlCase offers solutions for data assessment and discovery to assist organizations in achieving GDPR compliance.