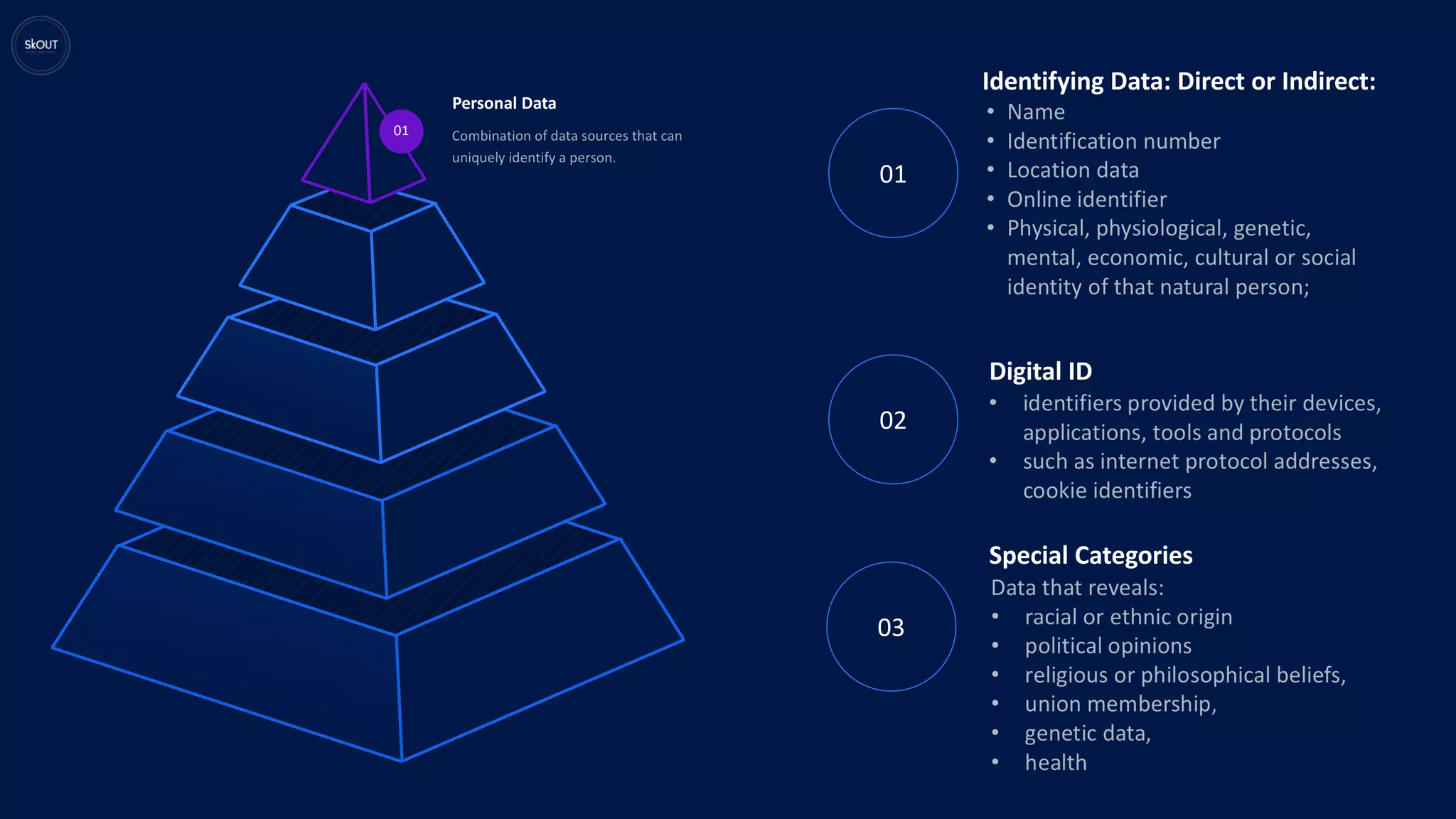
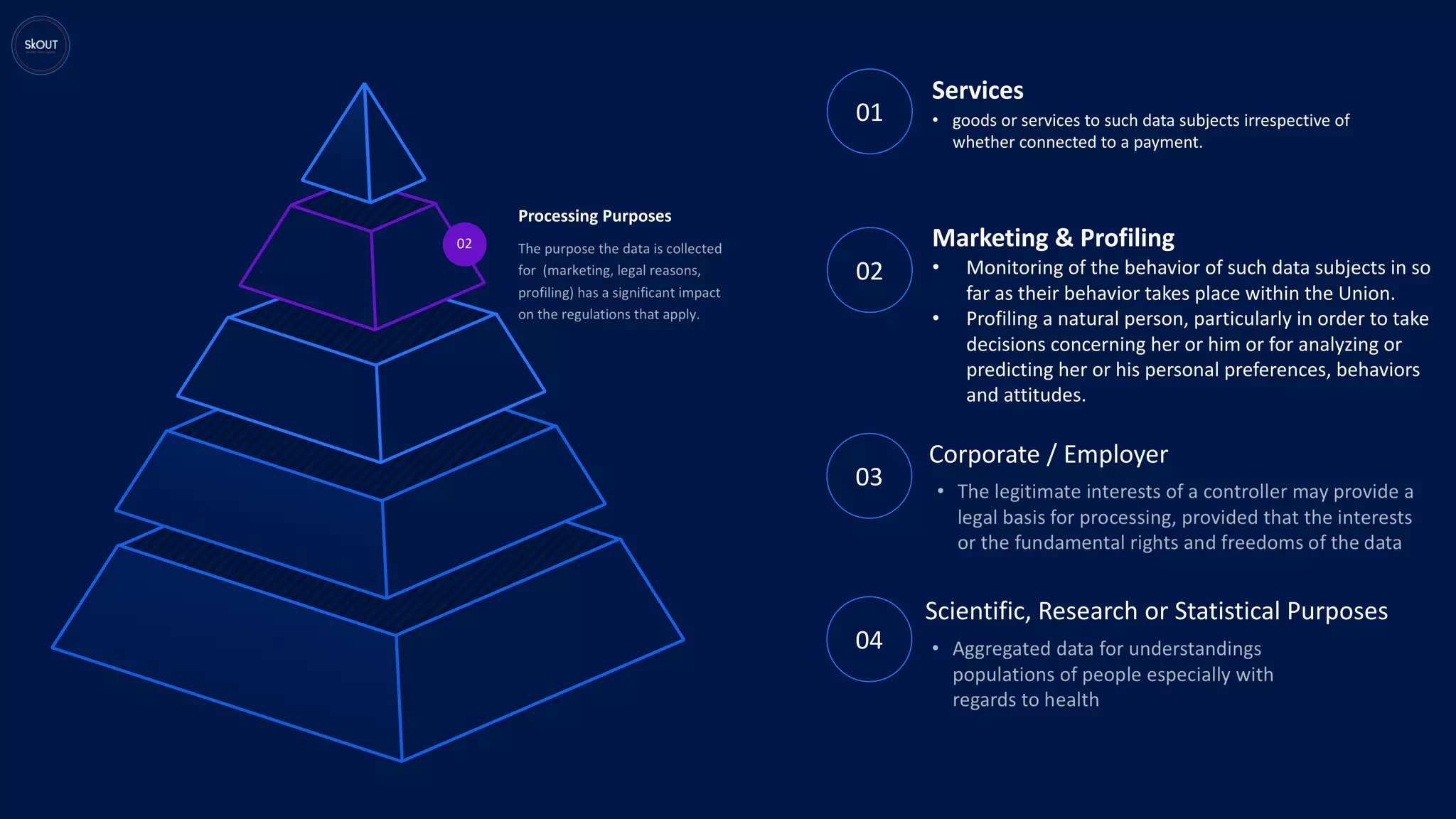
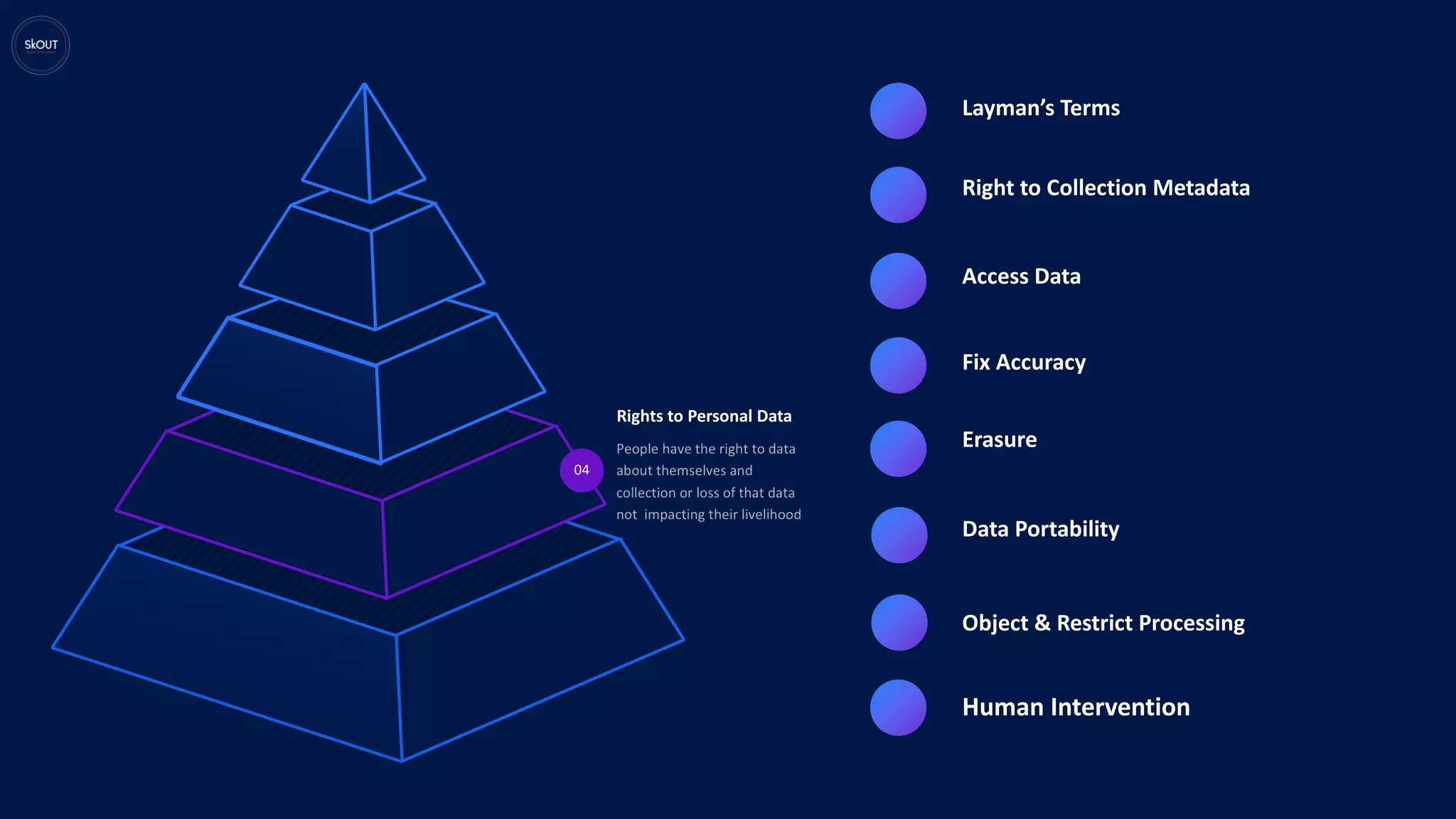
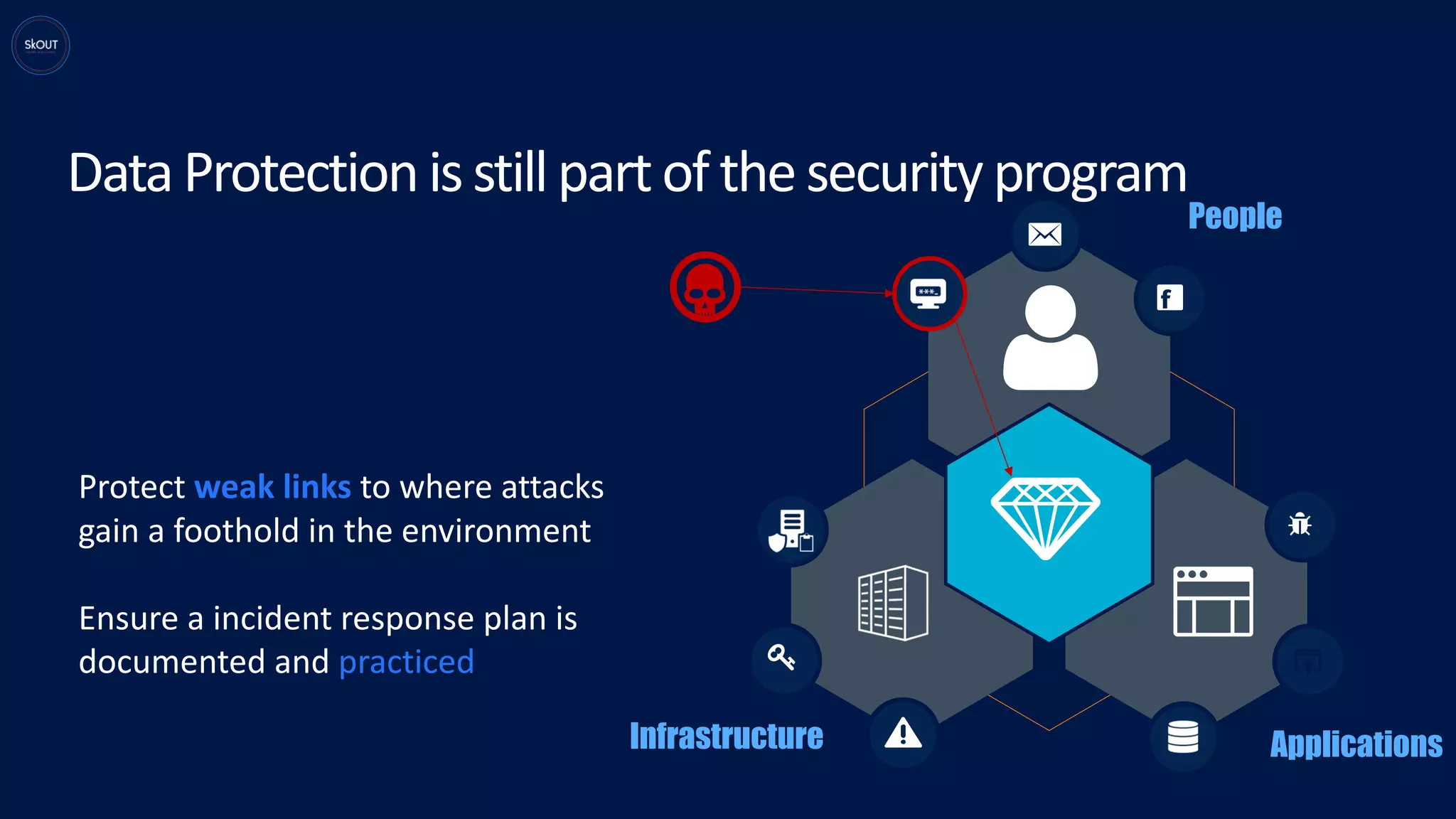
This document provides an overview of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for being ready to comply with it. It discusses how GDPR is different from previous regulations by focusing on personal data rights. It outlines the key principles of GDPR, including data protection by design. It describes the responsibilities of data controllers and processors. It presents a pyramid structure showing the levels of personal data, processing purposes, authorization for processing, and rights to personal data. It discusses requirements around records management, security, and breach notification. The key takeaways are that data protection involves both usage and disclosure of data, and that GDPR focuses on individual rights related to data analytics and identification.