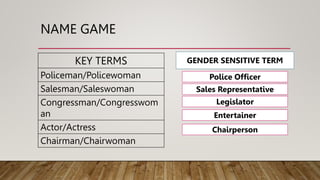
This document discusses gender and development in education. It defines key terms like gender, gender equality, and gender equity. It explains that gender refers to social and cultural differences between men and women, while sex refers to biological differences. The document outlines the composition and functions of a Gender and Development Focal Point System in schools. It emphasizes the importance of a gender-responsive teaching and learning environment that is safe, healthy, inclusive and conducive to learning for both male and female students. It also discusses strategies to promote gender-sensitive teaching and the importance of extracurricular activities and counseling skills.