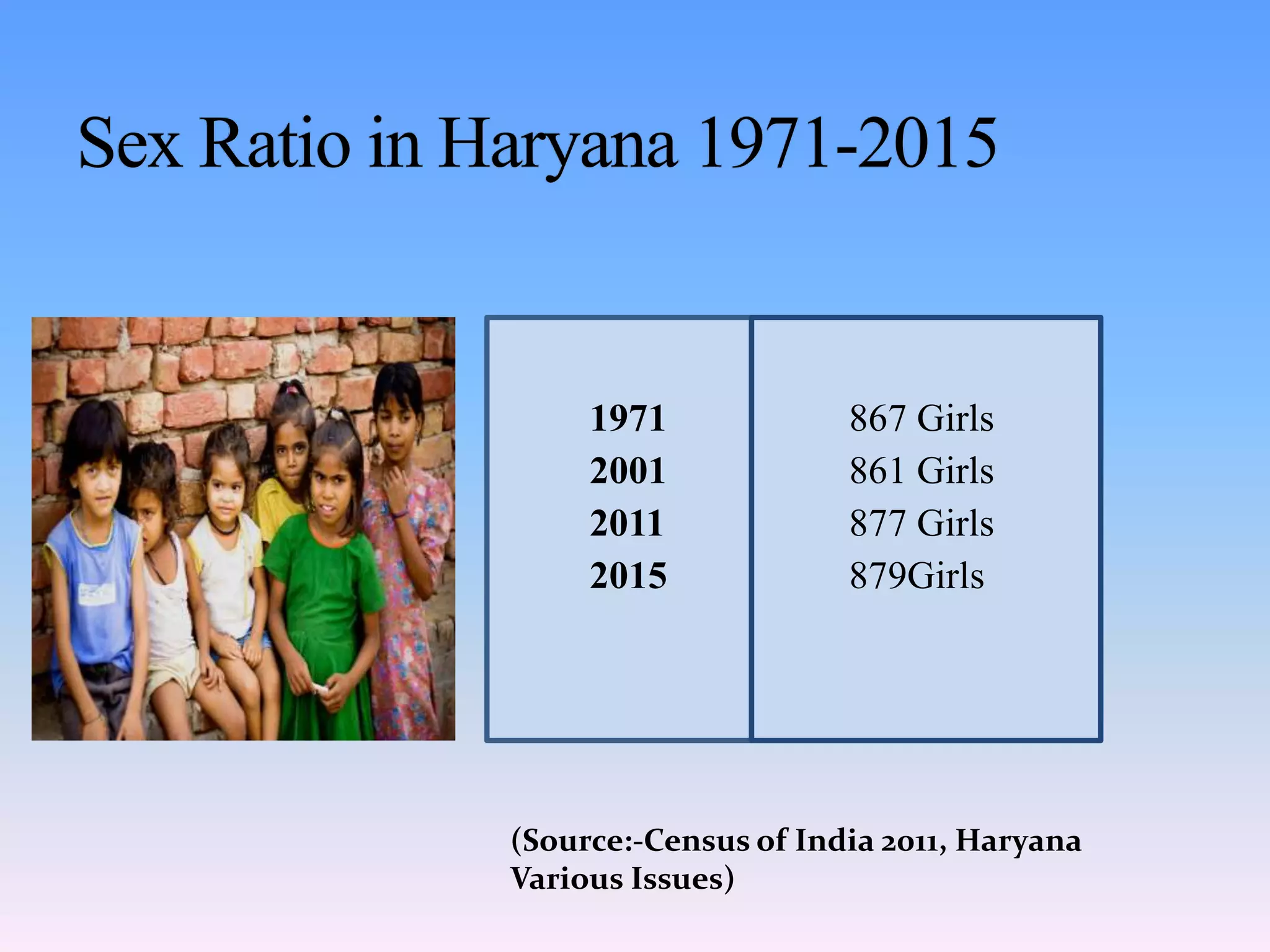
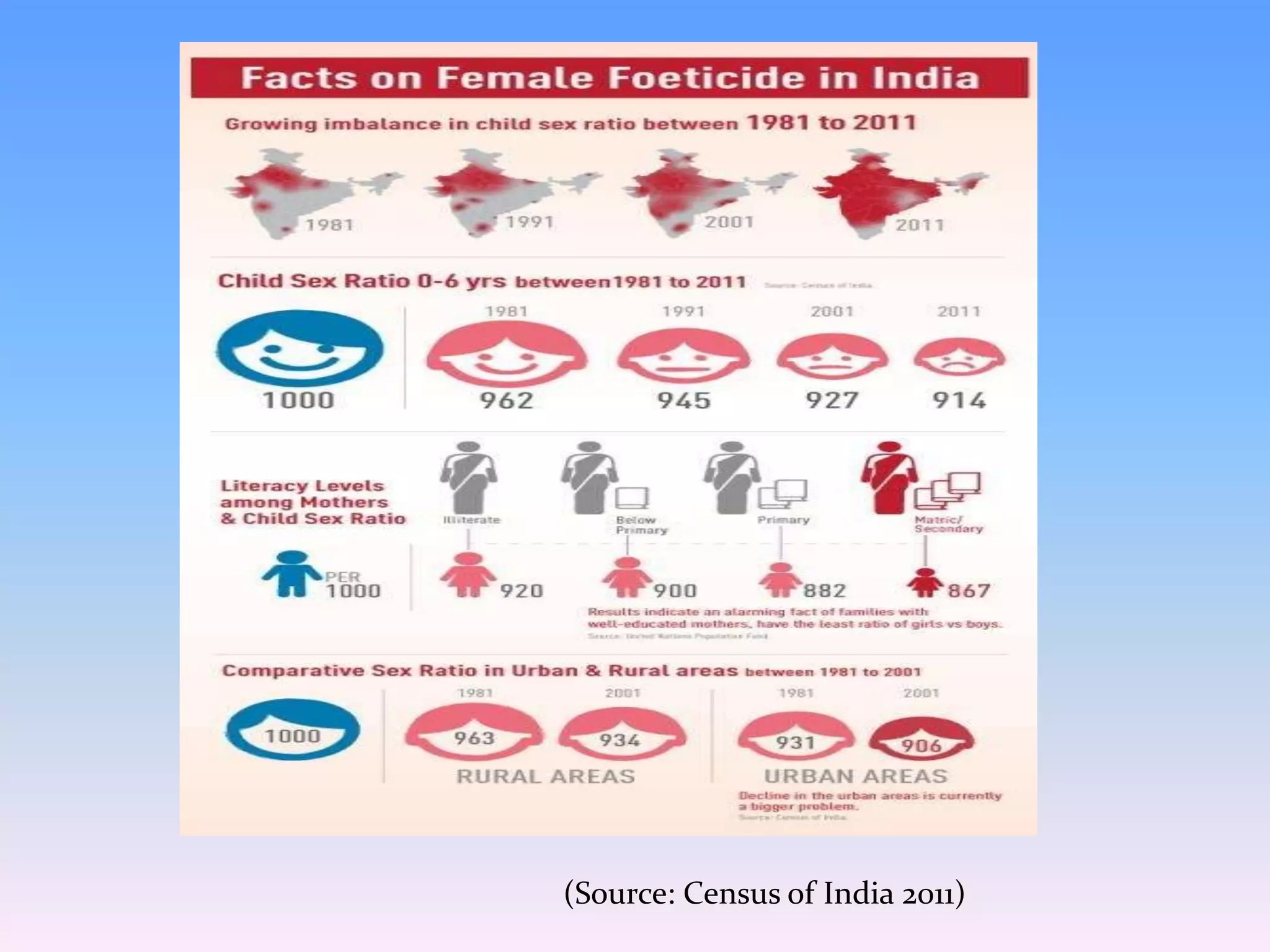
The document discusses gender discrimination and inequalities faced by women in India. It notes that gender refers to the socio-cultural roles, behaviors and attributes assigned to men and women in a society. In India, women face discrimination from birth, with female infants often seen as a burden. Women and girls are subjected to neglect, unequal treatment and violence throughout their lives. They have lower literacy rates and less access to education and opportunities than men. The document outlines some of the key issues related to gender inequalities in India such as female foeticide, dowry practices, gender-based violence, and disparities in health and nutrition.