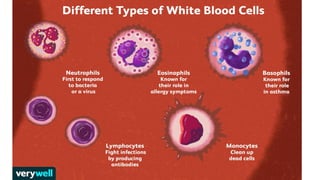
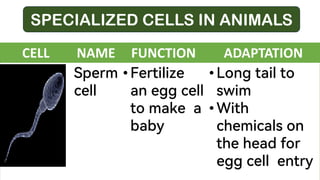
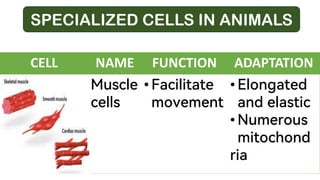
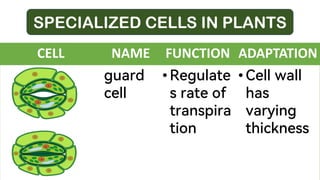
OBJECTIVES:
At the end of the lesson, the learners shall be able to:
K: distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells according to their
distinguishing features
S: classify different cell types (of plant/animal tissues) and specify
the functions of each
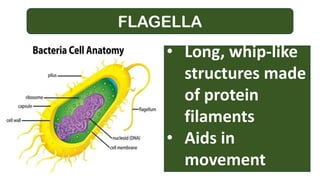
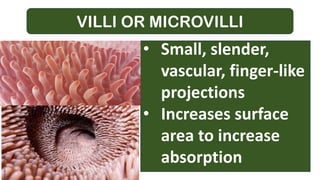
A: relate the importance of some cell modification by describing
their adaptation to carry out specialized function (e.g.,
microvilli, root hair)
LEARNING COMPETENCIES:
• Distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryo
Cells are the basic structures of all living organisms. Every
organism is composed of one or two structurally different types of cells:
prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.