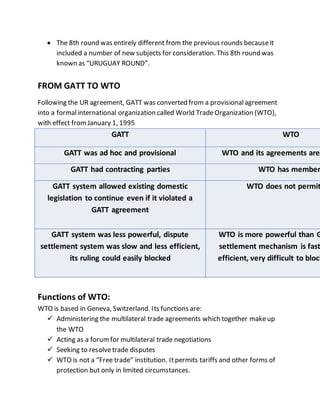
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) was established in 1947 with 23 founding member countries to promote international trade through negotiated tariff reductions. GATT underwent 8 rounds of negotiations and had grown to include 128 member countries by 1994. In 1995, GATT was replaced by the World Trade Organization (WTO) which has stronger rules and a more powerful dispute resolution system. The WTO continues GATT's mission of liberalizing trade to spur global economic growth and development.