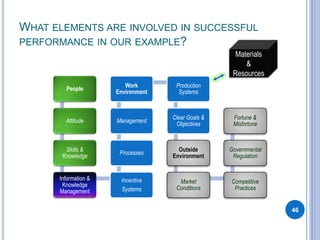
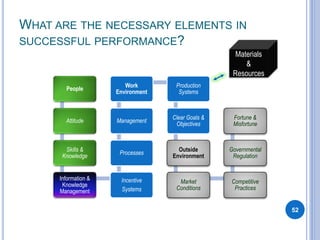
This document provides an overview of gap analysis, a tool used to analyze the difference between desired and actual performance. It discusses gap analysis in three parts: 1) Go for the Should - defining what the ideal or desired state of performance should be in terms of value creation, 2) Analyze the Is - examining what the current state of performance is, and 3) Pinpoint the Causes - identifying factors that cause gaps between the ideal and actual states of performance. The document uses an example of a construction company building houses to illustrate how gap analysis can be applied to identify performance gaps and determine solutions.