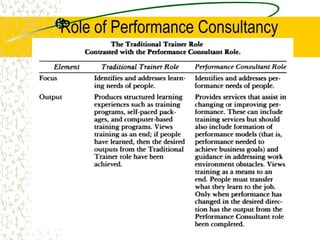
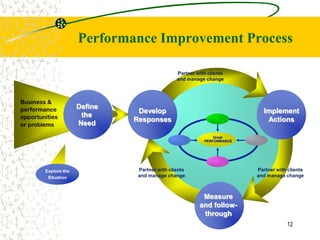
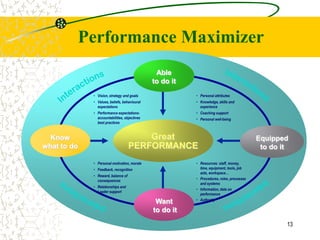
The document discusses performance consulting, which seeks to develop holistic strategies to improve performance through changes in measurement, education, staffing, and tools. Performance consulting can be divided into organizational development, professional development, and personal coaching. It is needed due to challenges like globalization and rapid change that demand broader skills from managers, leaders, and workers. As a result, human resources staff must become performance consultants who improve individual, team, departmental, and organizational performance through expertise, tools, and skills. The role of consultants is to partner with clients to define needs, develop responses, and implement and measure actions for performance improvement.