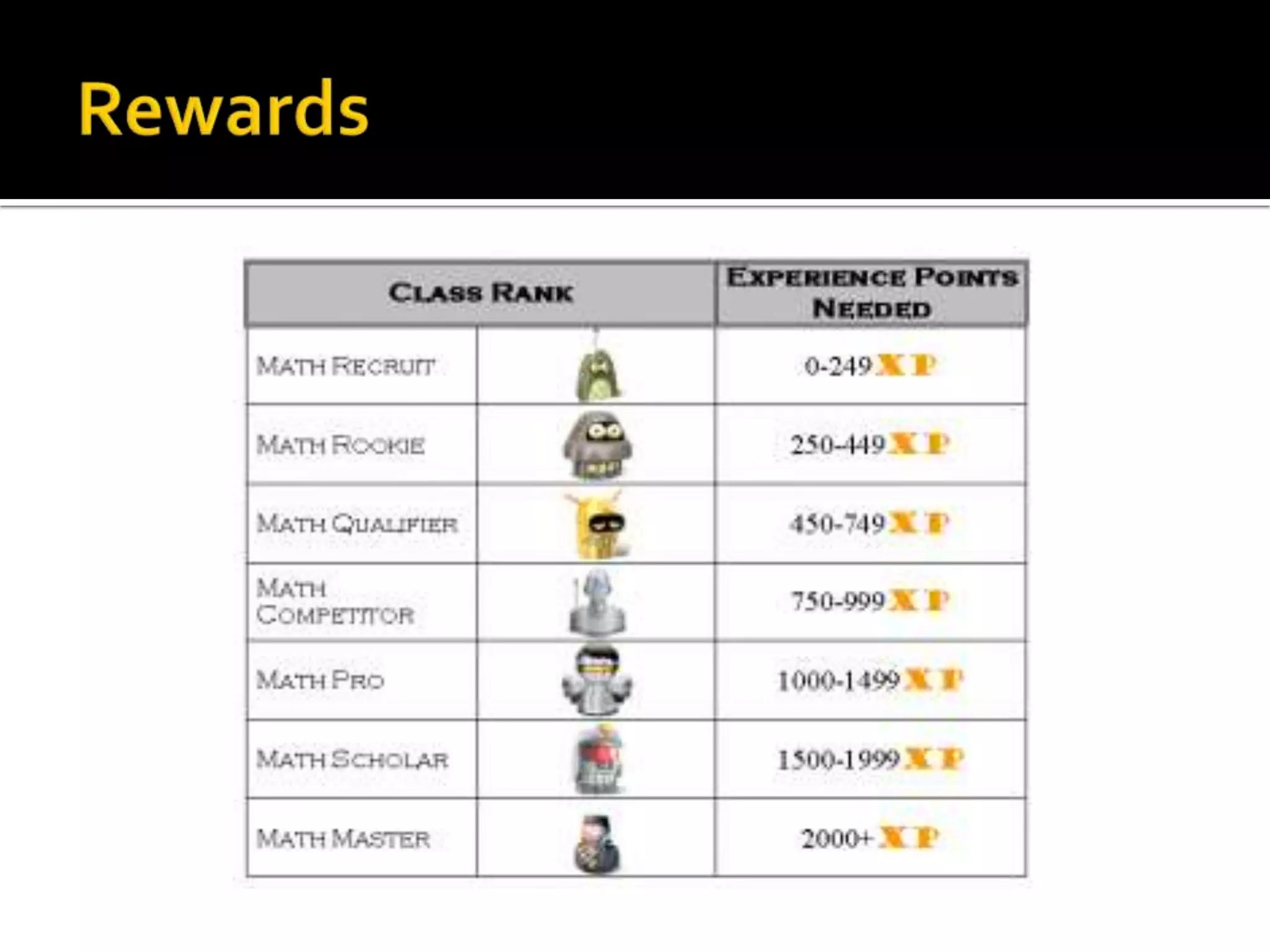
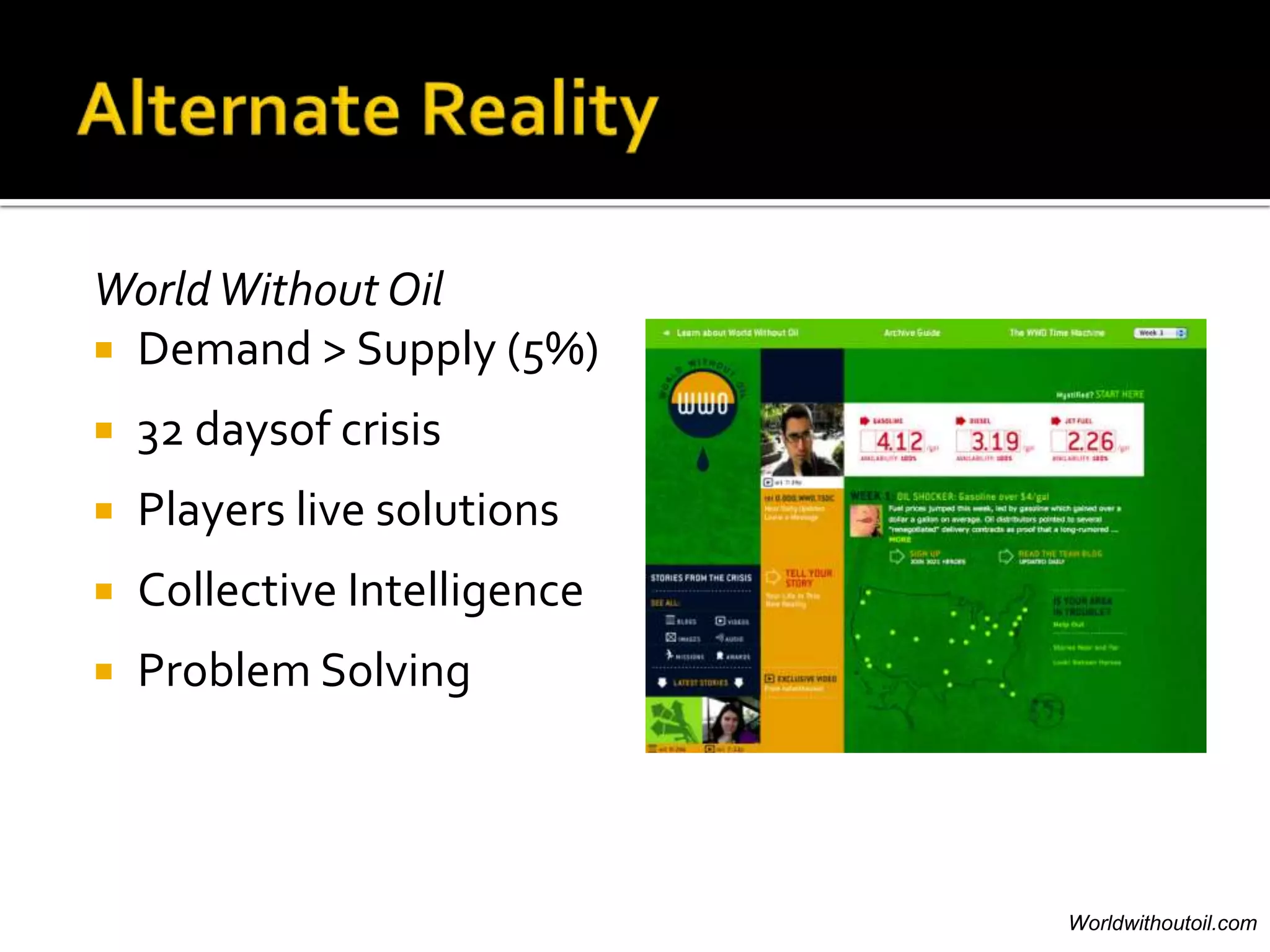
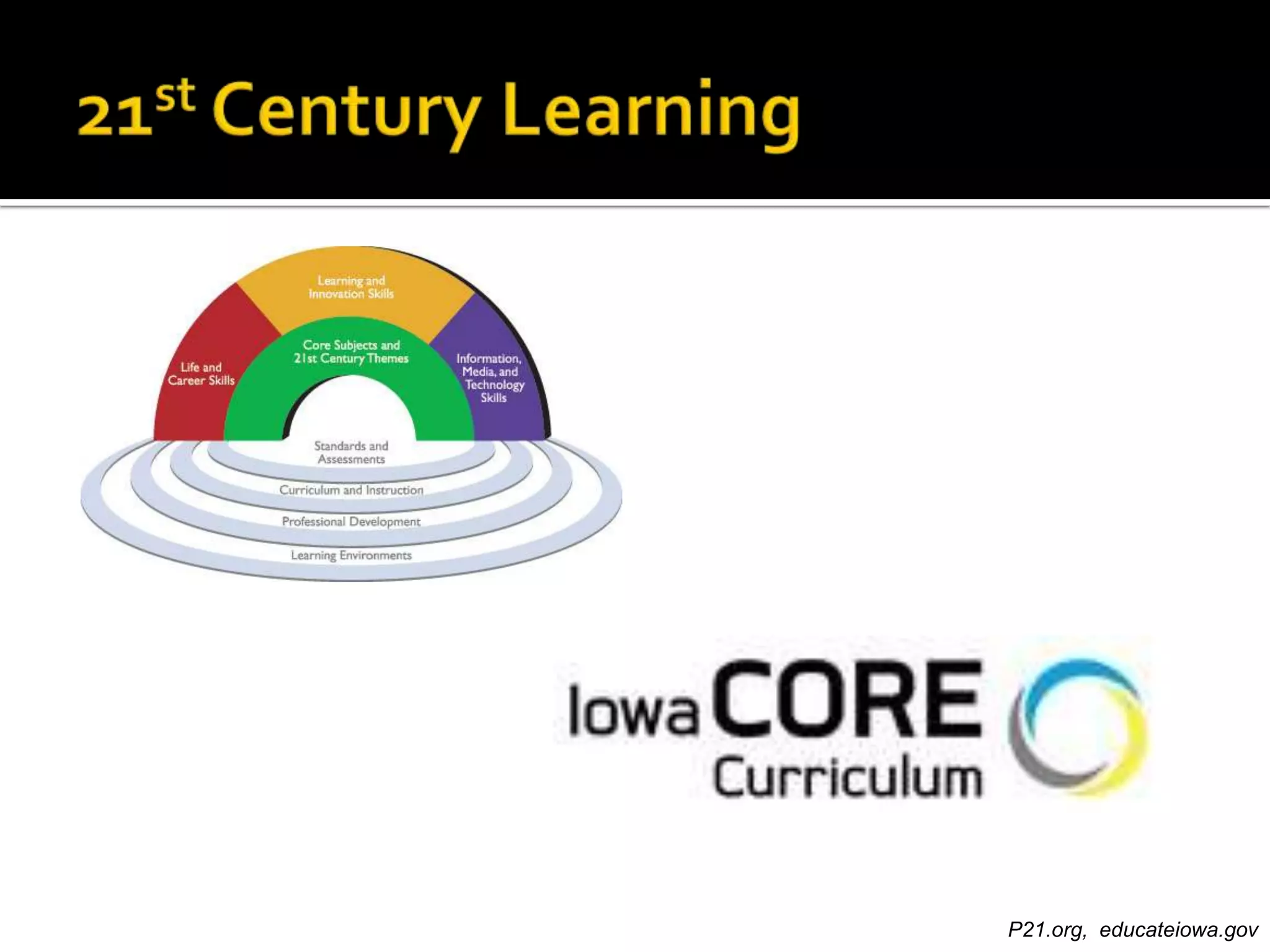
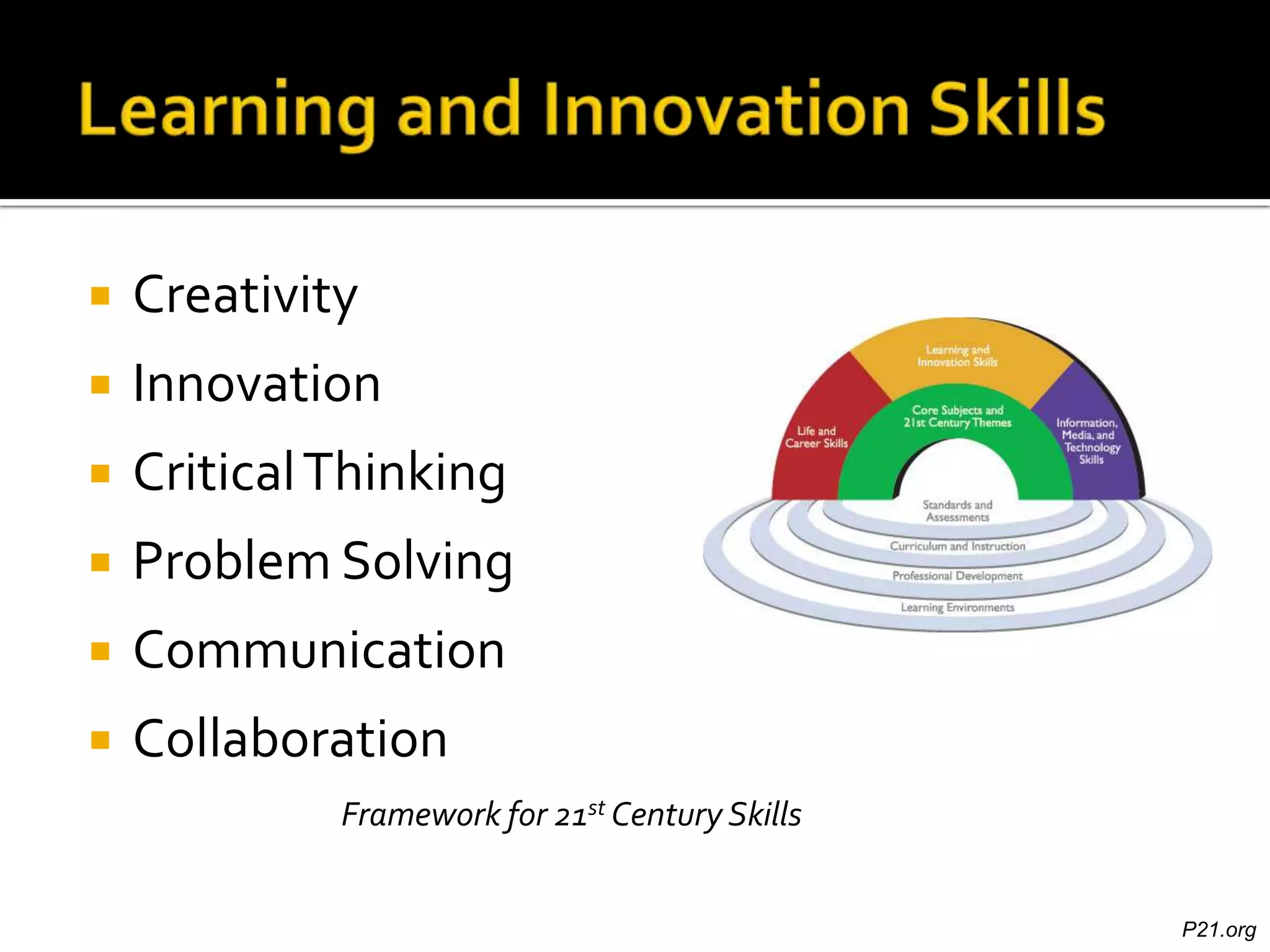
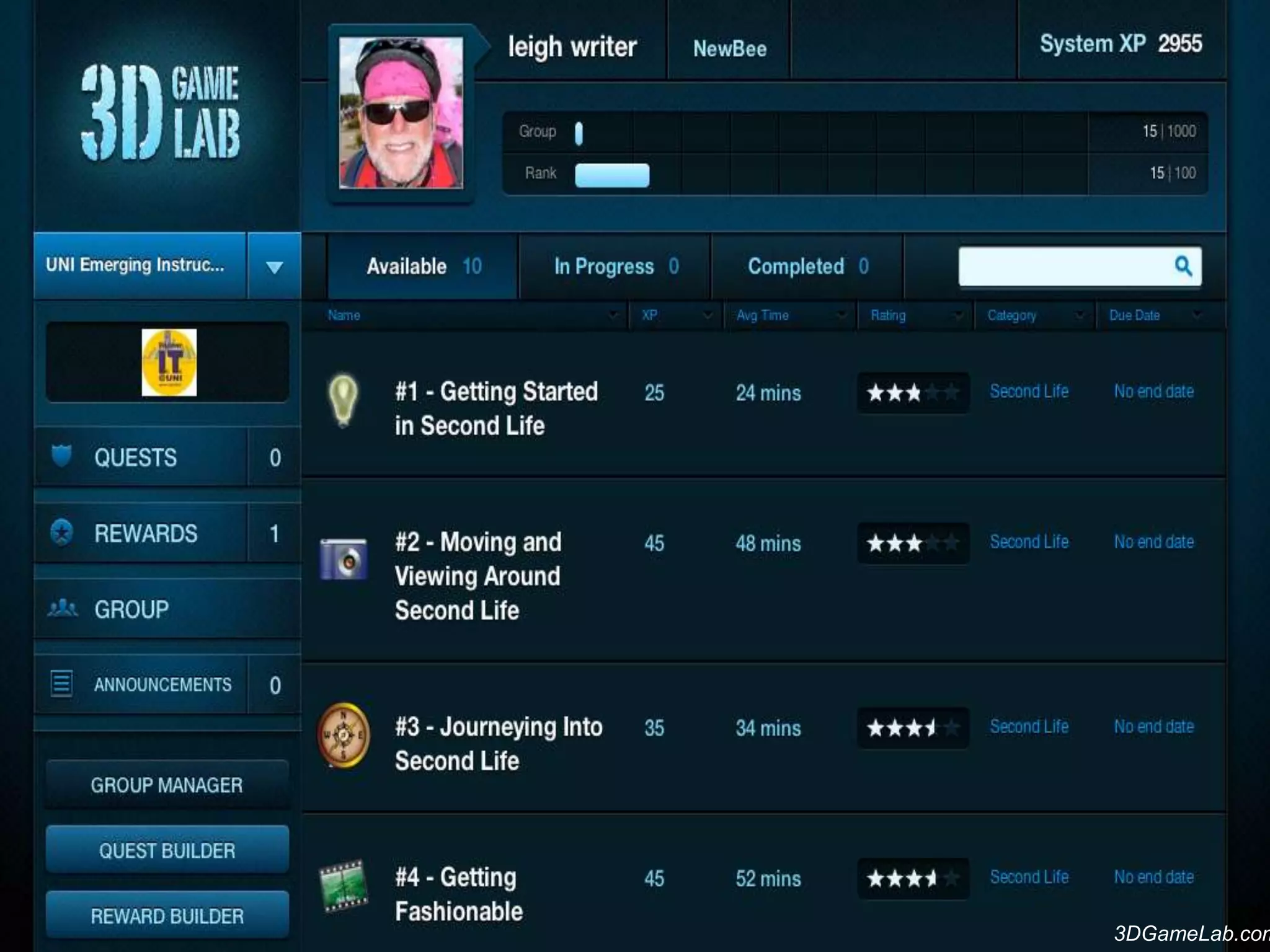
Dr. Leigh Zeitz discusses the integration of game design principles into education, emphasizing the use of positive and negative feedback to guide learners towards desired goals. He highlights key elements such as practice, meaningful feedback, and social interaction as crucial for effective learning. Additionally, he advocates for teaching students in a way that prepares them for future challenges, aligning education with modern needs.