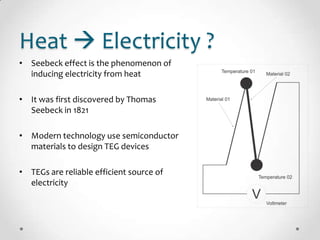
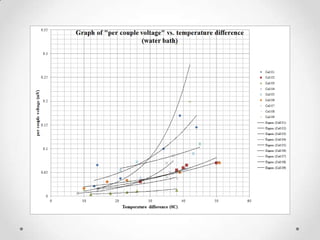
This document describes the design and development of a low-cost thermoelectric generator module that converts waste heat into electricity. The module uses the Seebeck effect to induce electricity from a temperature difference between aluminum and graphite strips. Several iterations were tested with improvements like clearer contact points between materials, more couples per slide to produce more power, and variations in strip widths and heights. Testing in an oil bath showed increased voltage output with greater temperature differences applied across the couples. The results demonstrate this simple module's potential as an efficient, renewable energy source from normally wasted heat.