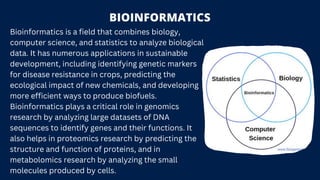
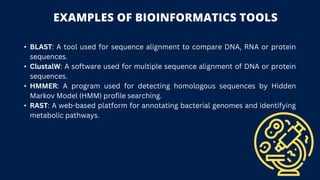
Bioinformatics and optimization tools are vital for sustainable development, aiding in addressing challenges such as climate change, food security, and disease control by providing efficient solutions. These tools facilitate data analysis and optimize resource management across various sectors, promoting informed decision-making and sustainable practices. Continued development in these fields is crucial for achieving global sustainability goals and enhancing environmental stewardship.