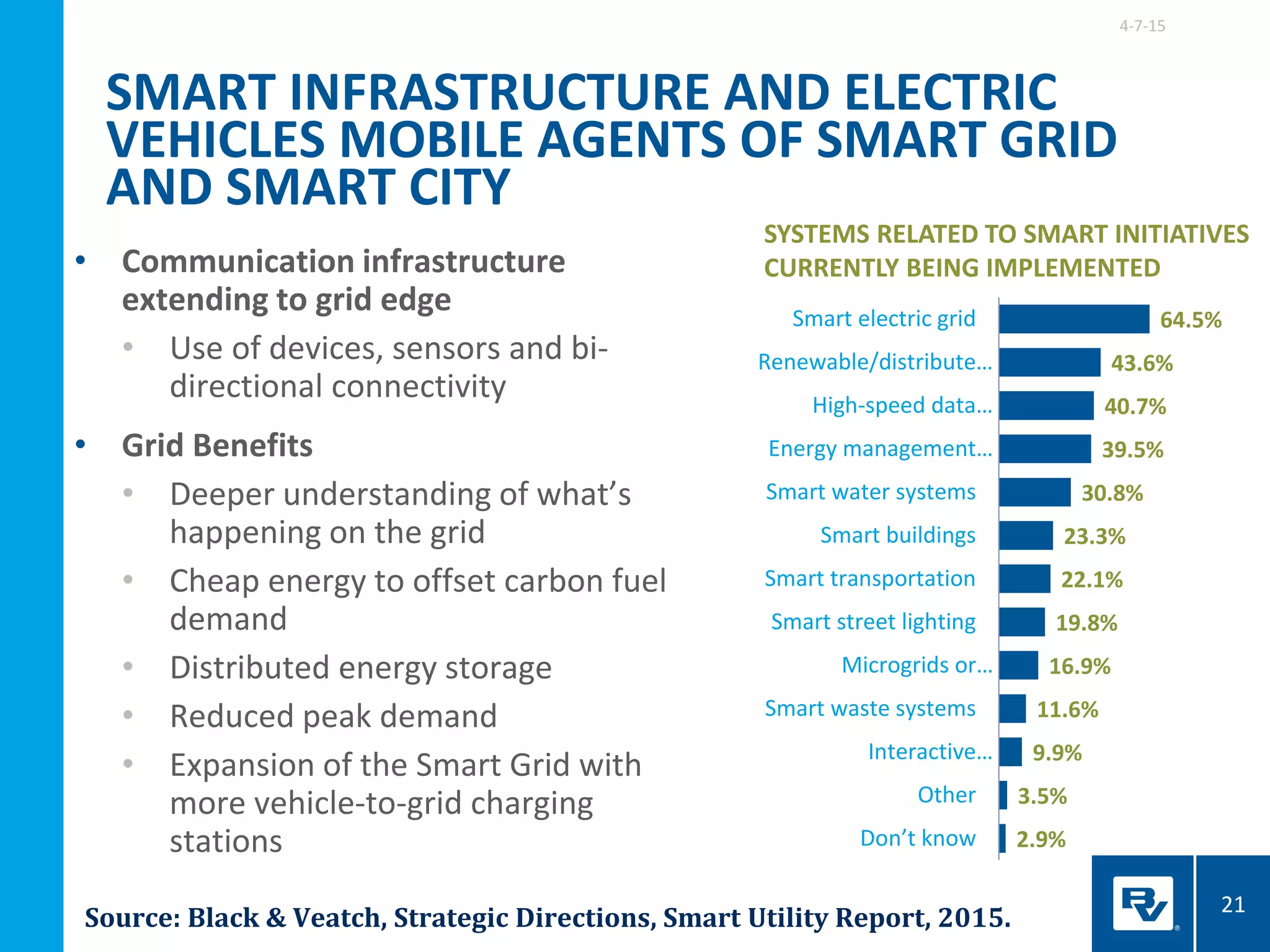
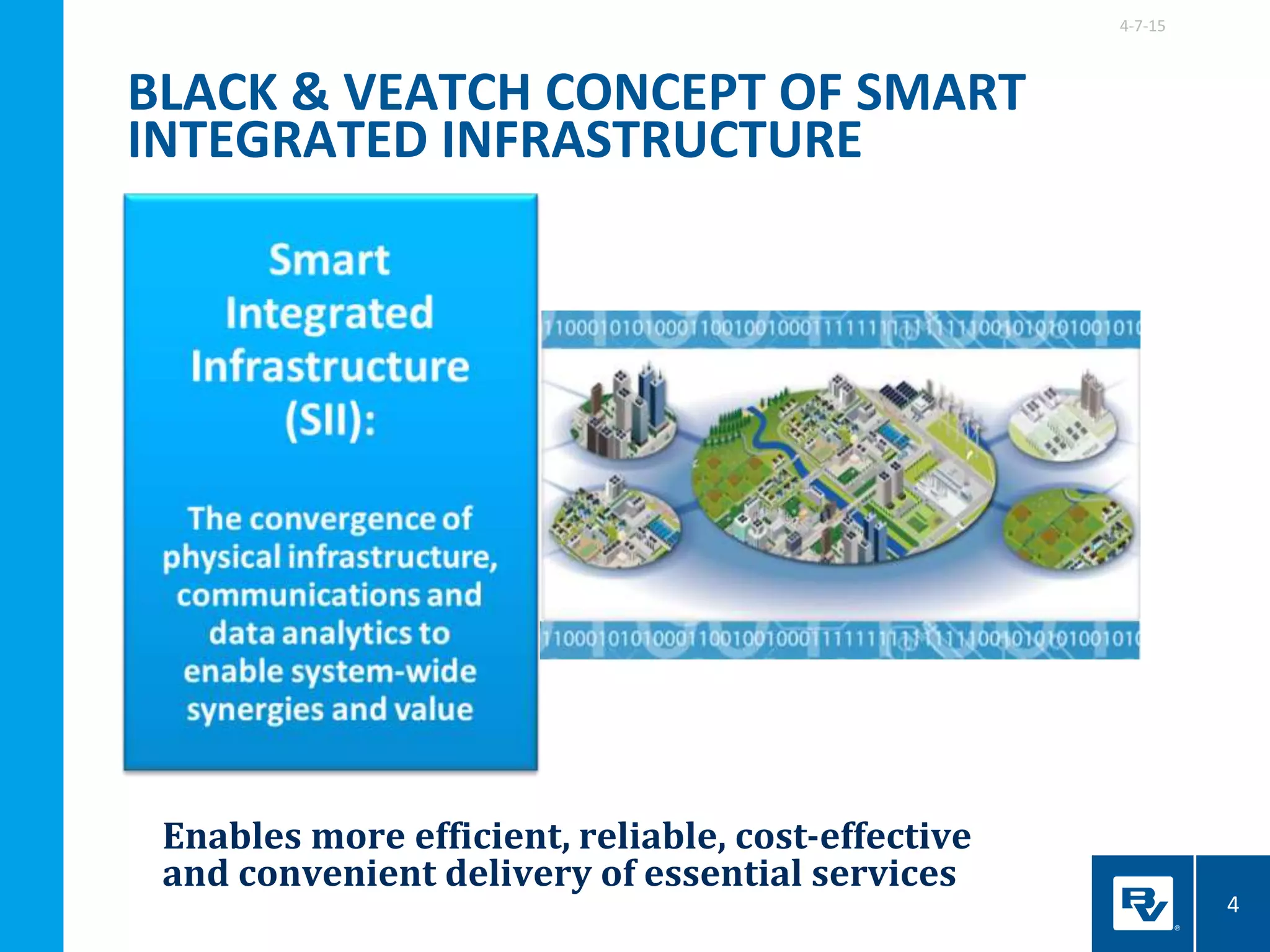
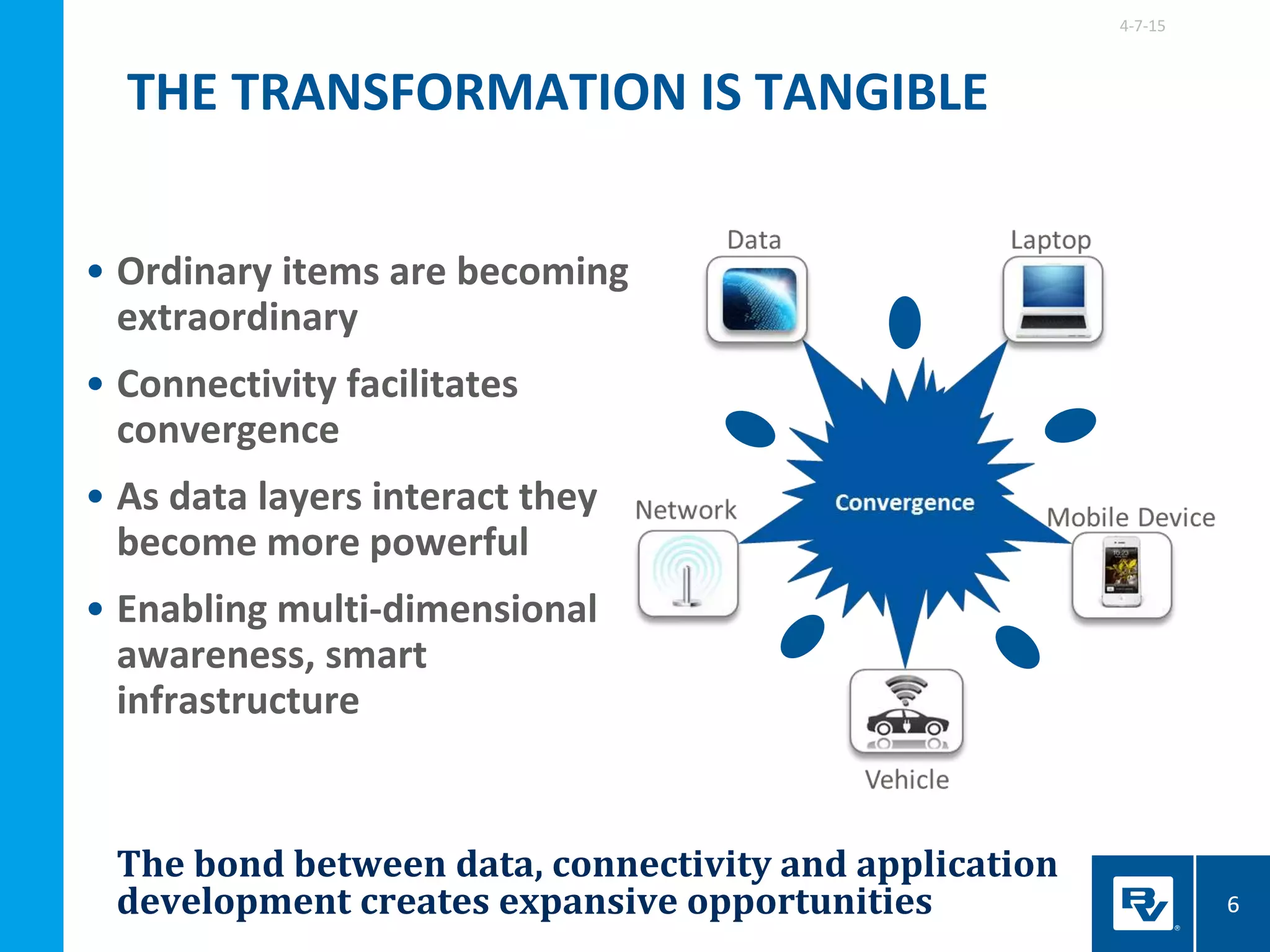
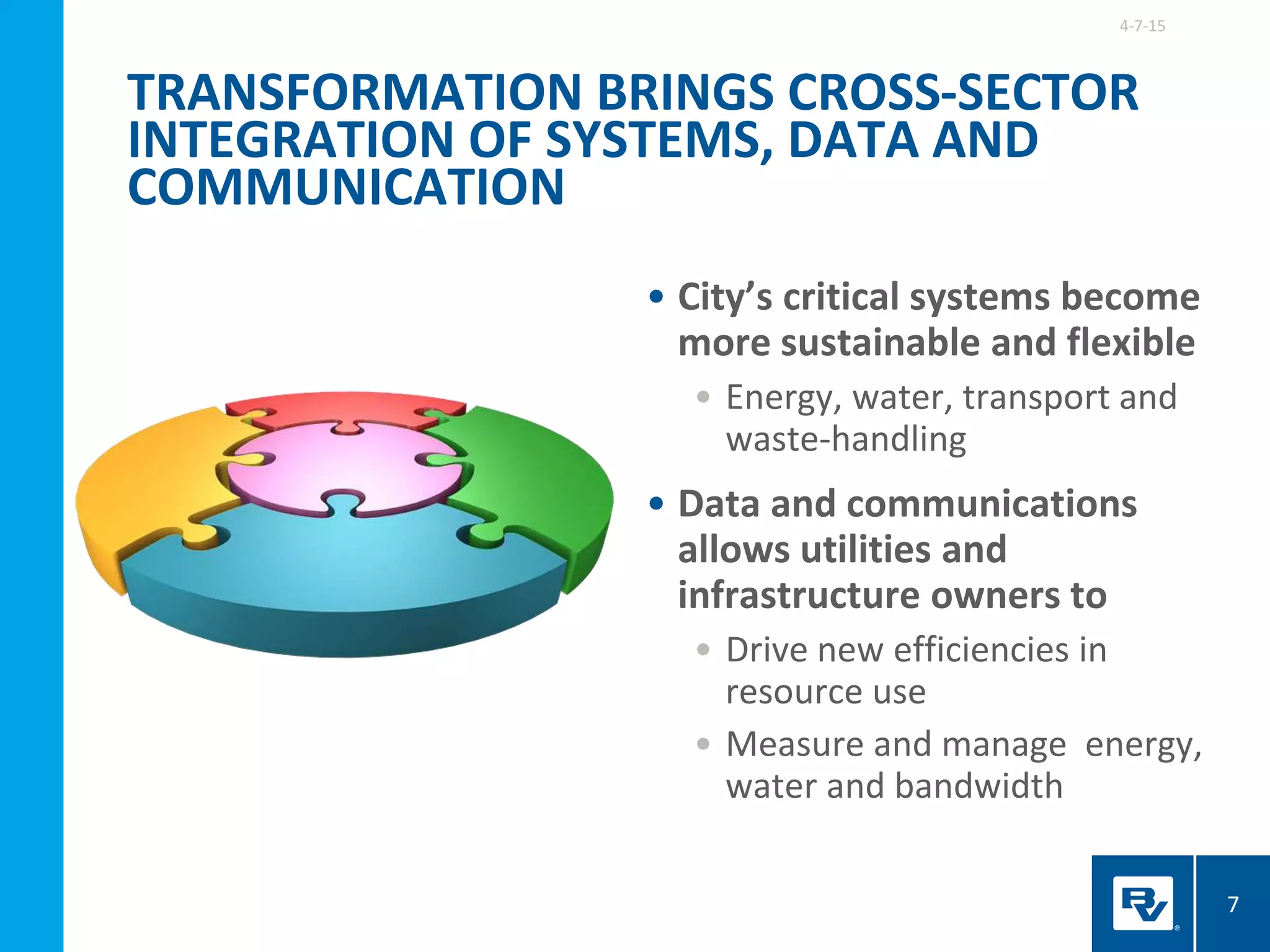
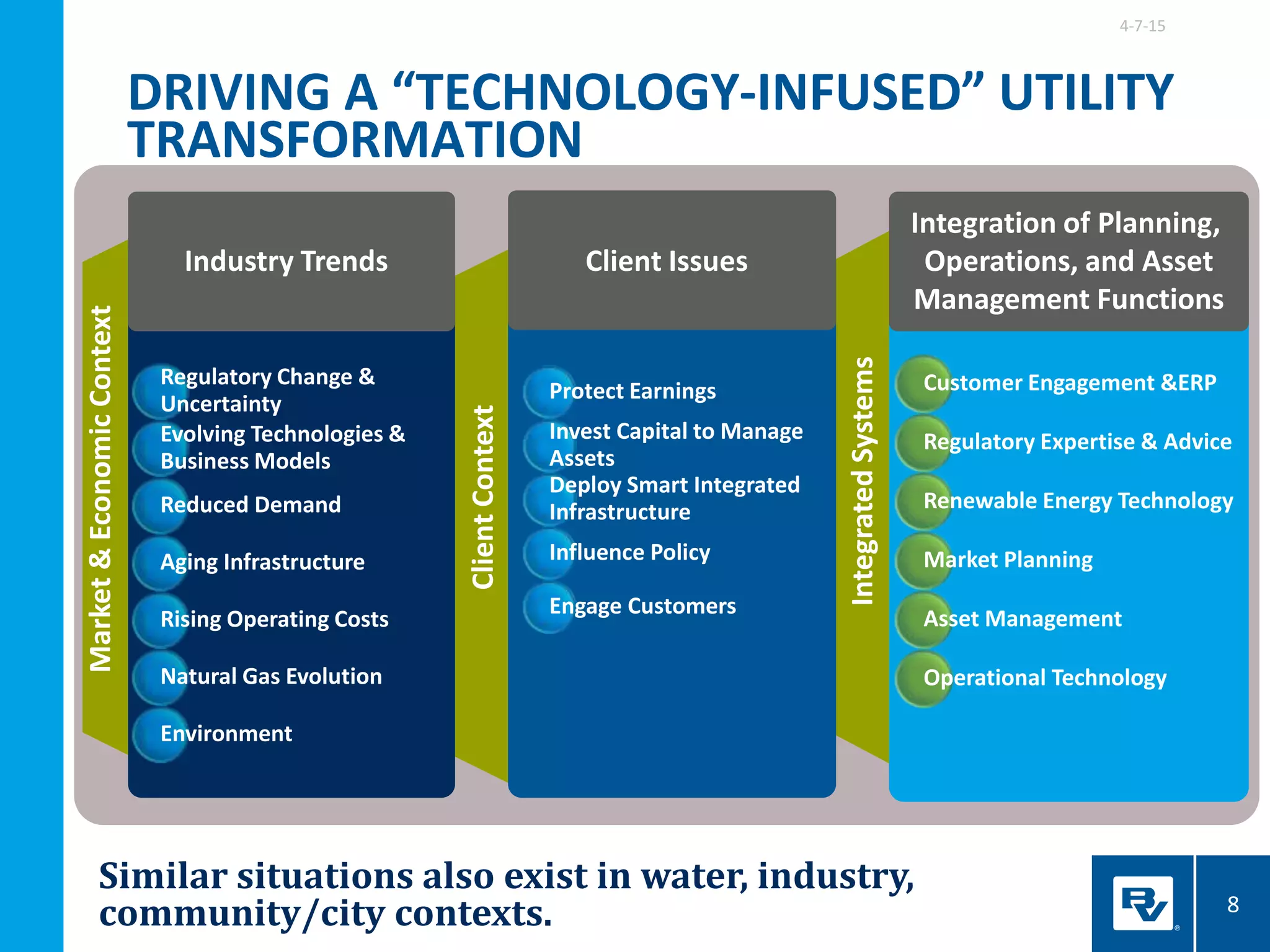
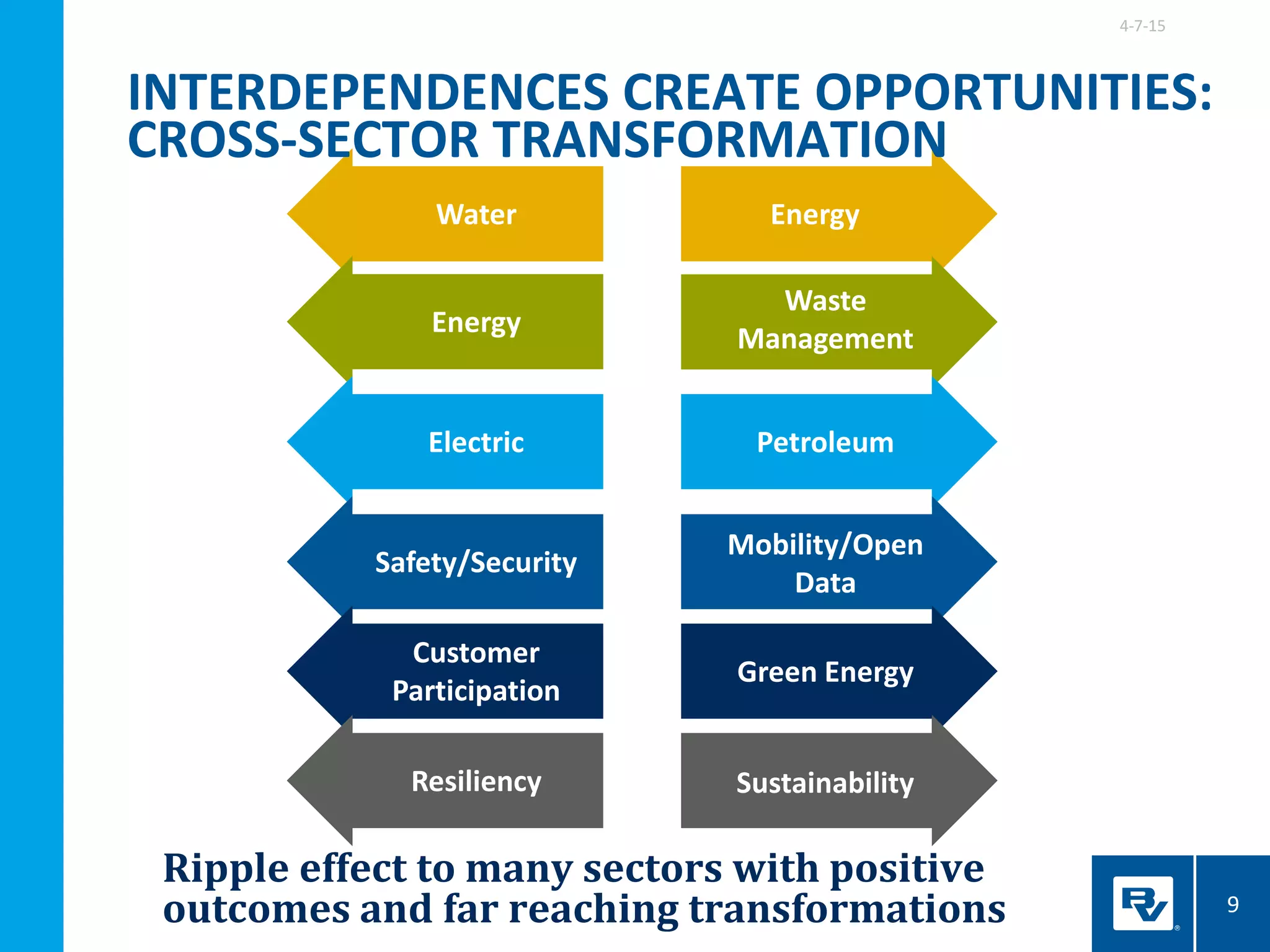
The document discusses the development of smart integrated infrastructure, highlighting the roles of key individuals in this field and the factors driving its rise, such as advancements in technology and data analytics. It emphasizes the importance of creating resilient, efficient urban systems that can adapt to challenges like climate change and aging infrastructure, ultimately improving the quality of life in cities. The document stresses the need for cross-sector integration and data-driven decision-making to achieve sustainable urban growth and enhance citizen engagement.




![18
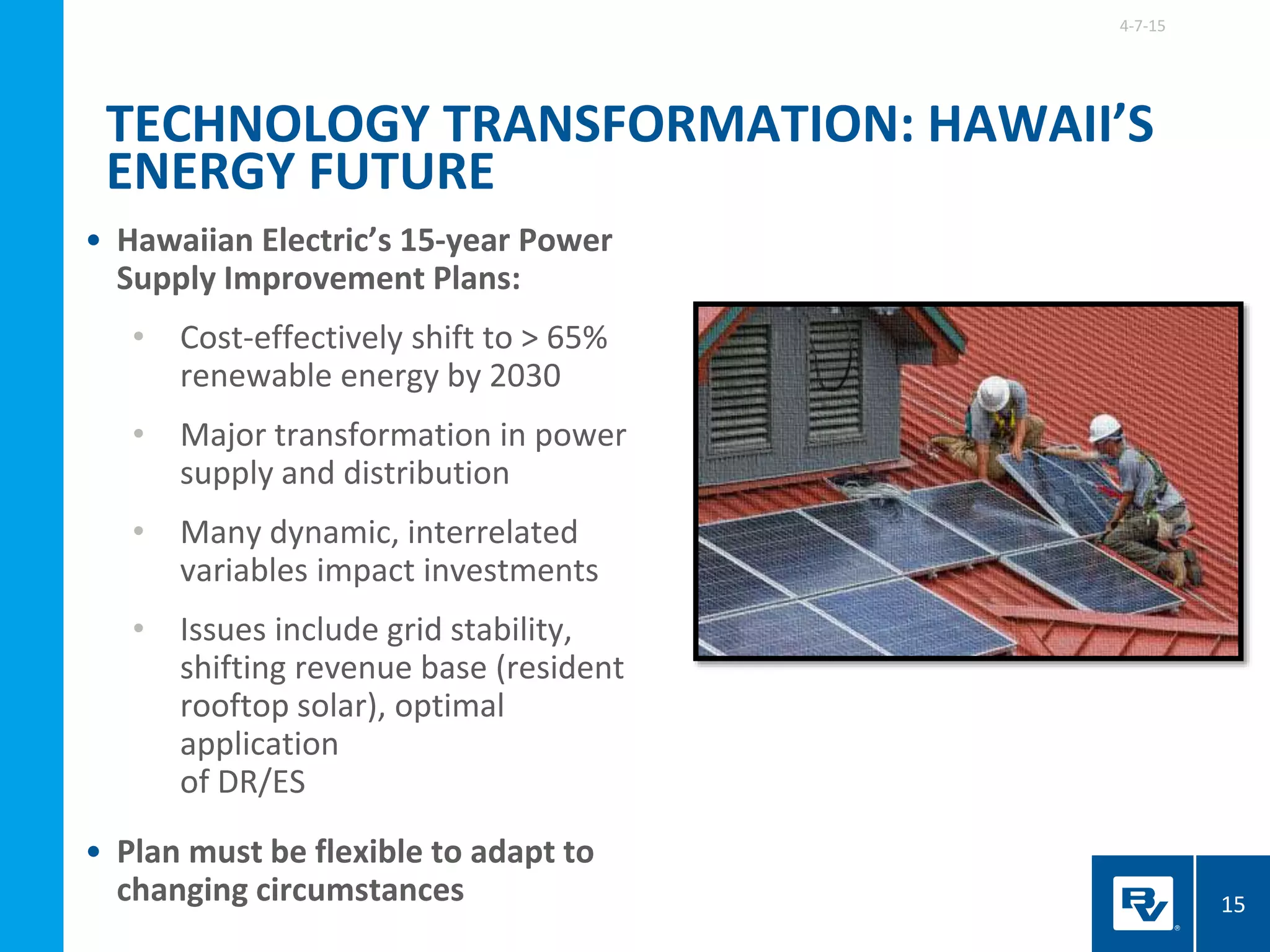
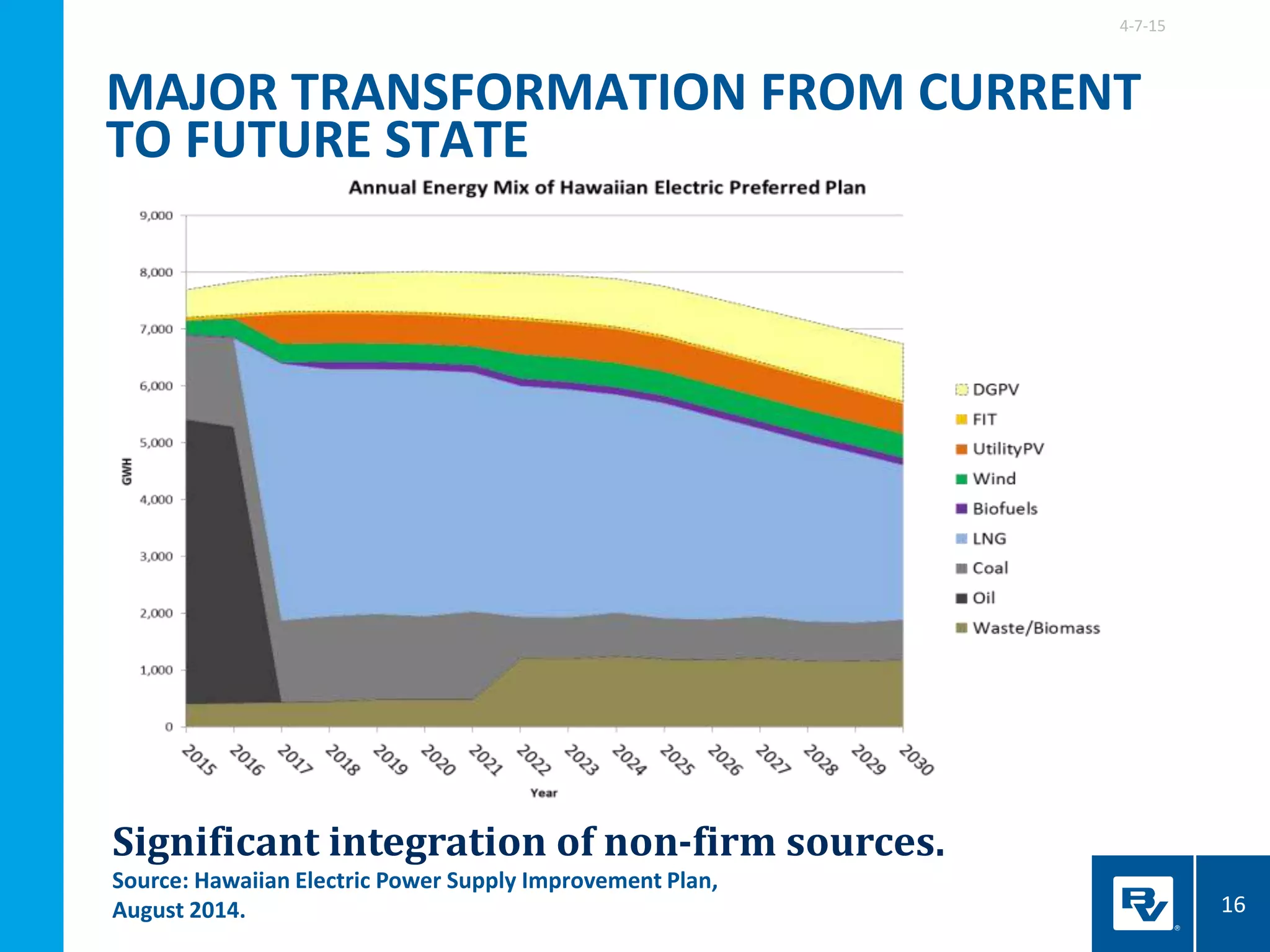
LET’S TALK SMART
TRANSPORTATION…
“The real benefits of these [connected
transportation] systems will come if cities use this
data to guide decisions about traffic management
and long-term planning.”
Knight, Will. ‘Car-Based Technology that Could Invigorate Cities’ in MIT Technology Review, 2014:
November 28.
Street-smart
sedans?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/motmwebinar4715final-150407125938-conversion-gate01/75/Future-Urban-Systems-The-Convergence-of-a-Smart-Integrated-Infrastructure-18-2048.jpg)