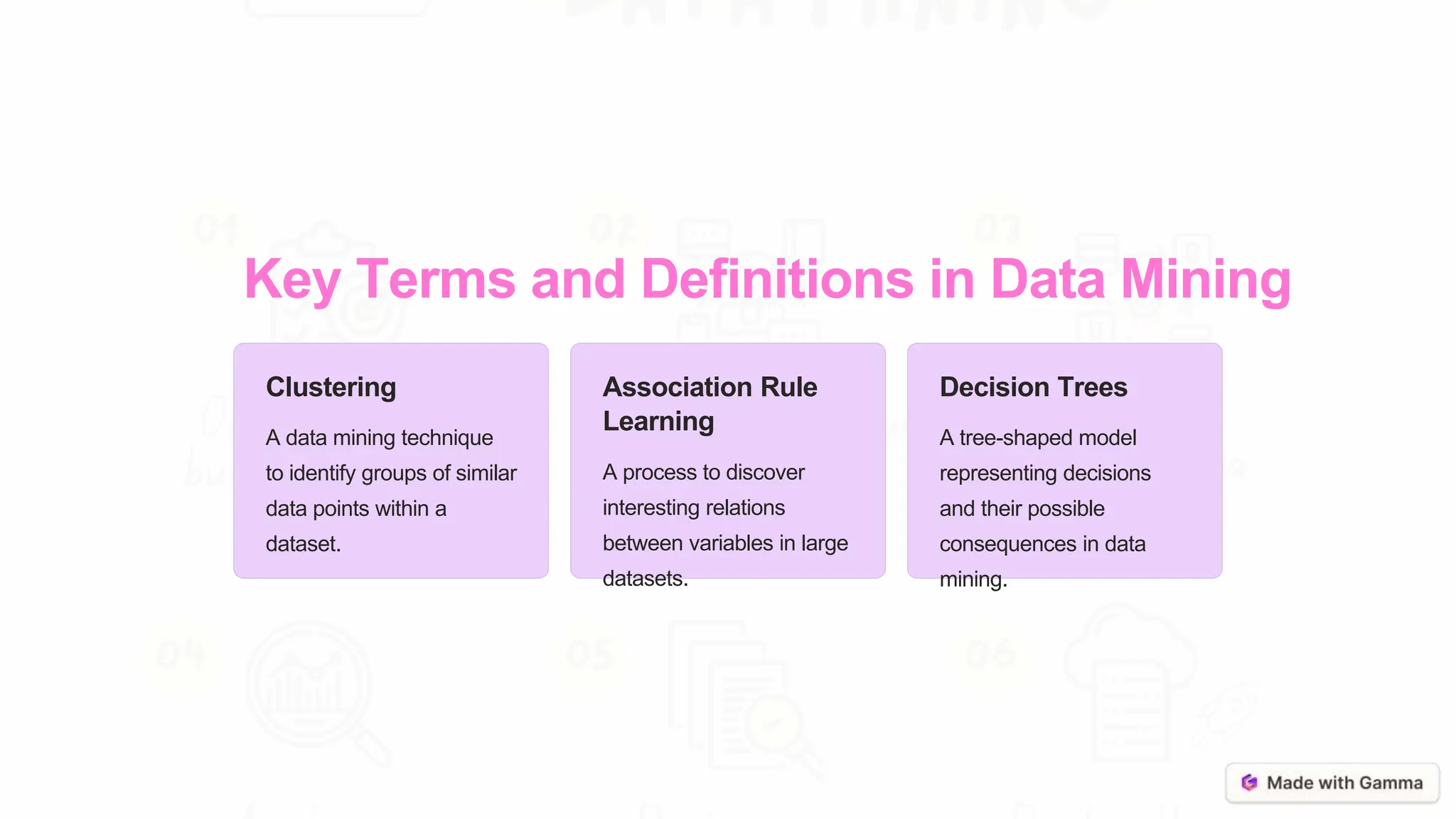
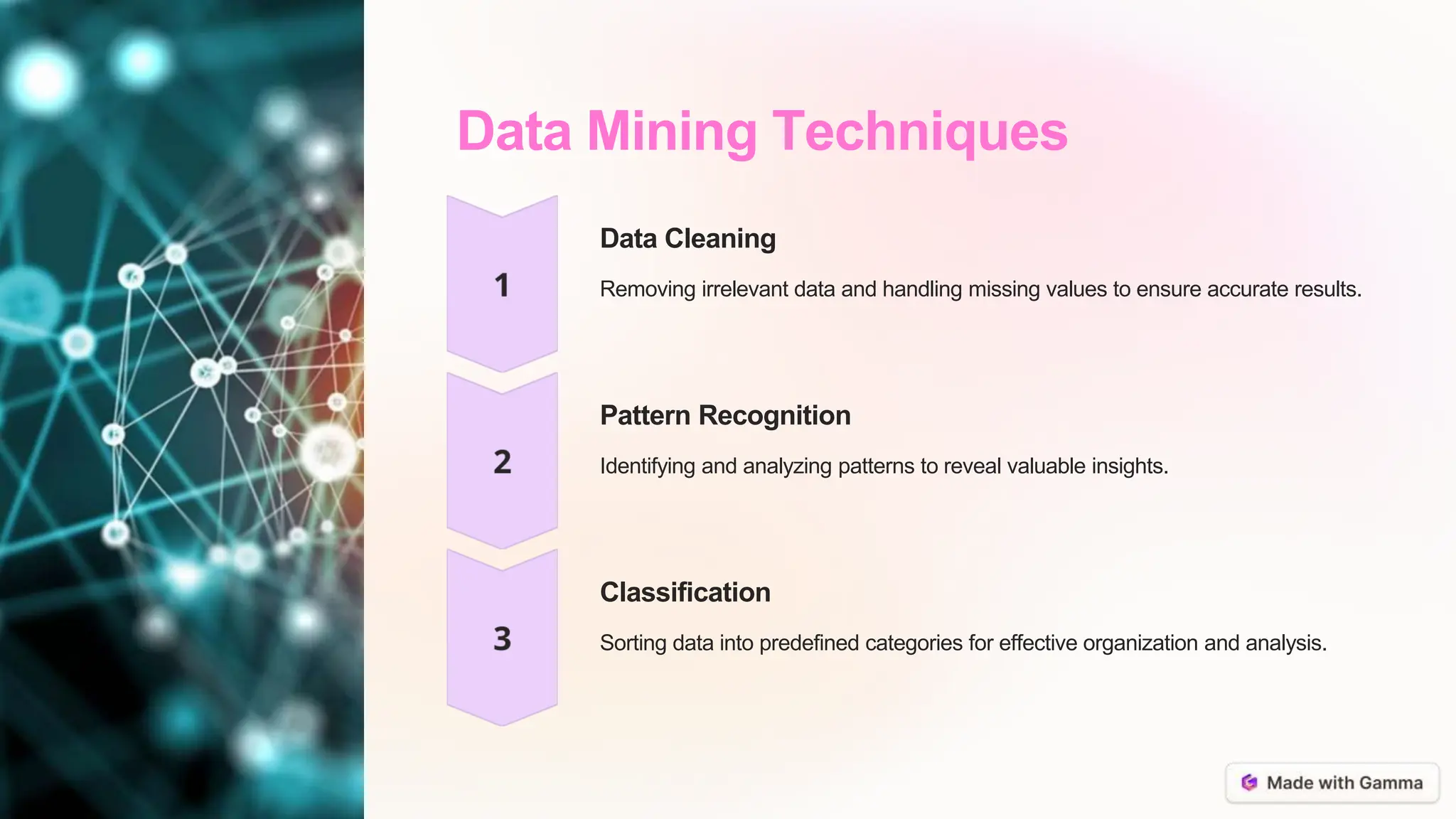
Data mining involves collecting, processing, and analyzing large datasets to discover hidden patterns and extract meaningful insights. It focuses on recognizing patterns within data and using these patterns to enable predictive analysis to forecast future trends. Data mining is important for making informed business decisions by analyzing customer behaviors and market trends, contributing to scientific research, and playing a critical role in risk management.