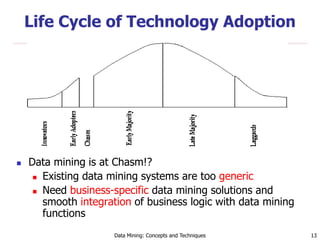
The document discusses data mining as an interdisciplinary field with applications in finance, retail, telecommunications, and biomedicine. It highlights the importance of understanding data mining principles, its potential benefits, and associated privacy and security concerns. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for domain-specific solutions and the evolving nature of data mining technologies.