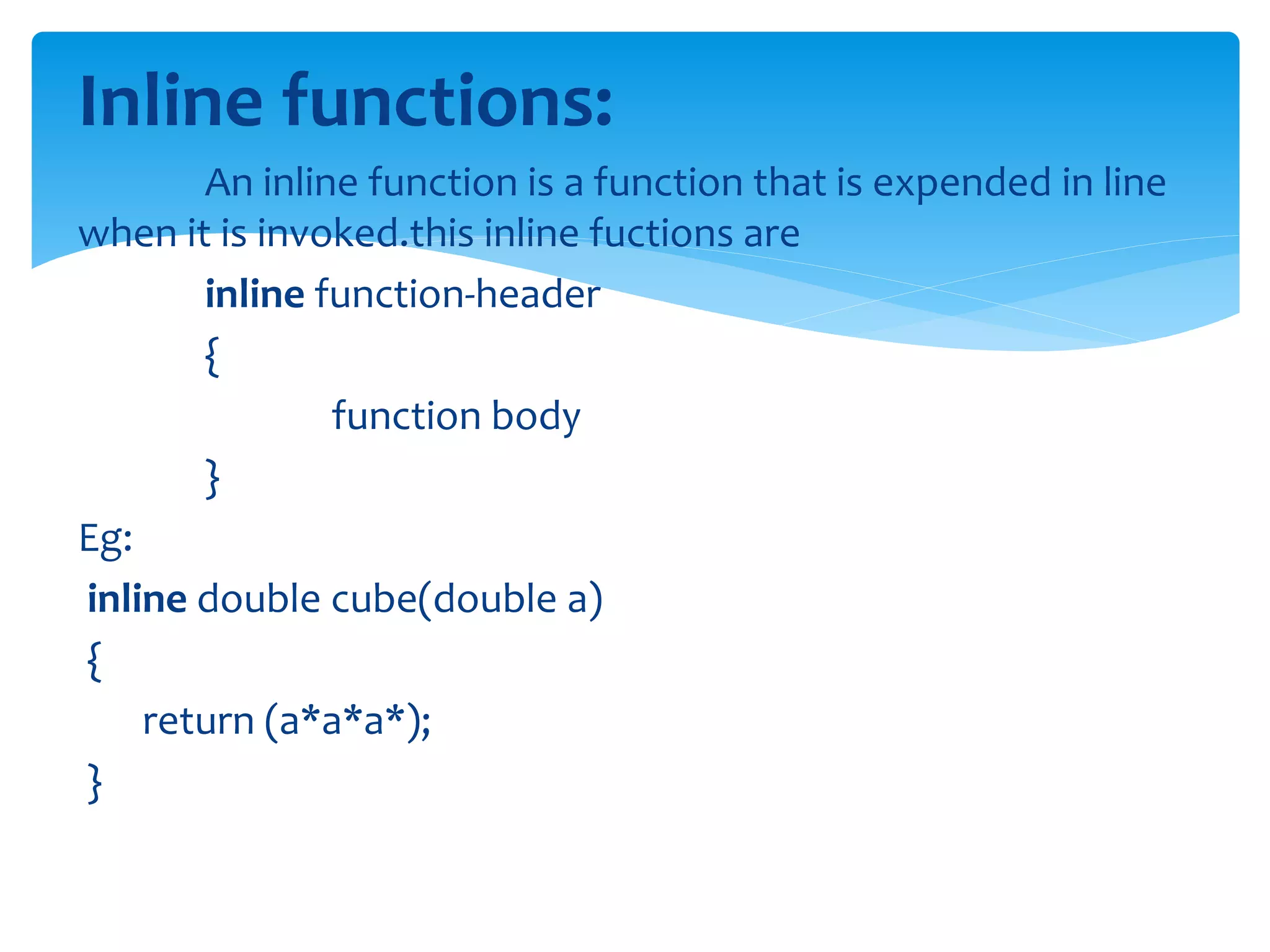
Functions in C++ can be defined and called in various ways. The main() function is the entry point of a C++ program and returns an int value. Function prototypes declare the signature of functions without defining the body, allowing for forward declaration. Arguments can be passed by reference, allowing the called function to modify the original variables. Functions can return values by reference as well. Inline functions avoid the overhead of a function call by expanding the body directly where called.



![The main() returns a value of type int to the operating system
.
Eg :
int main();
int main(int argc,char*argv[]);
The functions that have a return value should use the
return statement for termination.
The main() function in c++ is
int main()
{
………….
………….
return 0;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functionsinc-200420131537/75/Functions-in-c-4-2048.jpg)