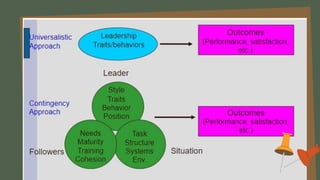
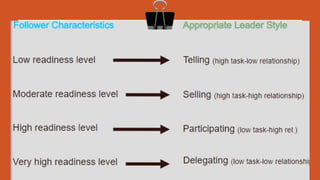
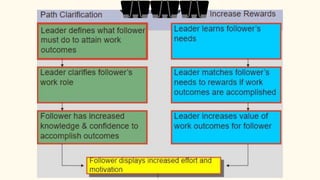
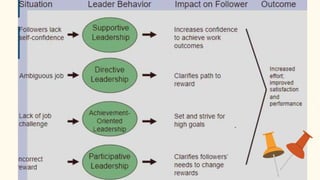
The document discusses the contingency or situational approach to management. It explains that the situational approach is based on the premise that all management is situational in nature and affected by contingencies in a given situation. There is no single best way to make decisions. The primary characteristics of the contingency approach are that there is no universal theory of management, decision-making depends on the situation, policies must adjust to environmental changes, and managers must have diagnostic and communication skills to deal with changes. The advantages are that it provides a realistic view and innovative style, while disadvantages include lacking a theoretical base and difficulty analyzing all situational factors. The document also discusses Fiedler's contingency model, Hersey and Blanchard's situational leadership theory