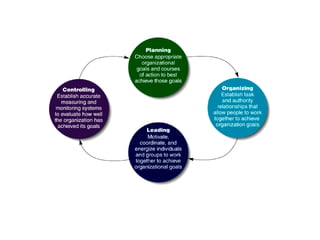
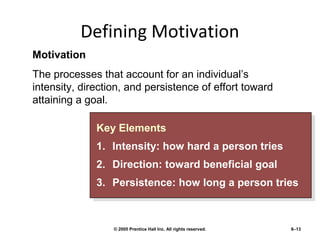
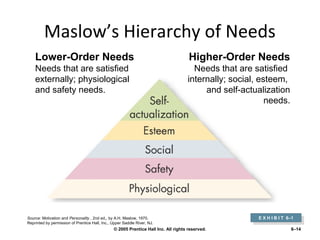
The document discusses the key functions of management which include planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve organizational goals efficiently. It provides details on each function such as planning involving objectives, goals, and plans. Organizing involves defining roles and coordinating resources. Leading styles include trait, transformational, and charismatic approaches. Monitoring or controlling involves checking performance against budgets, targets, costs, and quality. Motivation is discussed in relation to Maslow's hierarchy of needs. Industry sectors and globalization/localization strategies are also summarized.