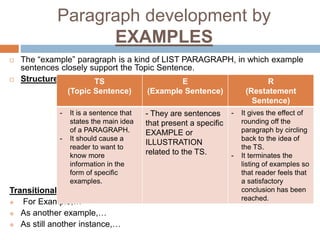
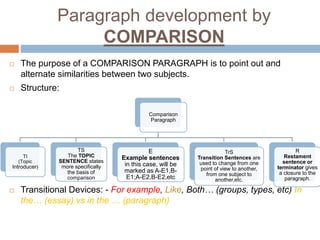
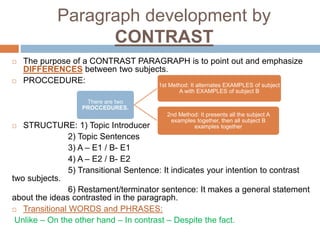
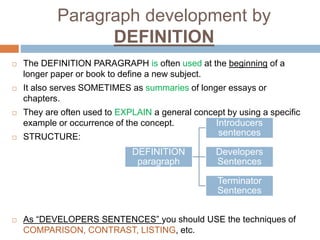
Rocio Soto Valic outlines various methods for paragraph development, including listing, examples, comparison, contrast, definition, and classification. Each method has a specific purpose and structure, such as using topic sentences, transitional devices, and restatement sentences to enhance coherence and clarity. The document emphasizes the importance of smooth transitions and logical conclusions to avoid disorganized writing.