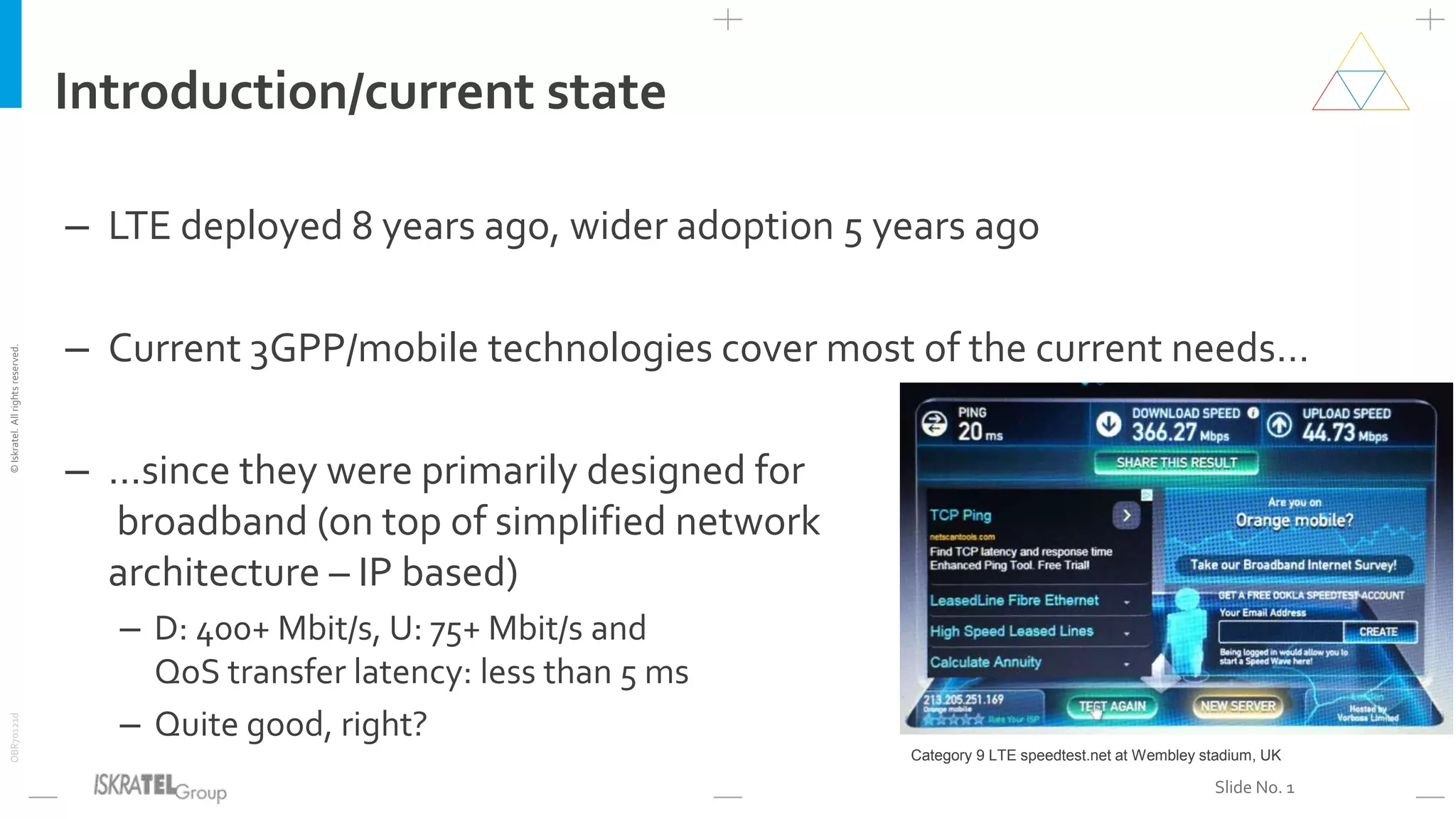
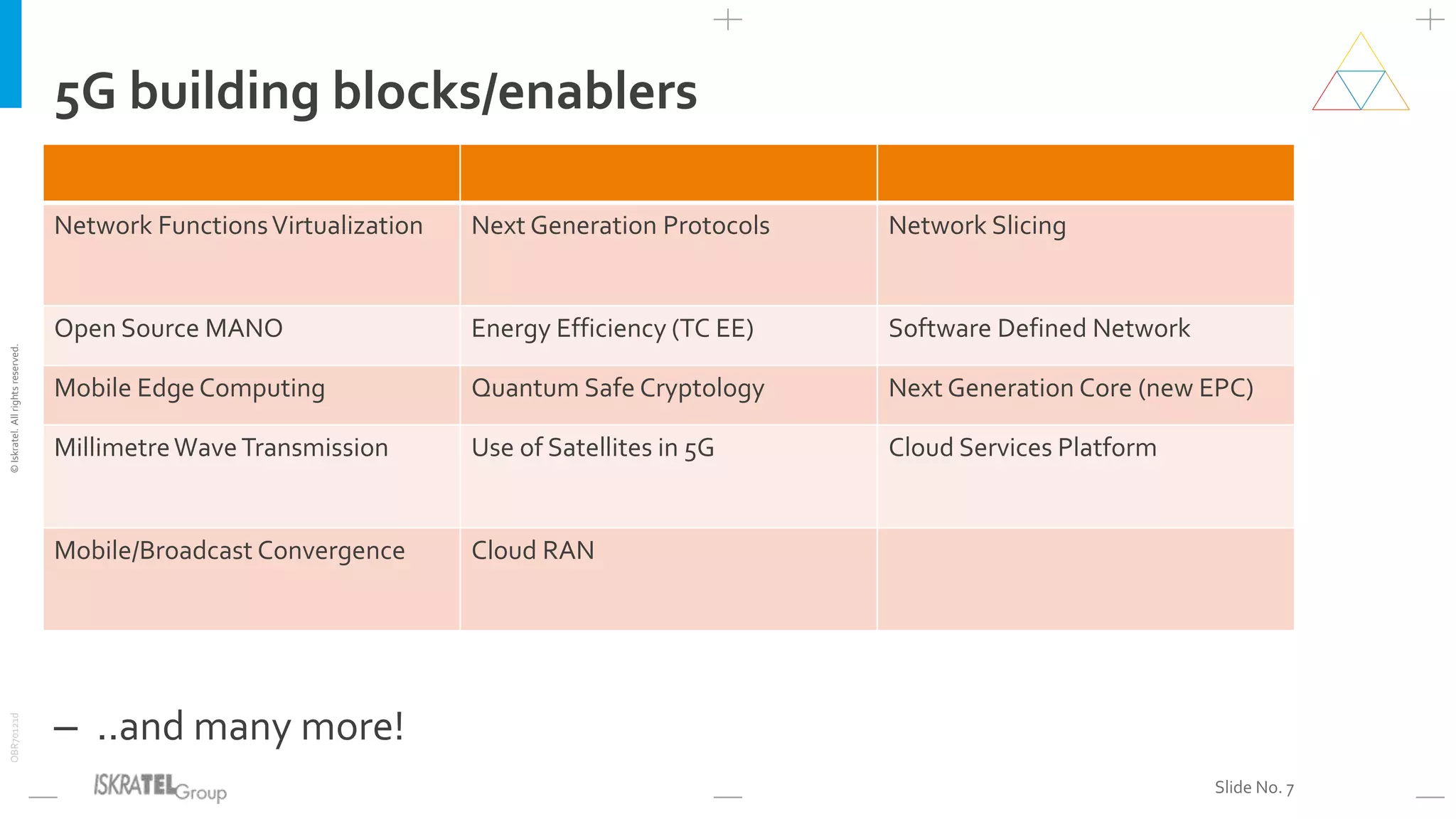
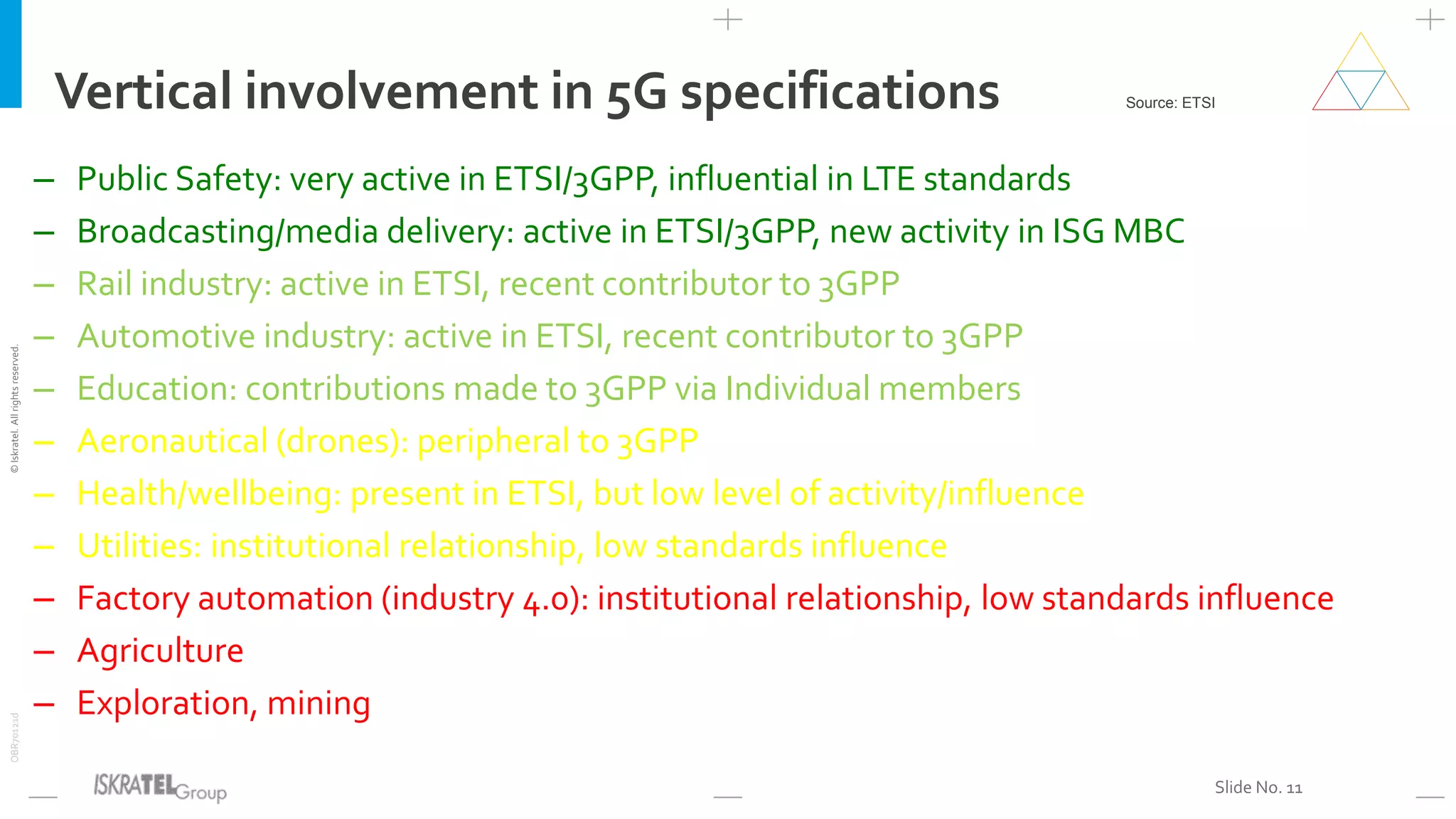
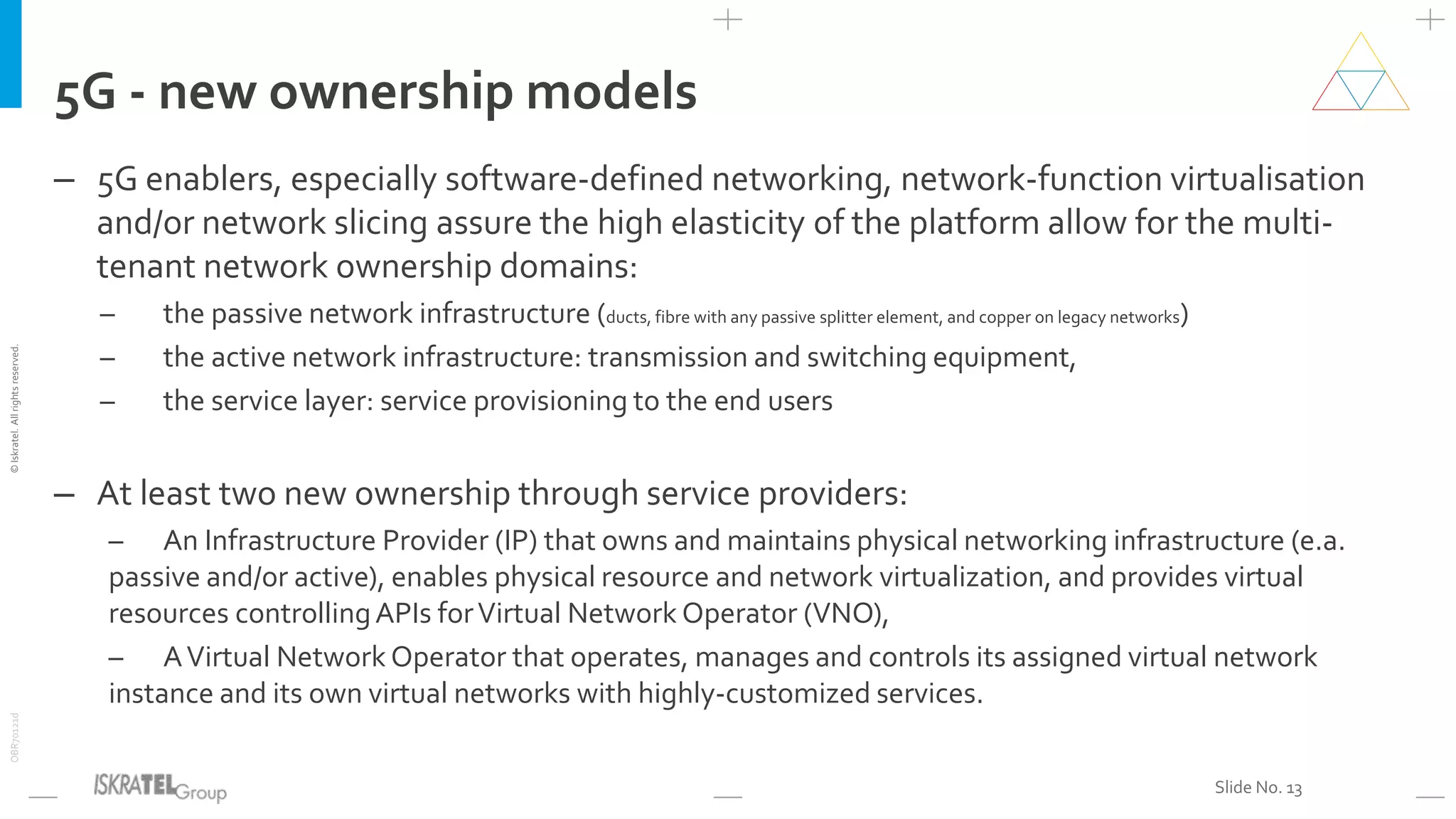
This document discusses the evolution from 4G LTE networks to 5G networks. It outlines the economic and technical drivers requiring the development of 5G, including the need for higher broadband speeds, improved quality of services like VR and 3D video, and connectivity for billions more IoT devices. 5G will fulfill three main use cases - enhanced broadband, massive machine communications, and ultra-reliable low latency communications. Realizing 5G's full potential will depend on new network architectures like network slicing, virtualization, and edge computing. 5G will also enable novel applications across many industries and require new ownership and business models for networks.