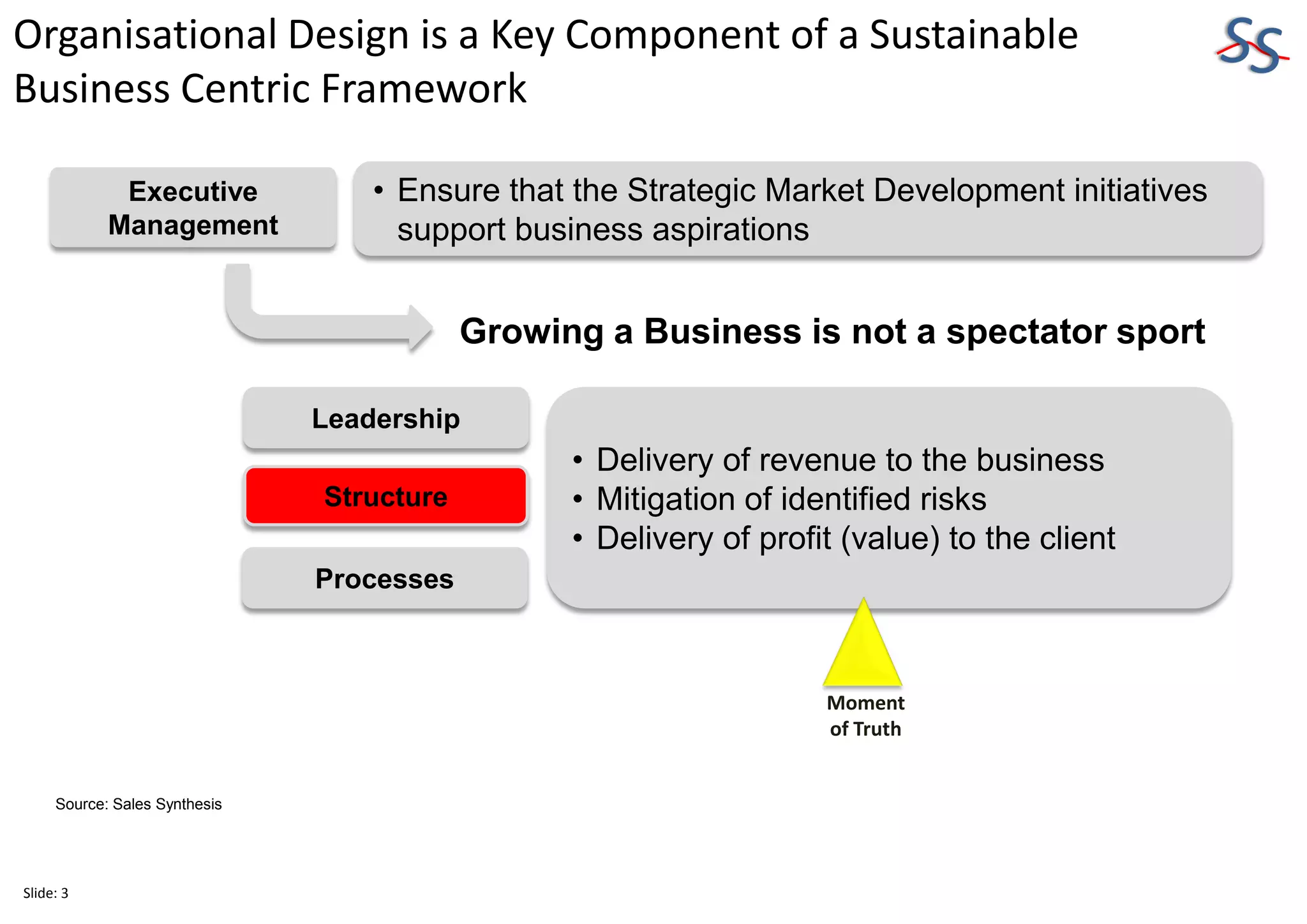
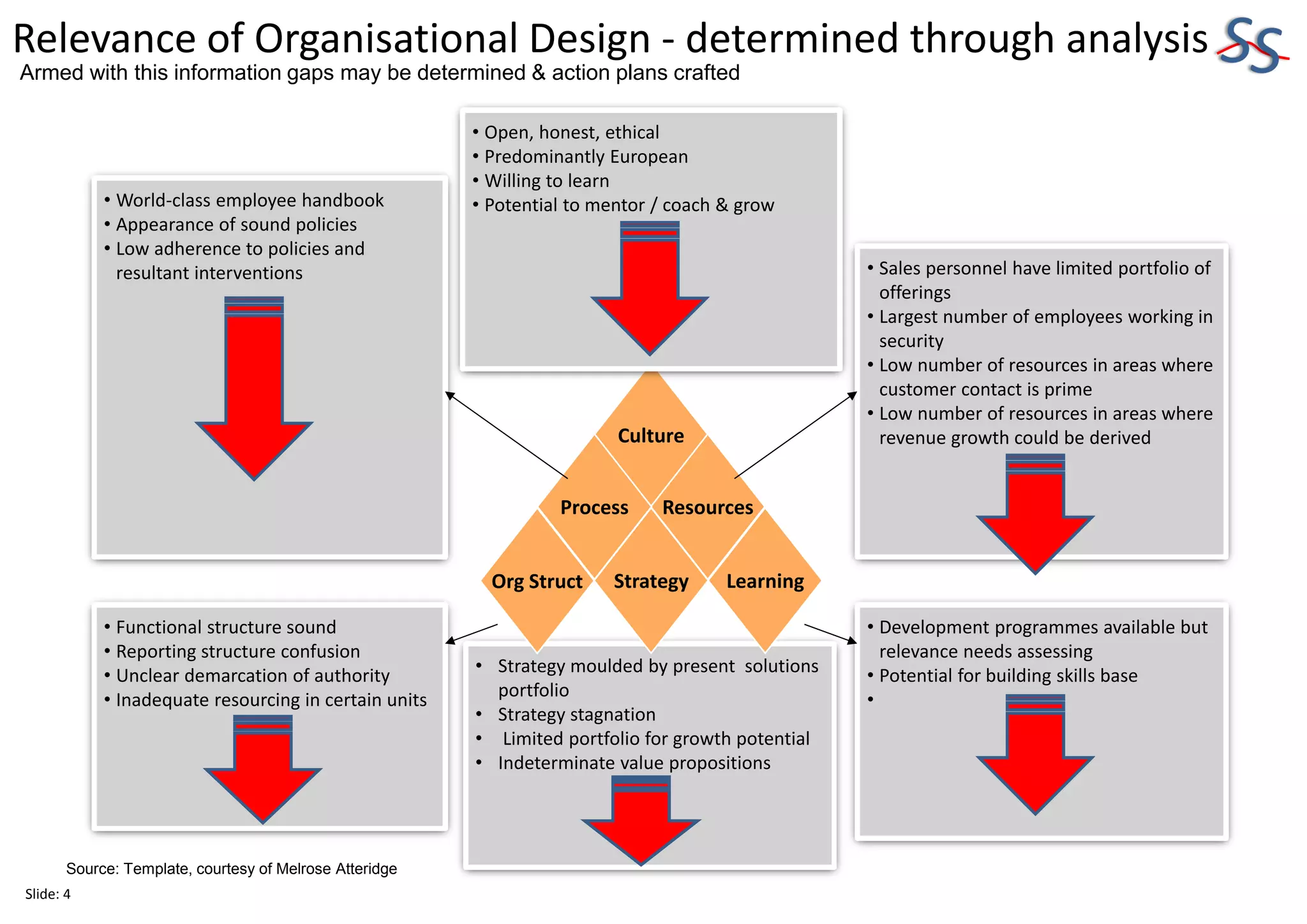
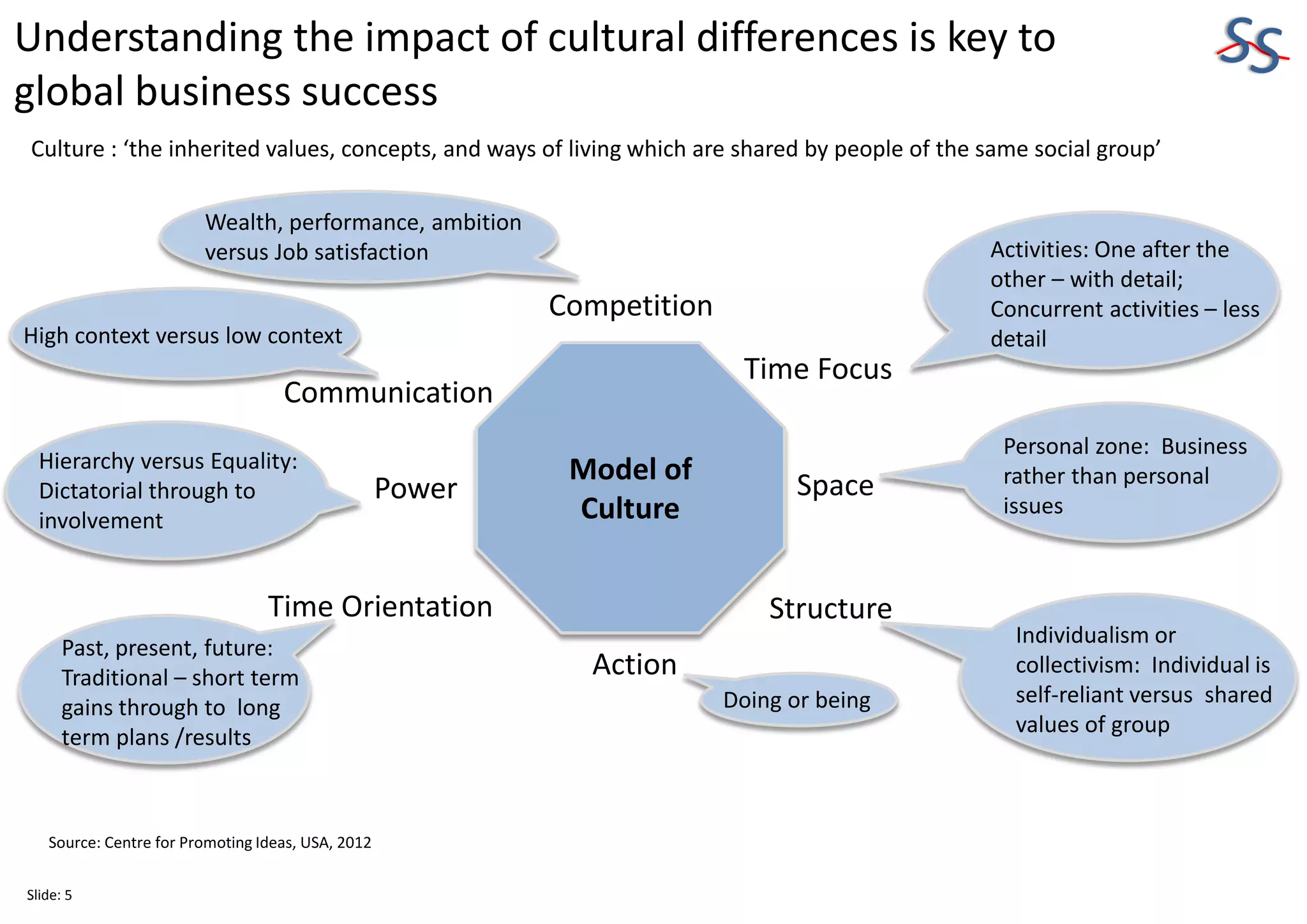
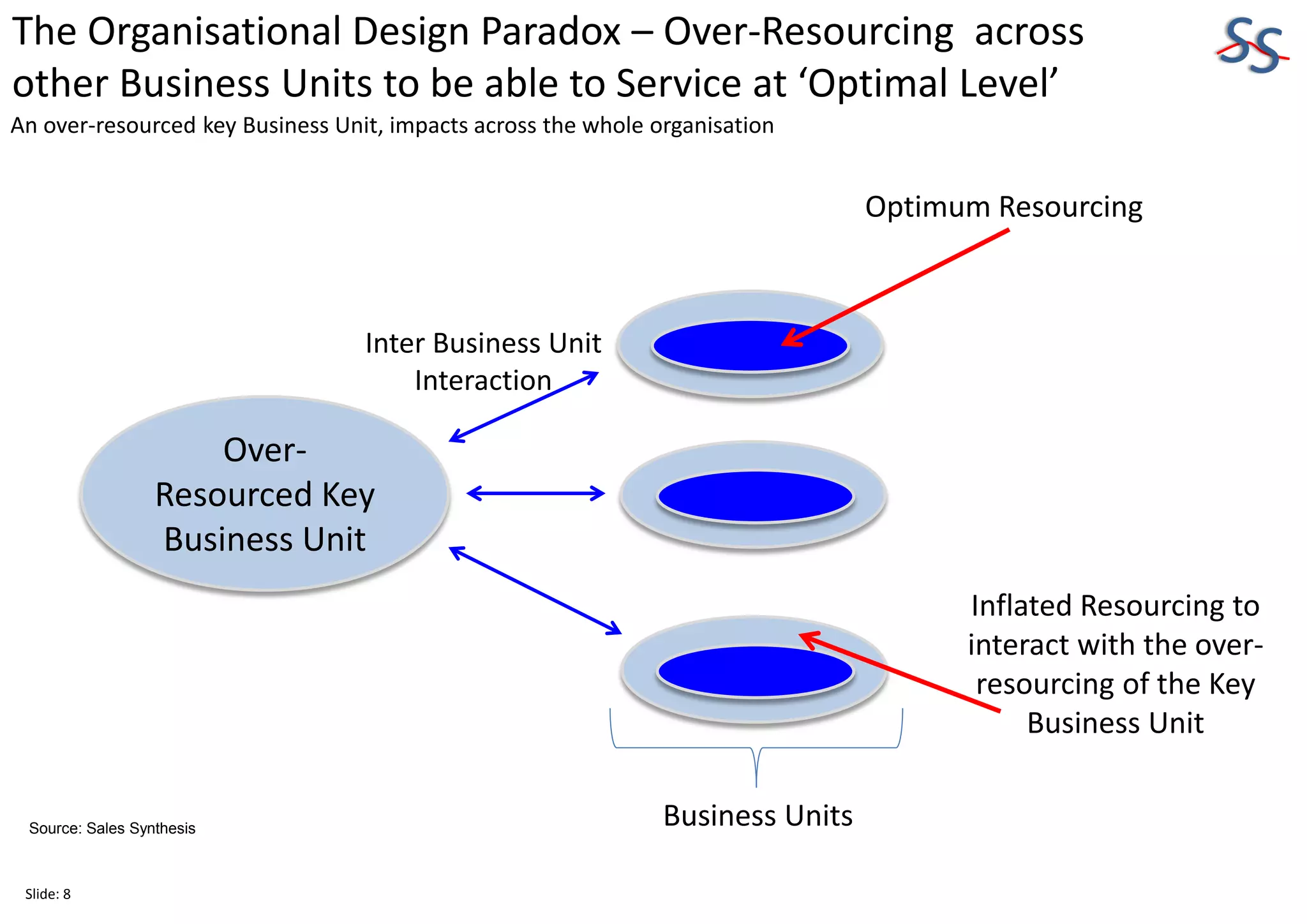
The 10-slide presentation provides an overview of organizational design and its importance for business sustainability. It discusses the need to align organizational structure, processes, culture and resources with strategy to maximize productivity and growth. Specifically, it notes that over-resourcing key business units can negatively impact productivity across the entire organization by requiring other business units to also be over-resourced to maintain optimal interaction levels. The presentation advocates analyzing differences in organizational design versus strategic needs to identify gaps and develop action plans for improvement.

![Dominant ExclusiveEmerging PervasiveAbsent
Symbiotic
relationship
with clients
Sustainability
Making the competitors irrelevant
Projects ParticularPerforming PertinentPeople Places
The Sustainable Business Imperative
Building mutually beneficial and sustainable long-term client relationships
Source: Sales Synthesis
Multi-National Companies [MNCs] may embrace a
new dawn or a long dark night.
Know where you are going
Slide: 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tenslidesintenminutes-aperspectiveonorganisationaldesign-130715023338-phpapp02/75/Ten-slides-in-Ten-minutes-A-Perspective-on-Organisational-Design-2-2048.jpg)

![The Organisational Design Paradox – Lowering of Productivity
Source: Sales Synthesis
Number of Resources in a key Business Unit
Productivity
The crest of sensibility
[Optimal Design]
Slide: 7
An over-resourced key Business Unit, impacts across the whole organisation
The trajectory of hopelessness](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tenslidesintenminutes-aperspectiveonorganisationaldesign-130715023338-phpapp02/75/Ten-slides-in-Ten-minutes-A-Perspective-on-Organisational-Design-7-2048.jpg)
![Points to Ponder
Slide: 9
• Most businesses reward those that are supportive of the group’s strategies and
punish those who challenge the authority of the leaders by raising doubt/s
• 'The mere fact that a man is noted in his particular field of research, astronomy,
physics, or mathematics should not be considered as presumptive evidence of
his ability to see correctly things outside his experience.'
- Joseph Rinn
• Business Personality: The shared culture, about a company, about each other,
about the value of treating others with respect, about being proud of who you –
and your colleagues are - and about loyalty and integrity [Being good when no
one is watching]
• ‘If you are riding a dead horse, the best strategy is to dismount.'
- unknown
• Legacy structures cannot drive new business opportunities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tenslidesintenminutes-aperspectiveonorganisationaldesign-130715023338-phpapp02/75/Ten-slides-in-Ten-minutes-A-Perspective-on-Organisational-Design-9-2048.jpg)
