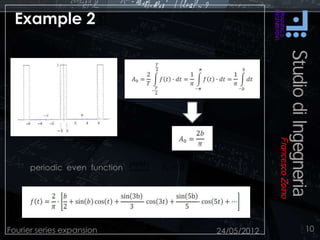
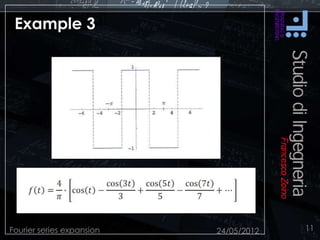
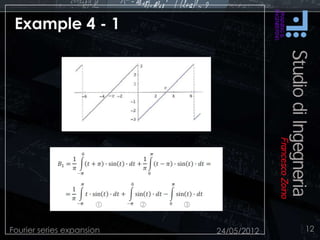
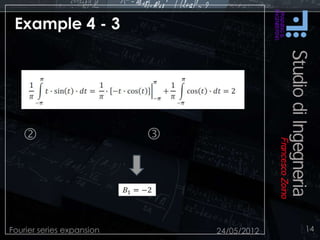
This document discusses Fourier series expansion and spectral analysis. It explains that while signals exist in the time domain, they can be represented in the frequency domain as a series of sinusoidal components at different frequencies. This frequency domain description is called spectral analysis. Spectral analysis of signals coupled with the frequency response of systems allows for better design work, as the behavior of a linear time-invariant system can be studied using sinusoidal signals. Fourier series expansion represents periodic functions as a series of sinusoidal functions, and was developed based on the work of French mathematician Jean Baptiste Joseph Fourier.







![Example 1 - 3
24/05/2012Fourier series expansion 9
in the end:
If b=0, the function represents the restriction of function sgn(t)
into the ] interval, periodically extended outside. In the
figure below (left) are represented the first five Fourier
polynomials of this function.
The amplitude spectrum is a line spectrum (right figure).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fourierseriesexpansion-120522144729-phpapp02/85/Fourier-series-expansion-9-320.jpg)