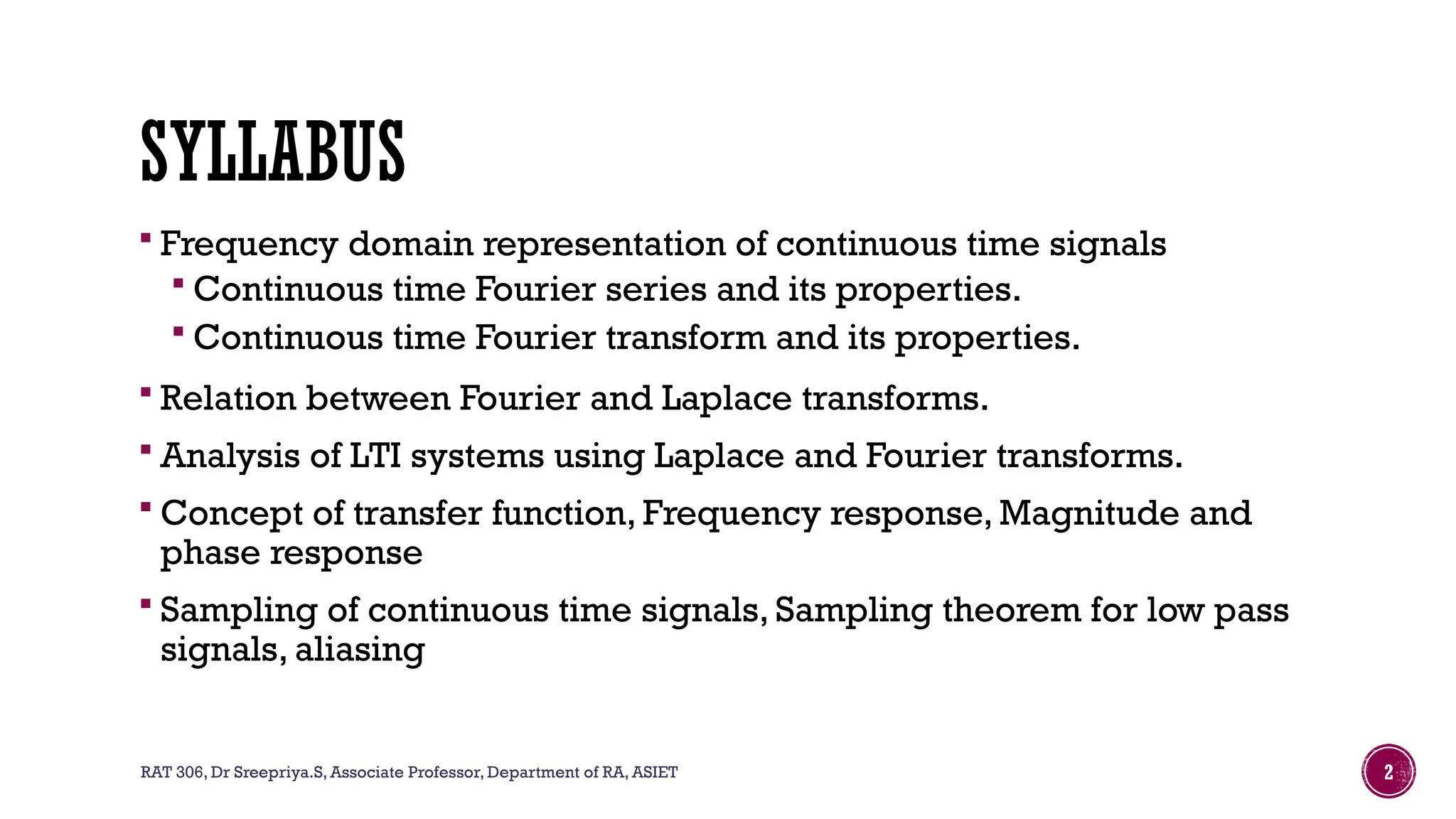
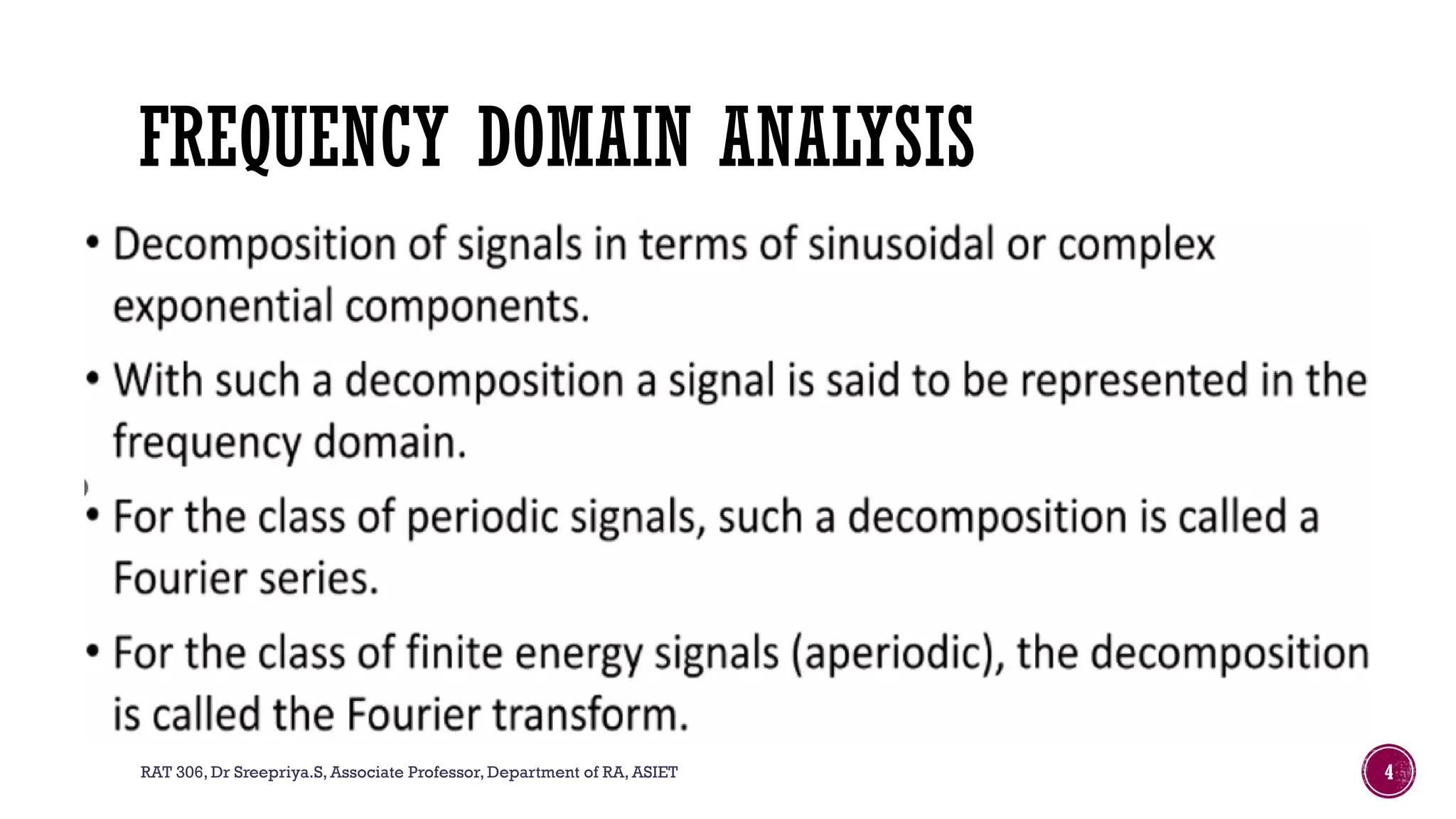
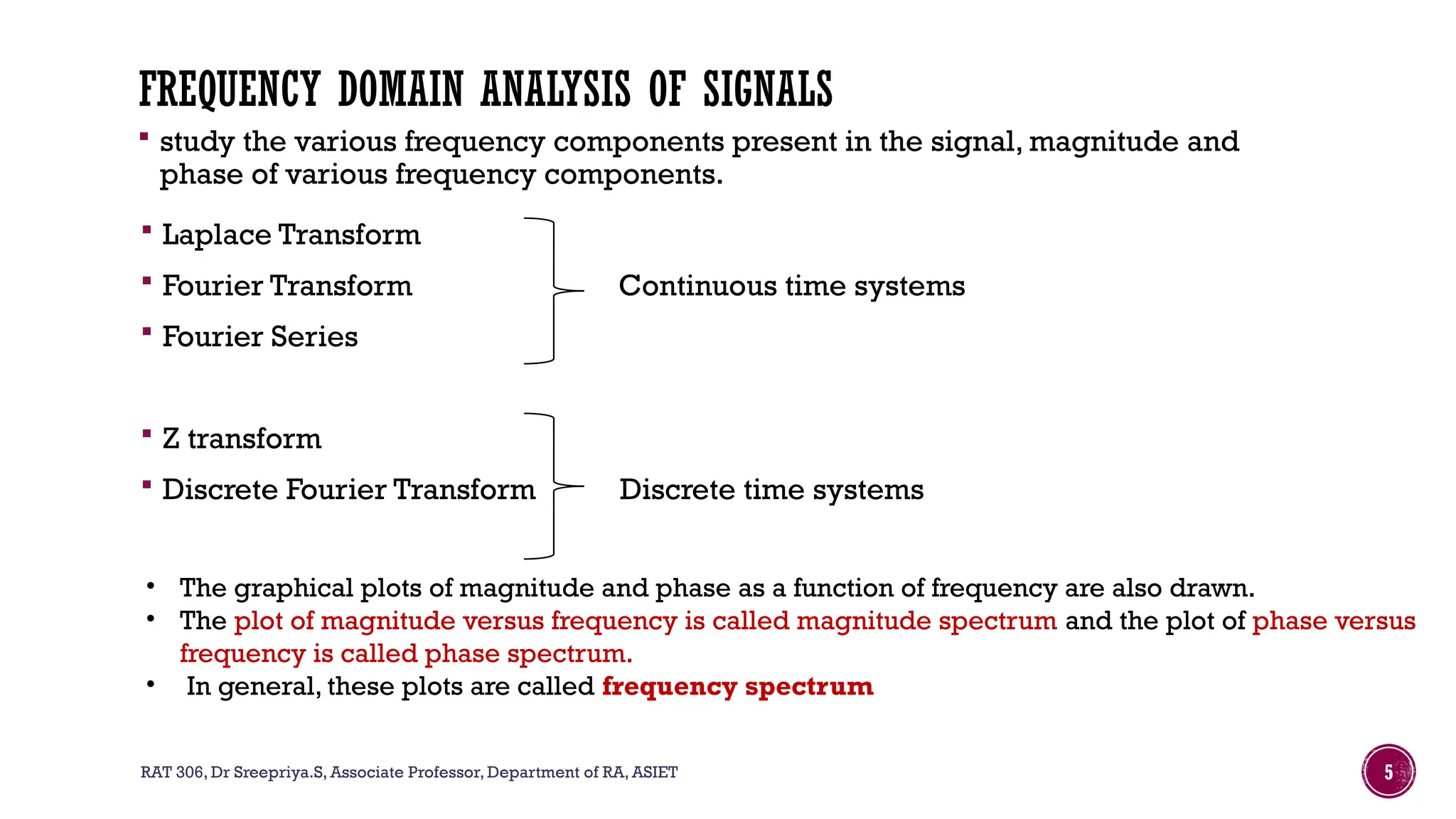
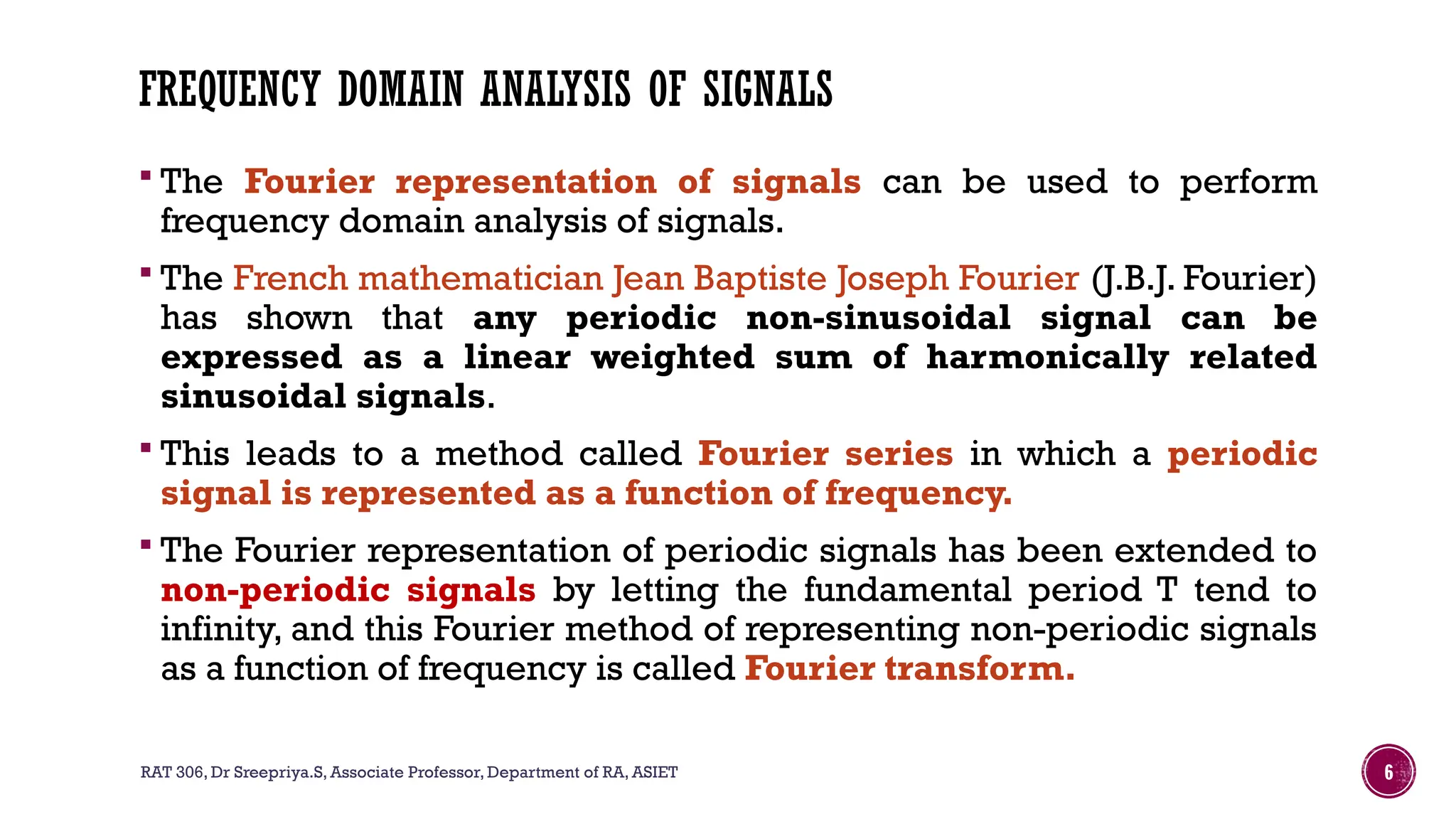
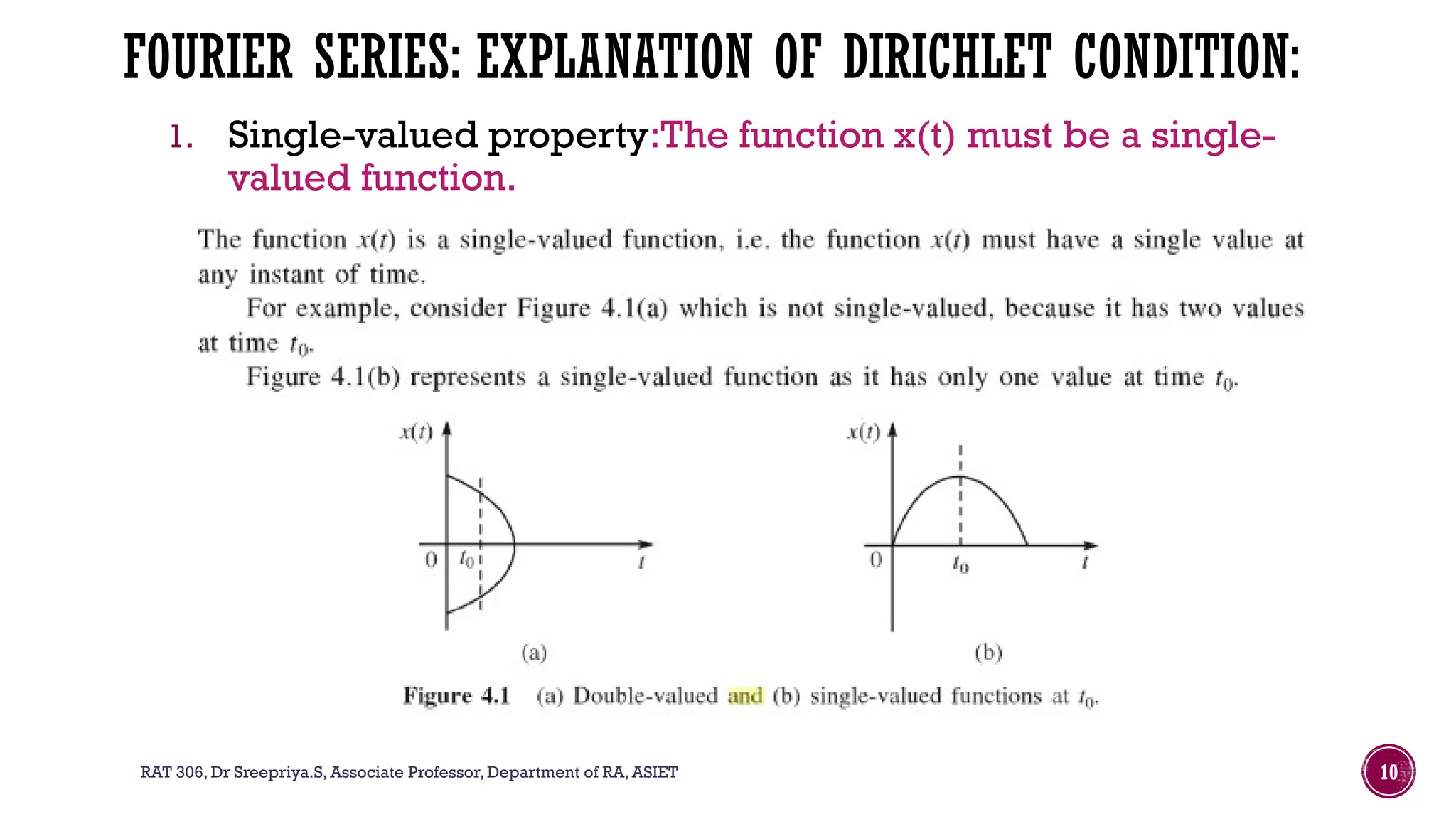
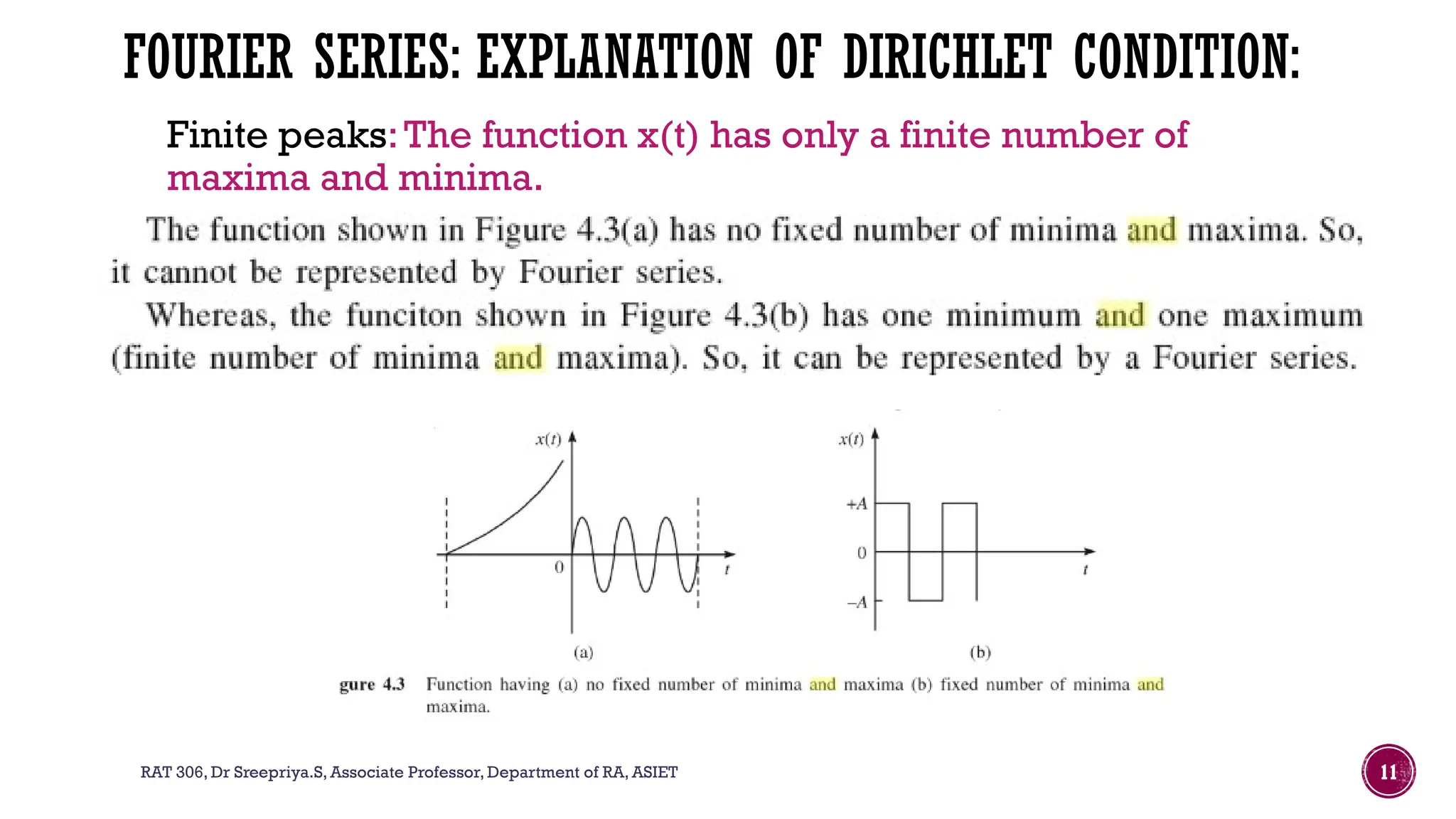
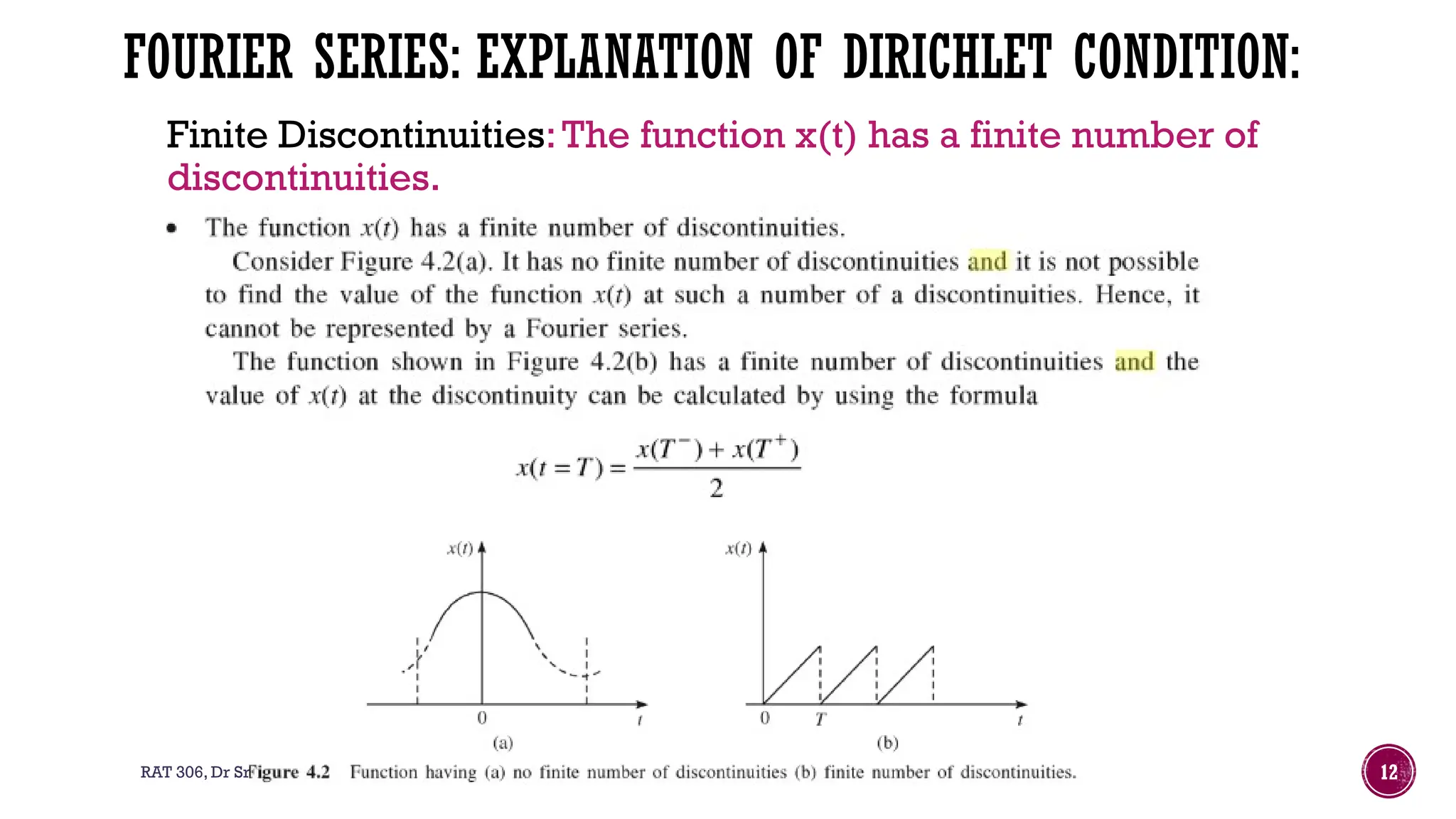
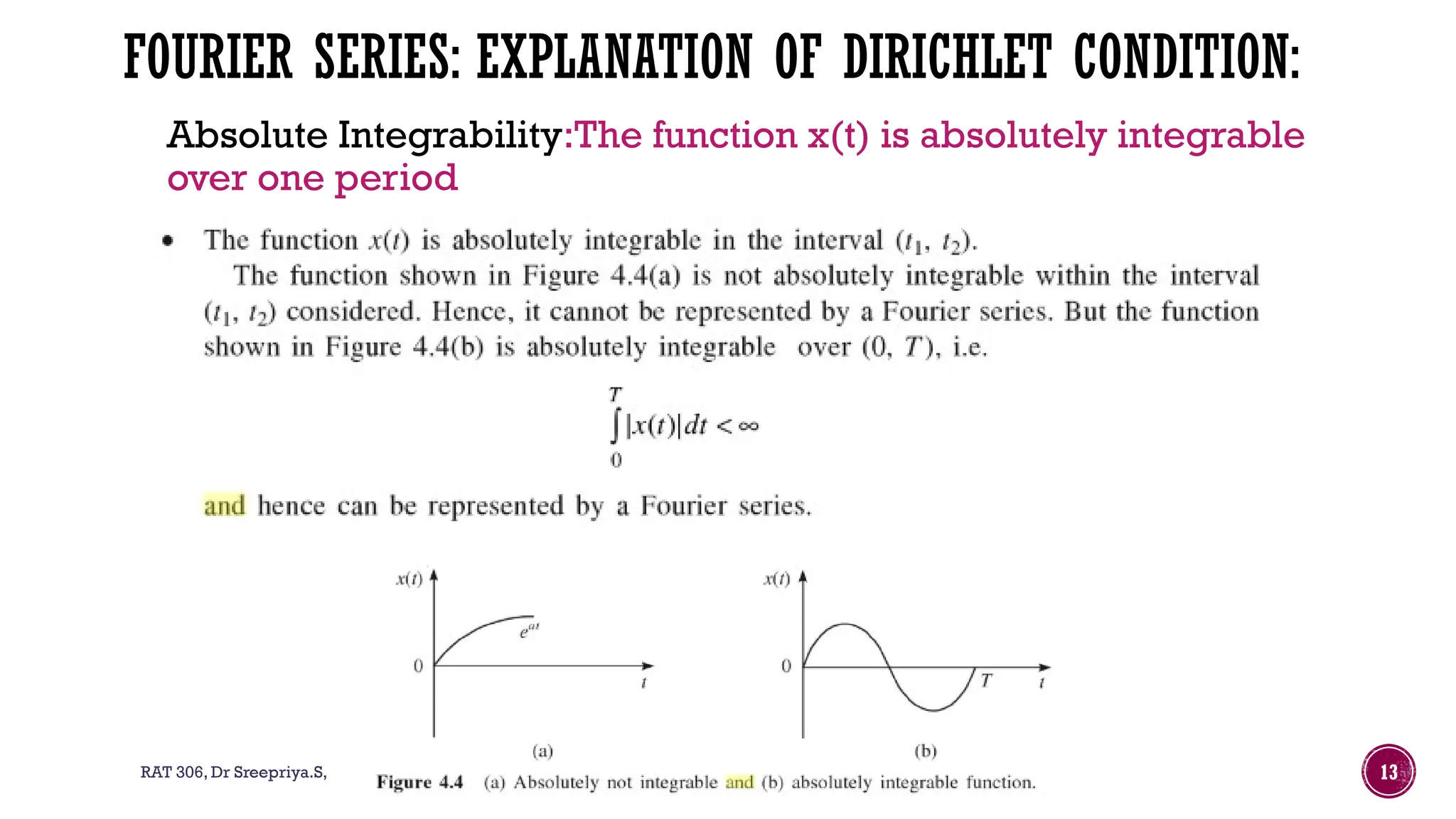
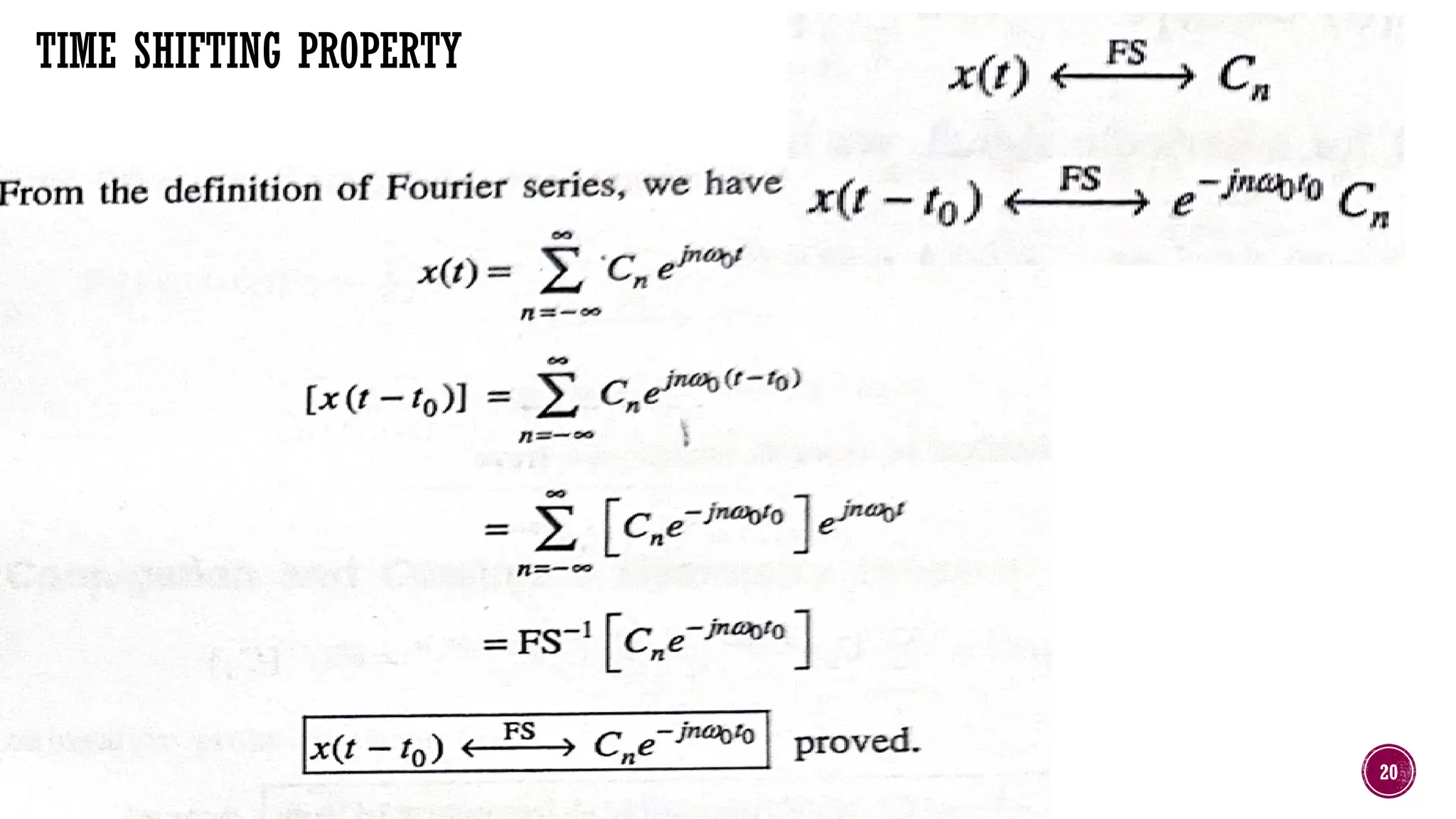
The document outlines the syllabus for a course on signals and systems taught by Dr. Sreepriya S. at ASIET, covering topics such as frequency domain representation, Fourier series and transforms, and analysis of LTI systems. Key concepts include sampling theorems, transfer functions, and properties of Fourier representations for periodic and non-periodic signals. Additional details on Dirichlet's conditions for Fourier series and their graphical representations are also provided.