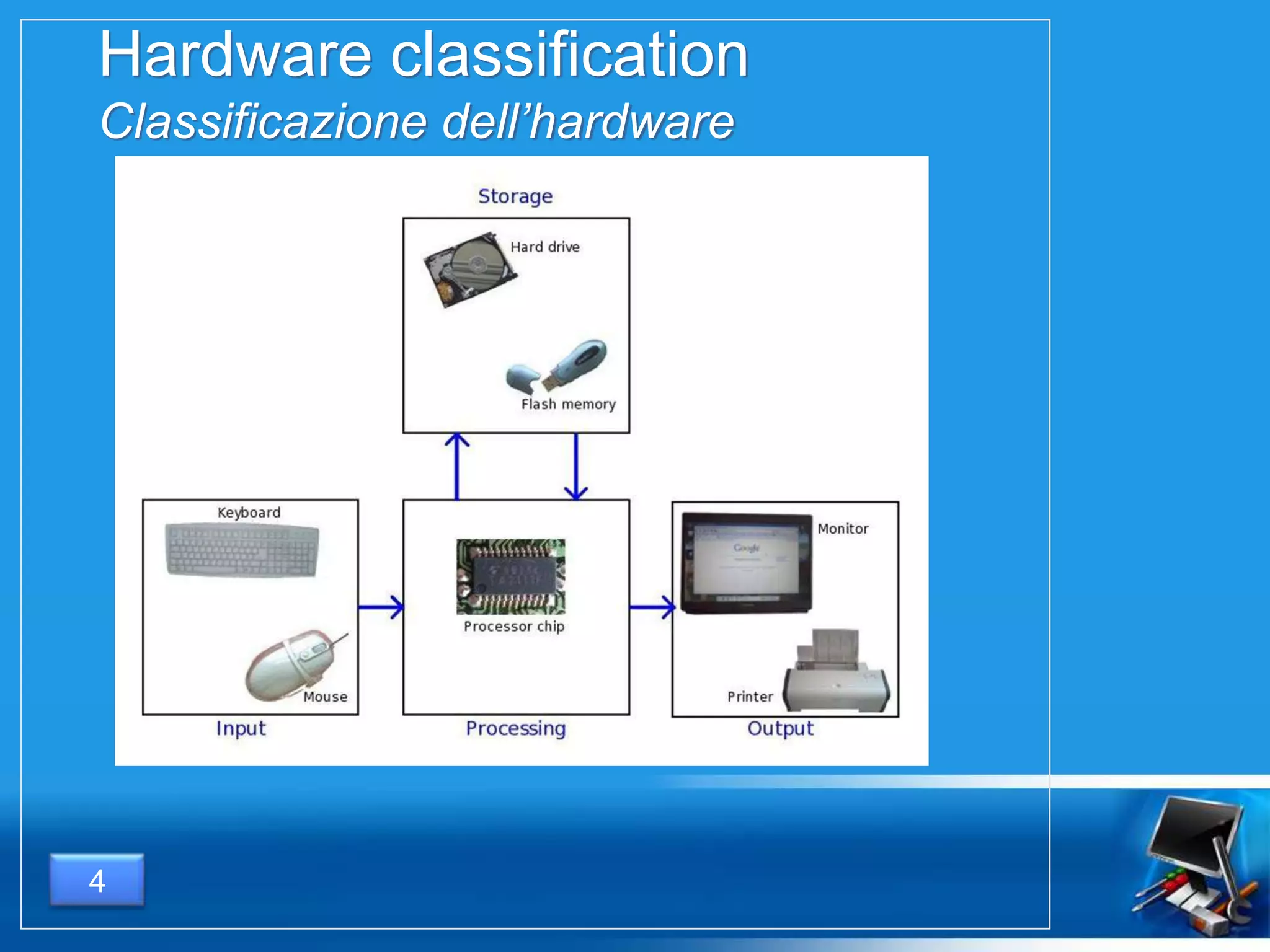
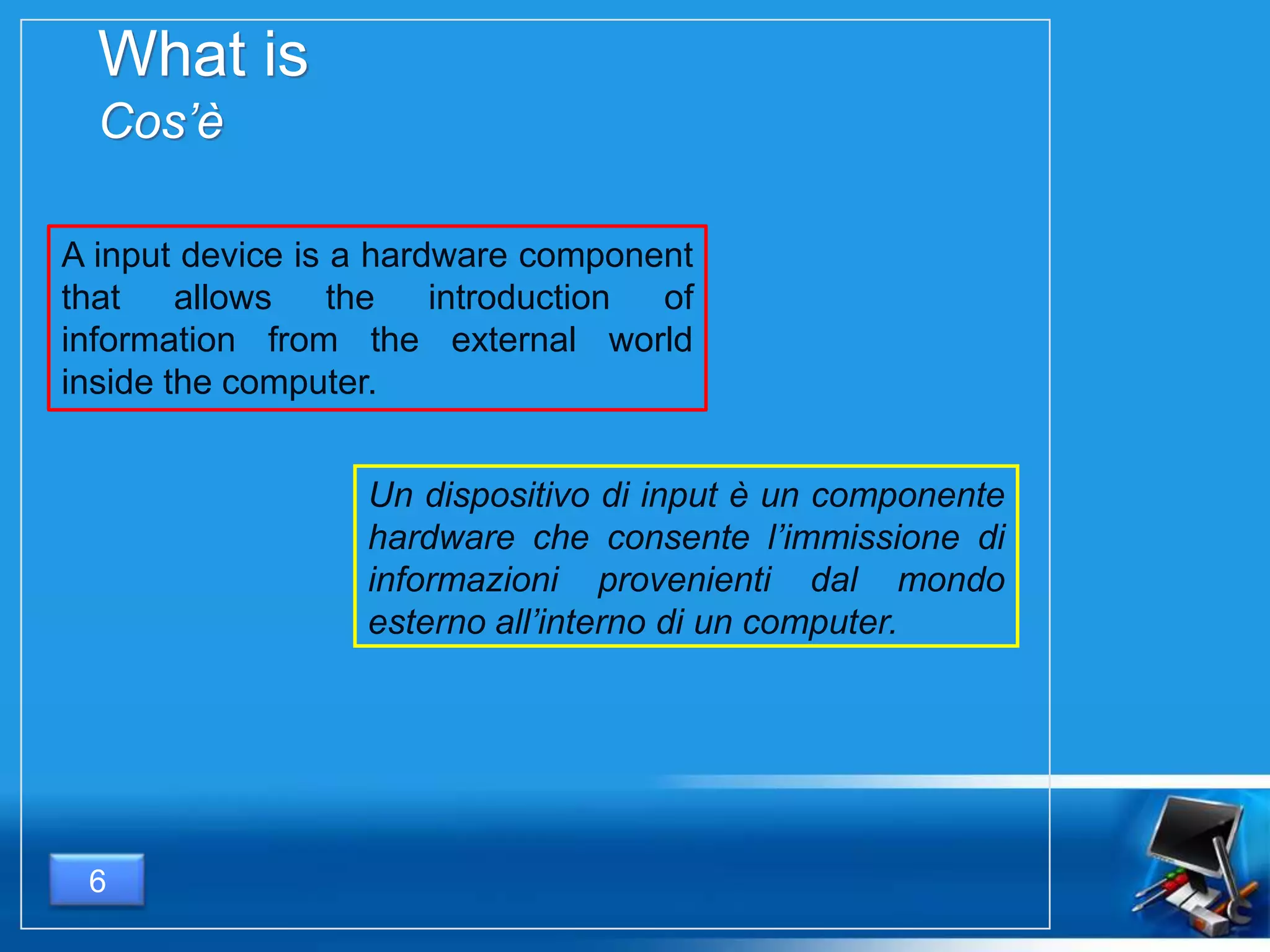
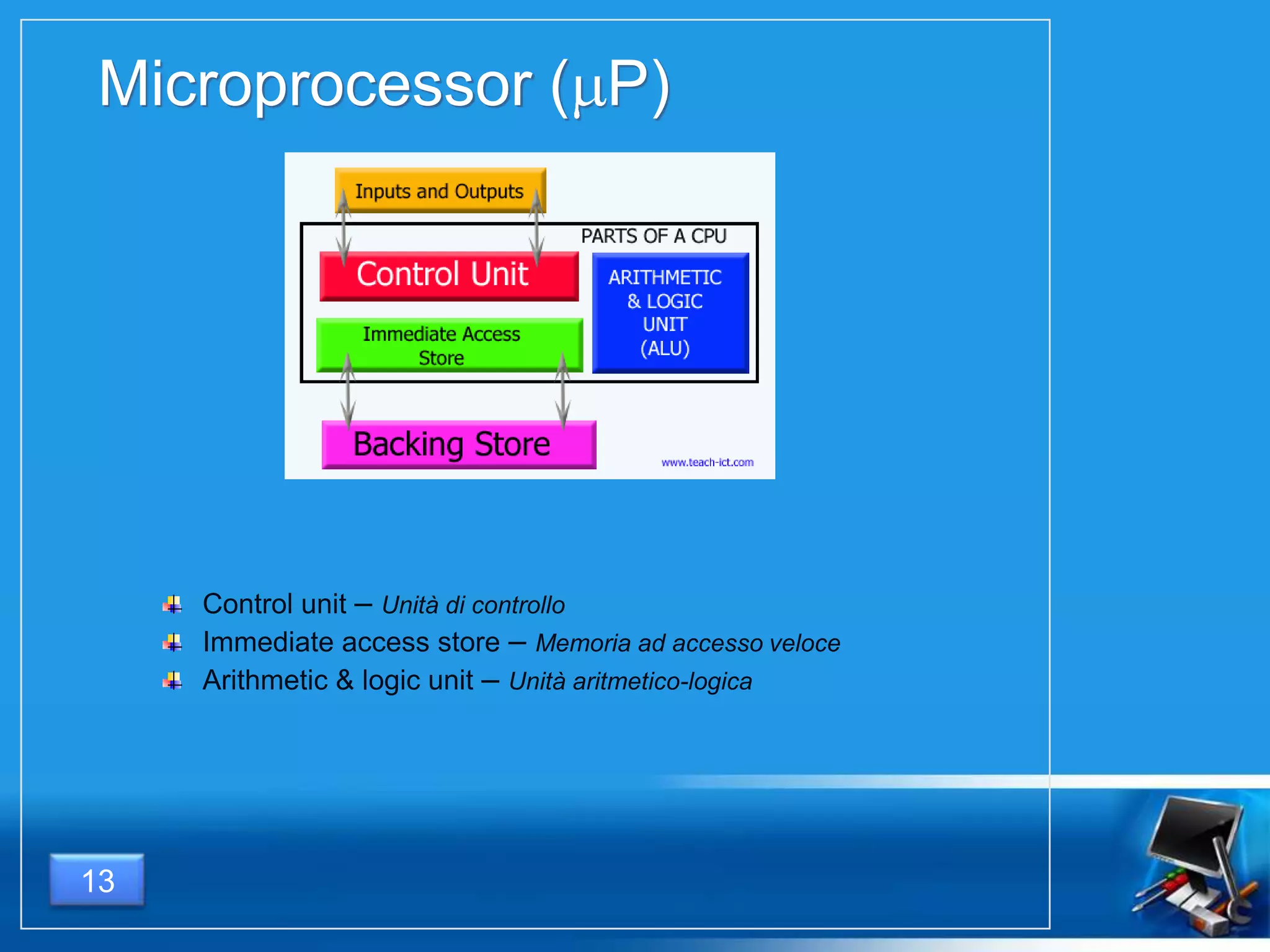
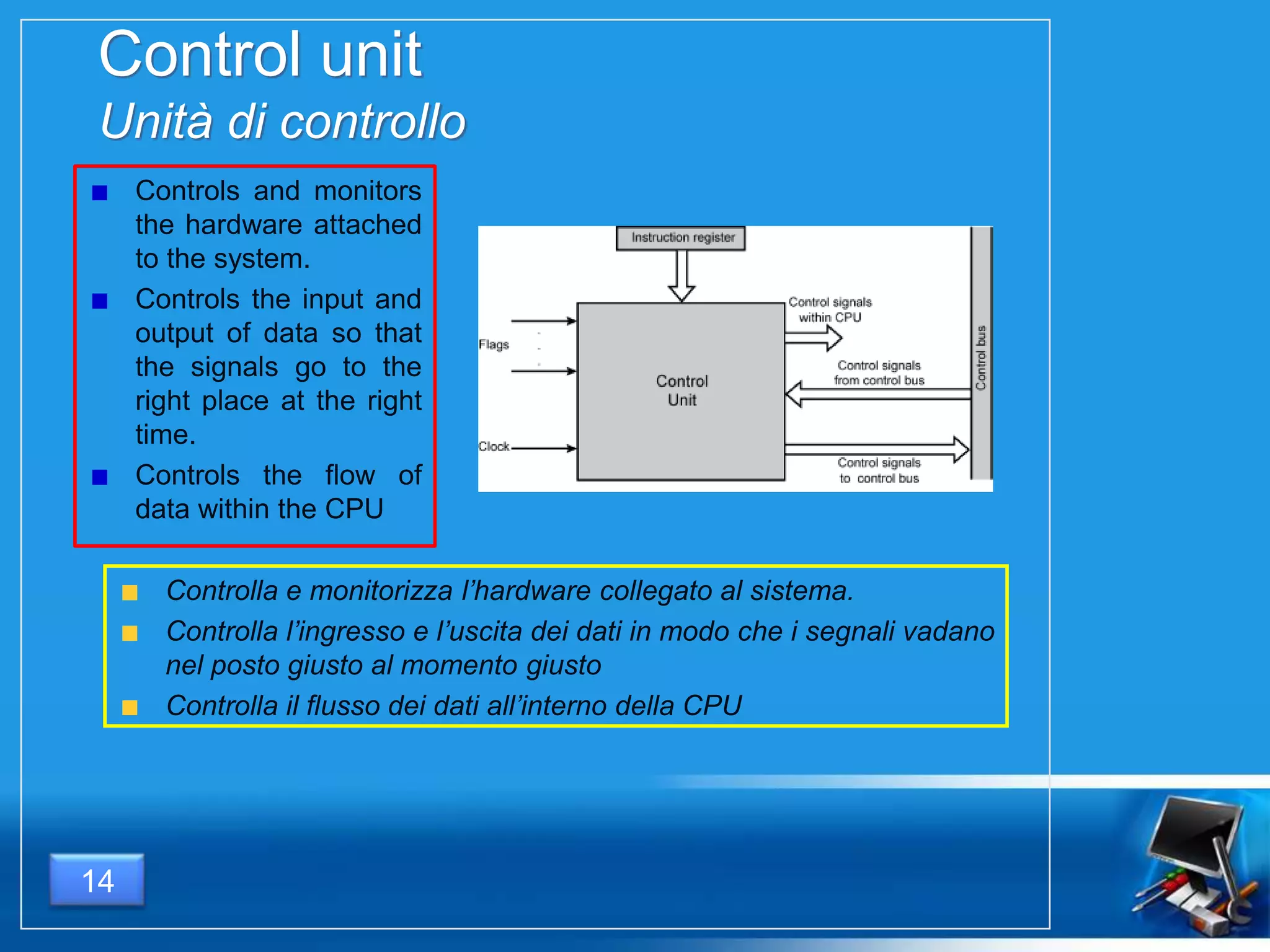
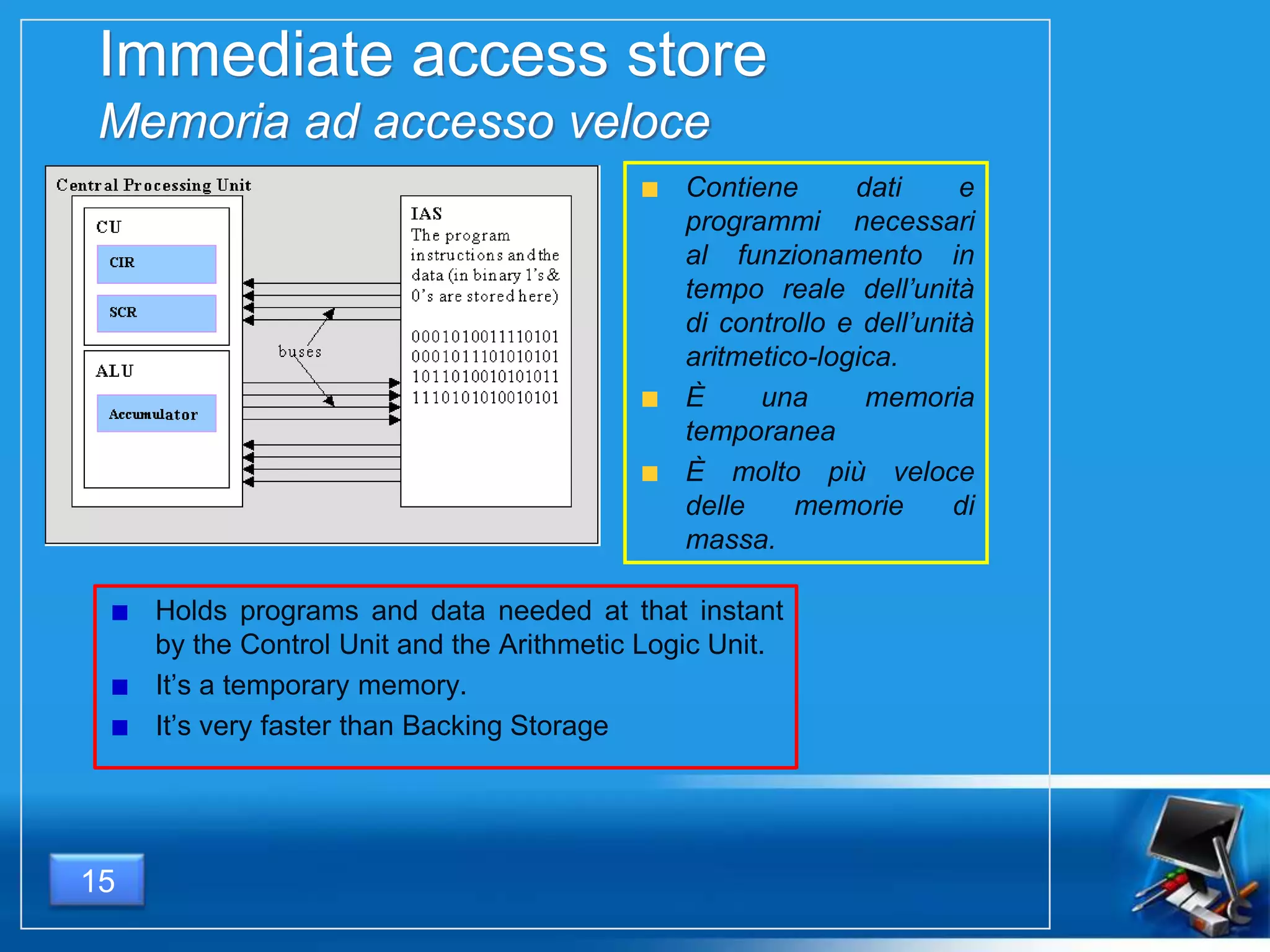
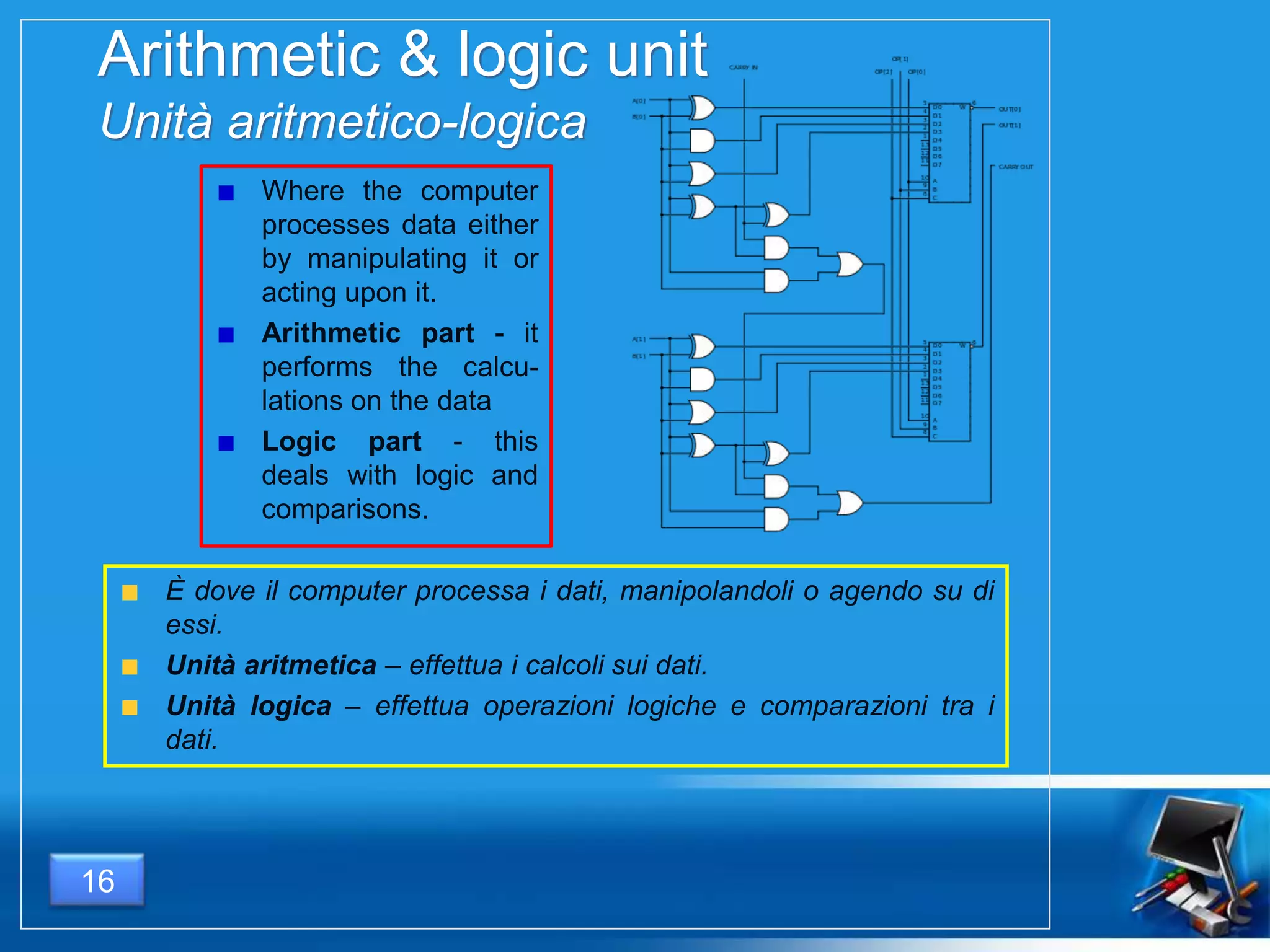
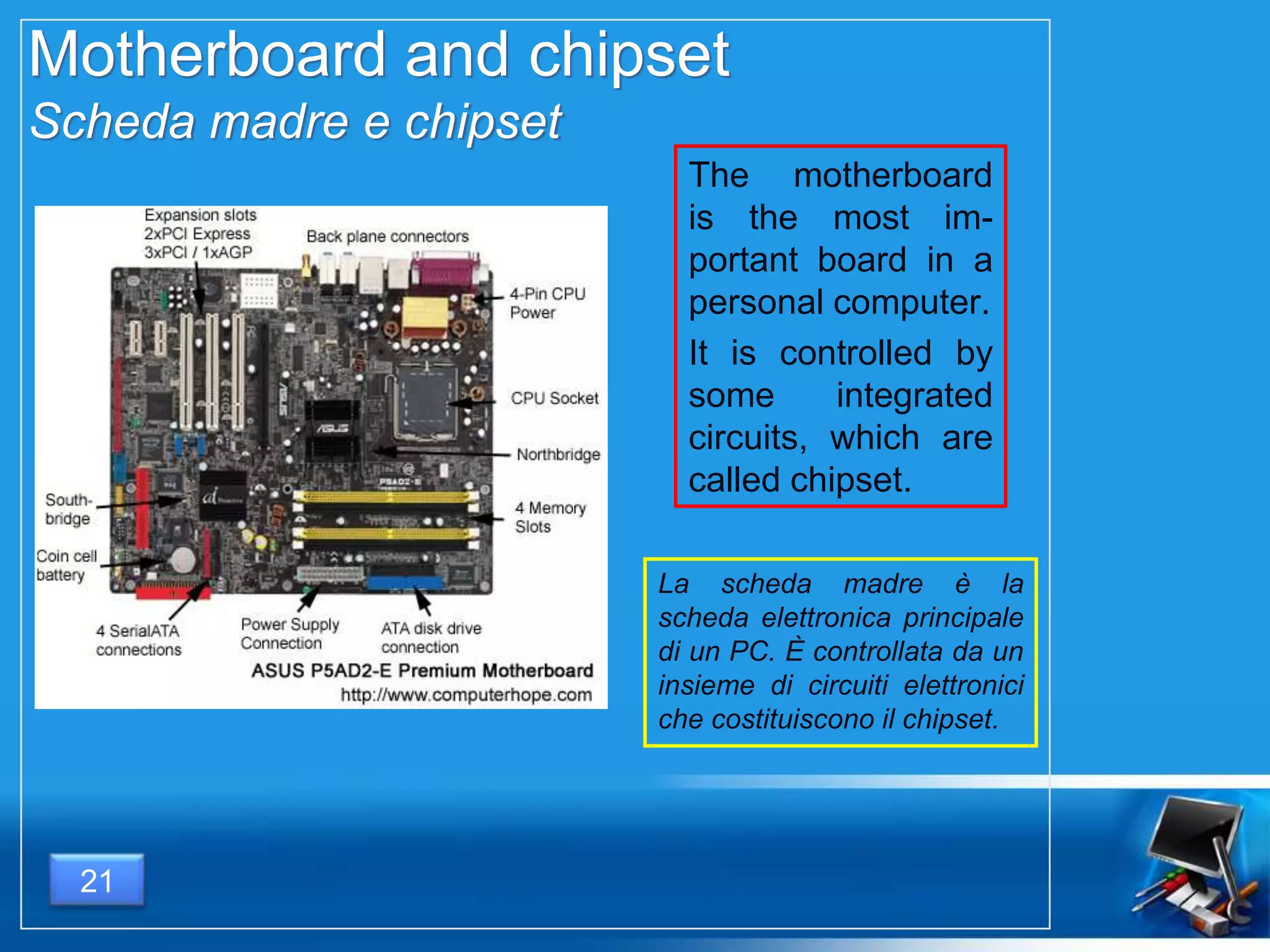
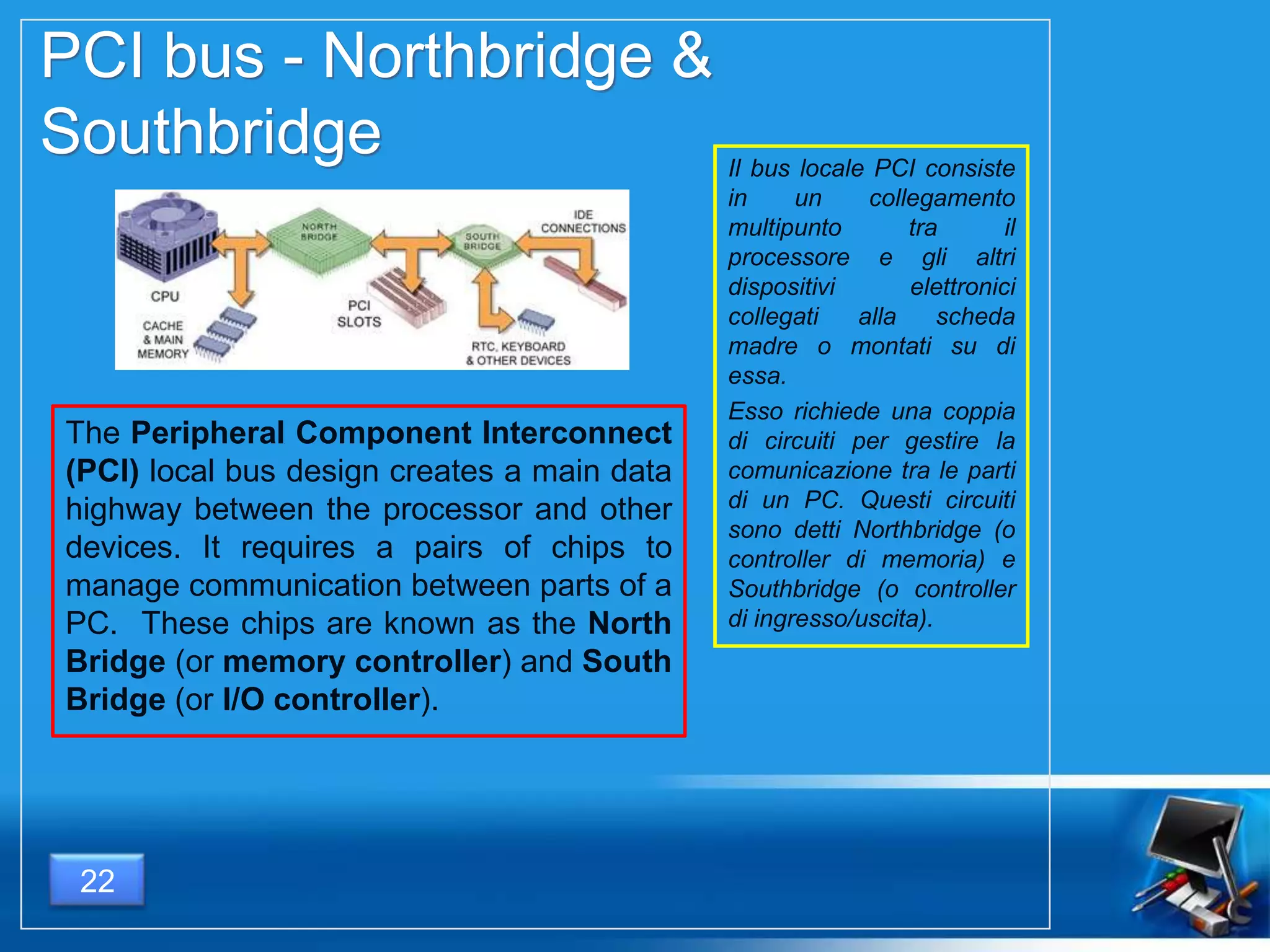
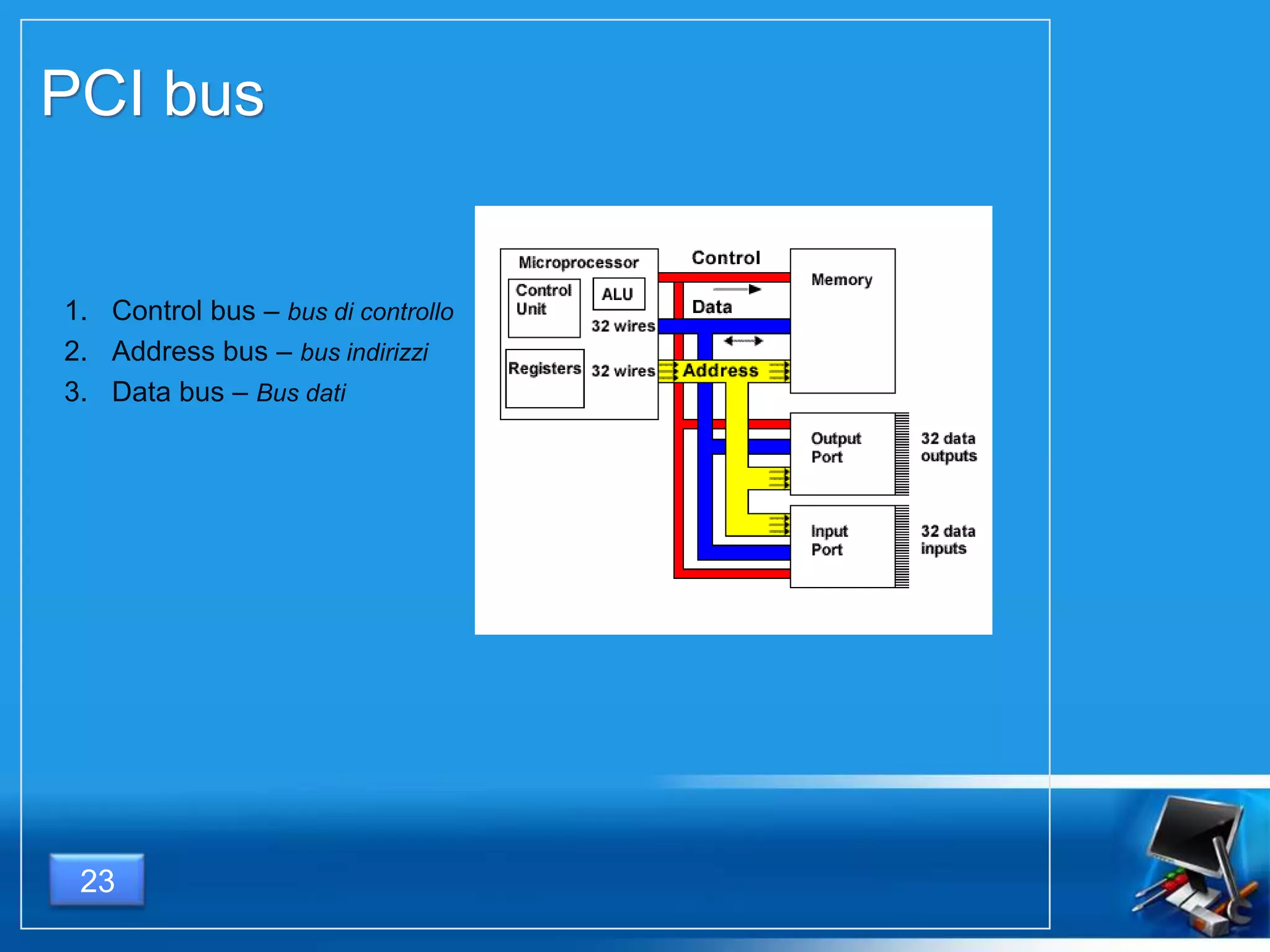
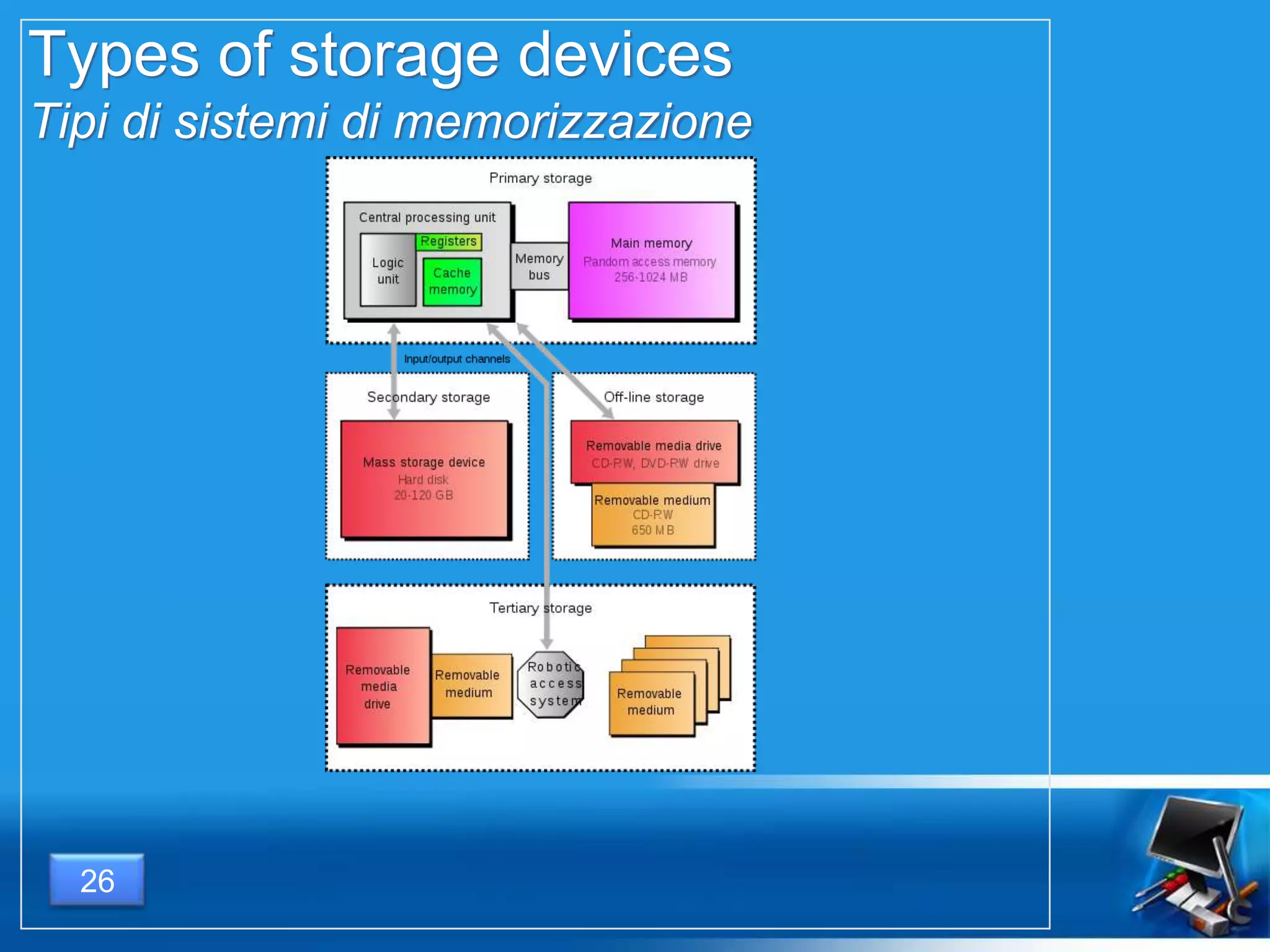
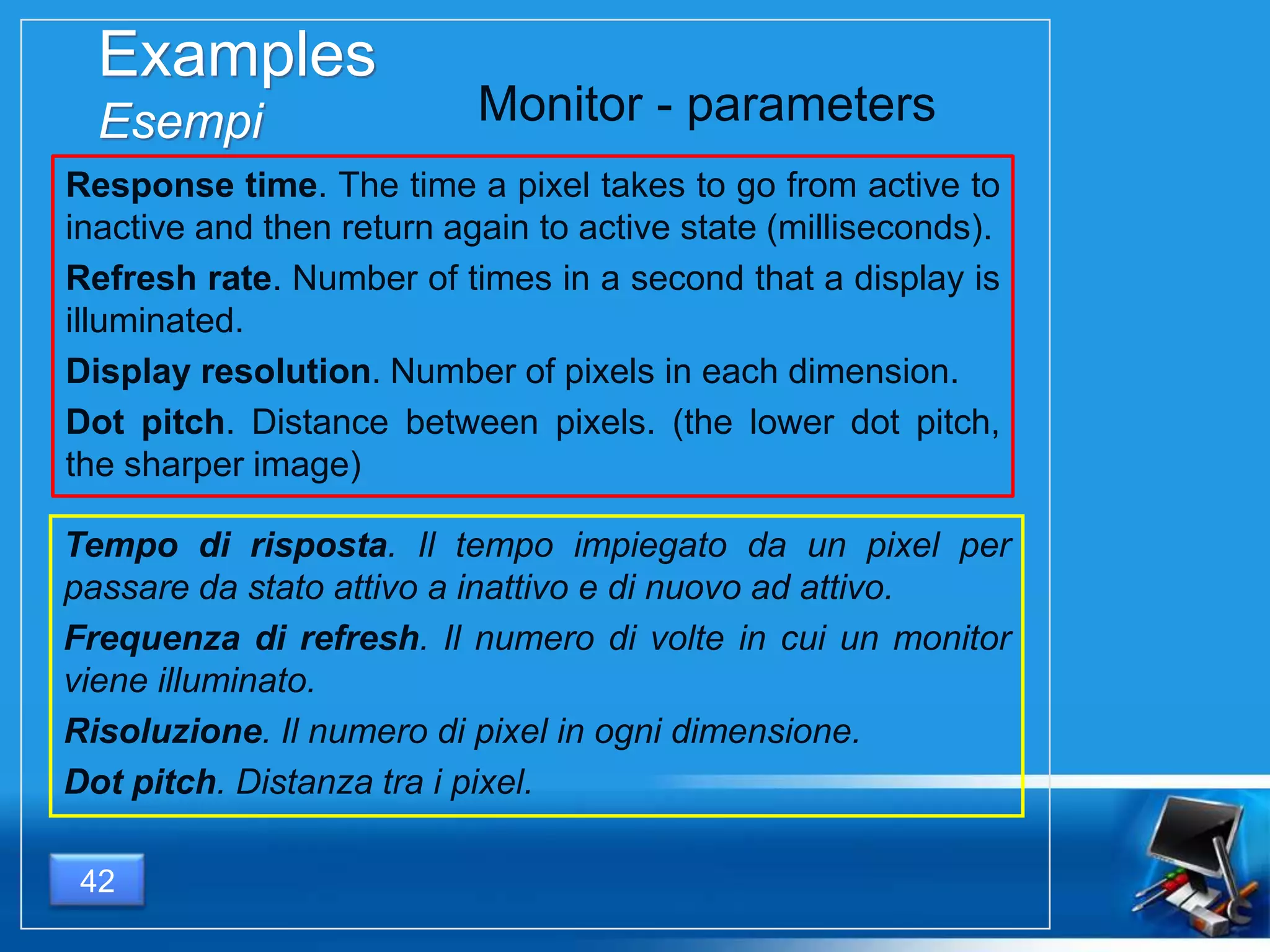
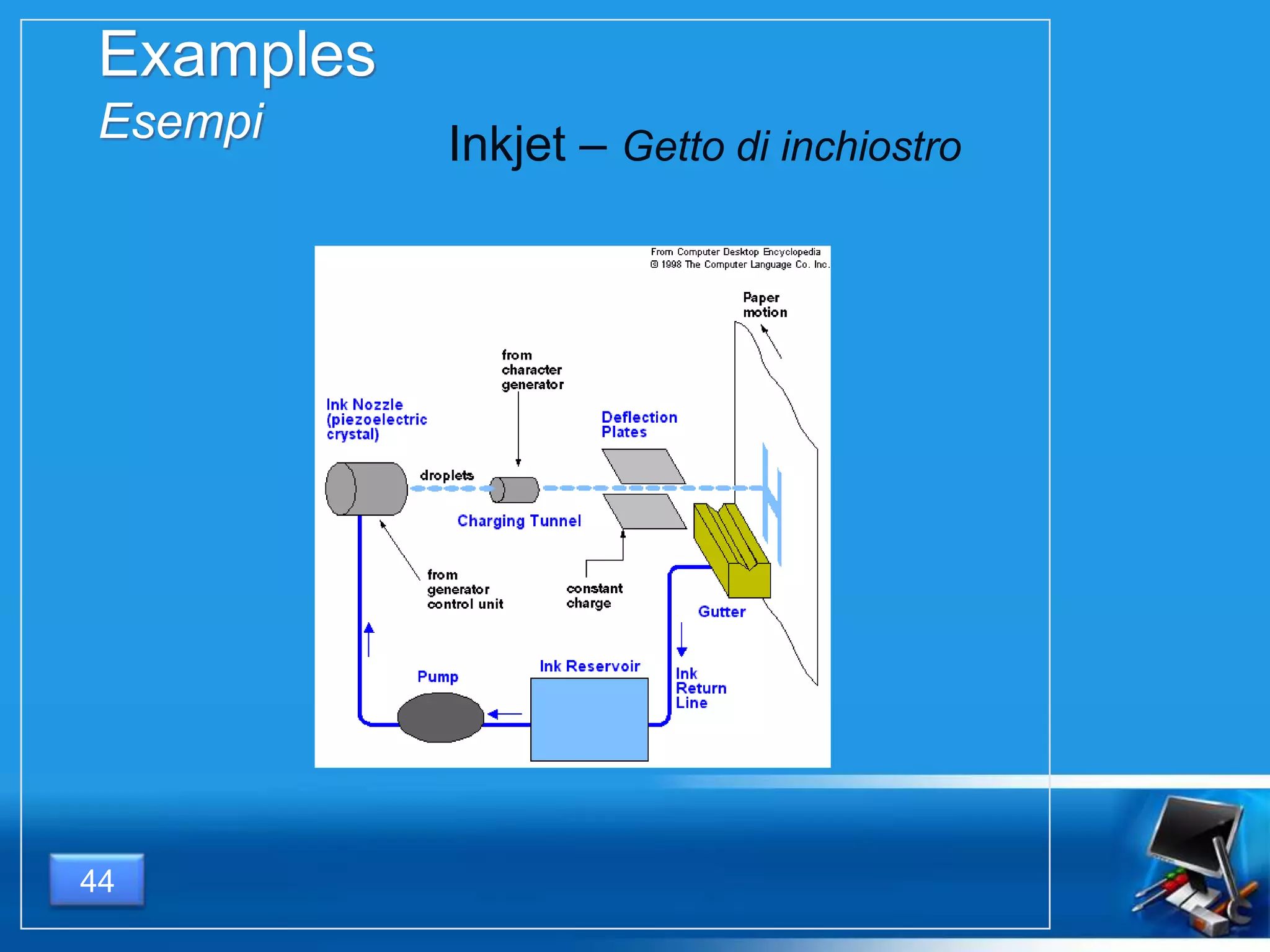
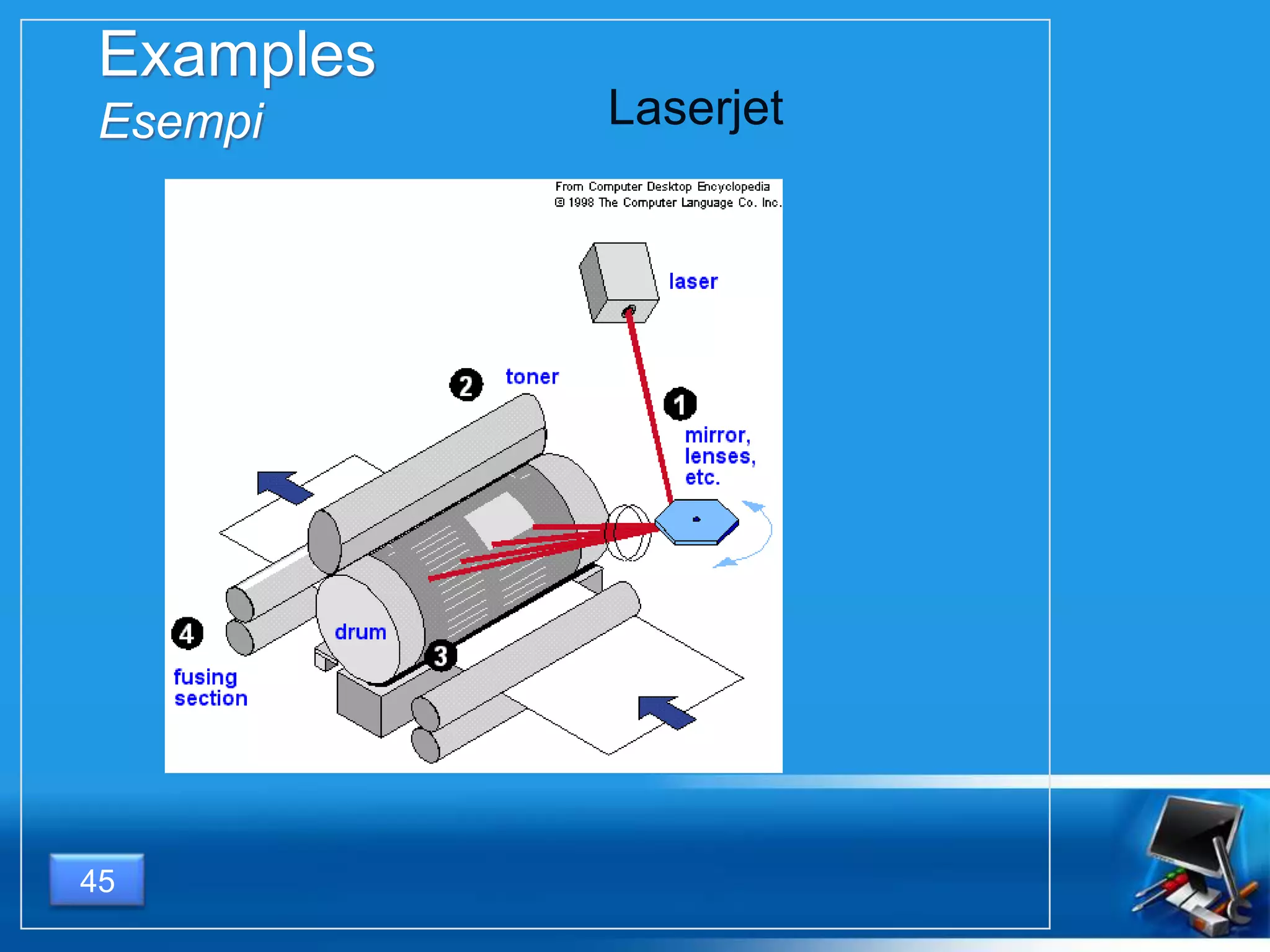
Il documento fornisce una panoramica dei componenti hardware essenziali di un personal computer, inclusi monitor, motherboard, CPU, RAM e dispositivi di input/output. Viene spiegata la classificazione dell'hardware e le differenze tra microprocessori CISC e RISC, nonché tra vari tipi di memoria. Inoltre, si discute delle prestazioni di CPU, dei dispositivi di archiviazione e delle interfacce di connessione.