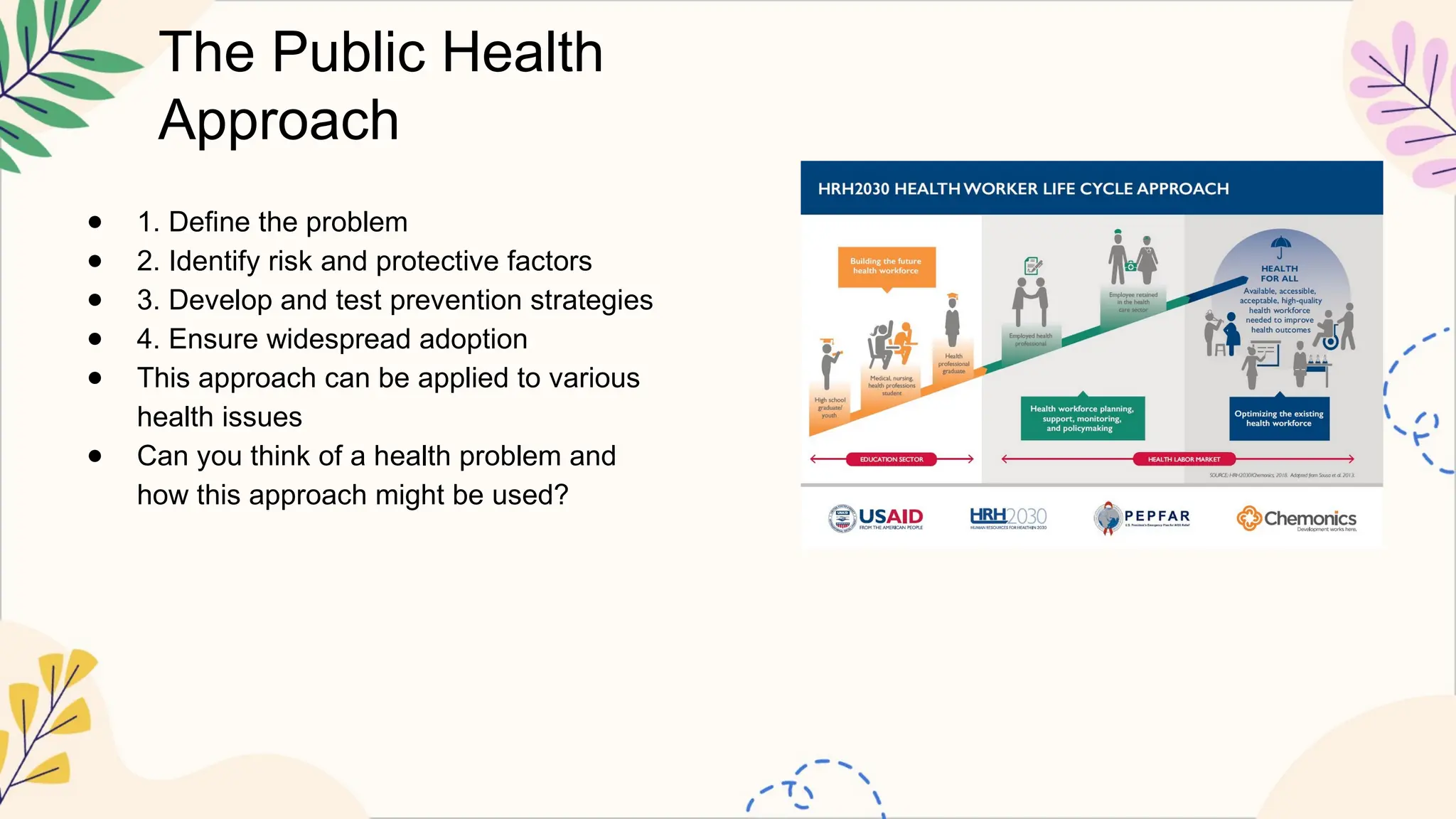
The document outlines the foundations of public health, focusing on its definition, core functions, historical milestones, social determinants, and major global health challenges. It emphasizes the importance of epidemiology, health promotion, disease prevention, ethics, and the interplay between health and environmental factors. Additionally, it discusses the future of public health, emerging trends, and diverse career opportunities in the field.