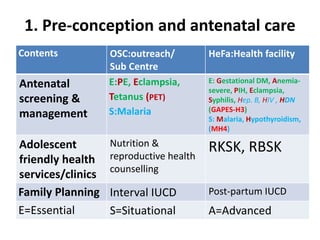
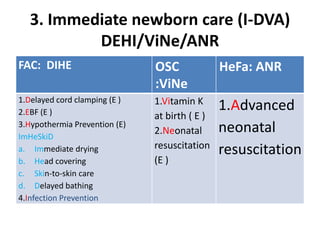
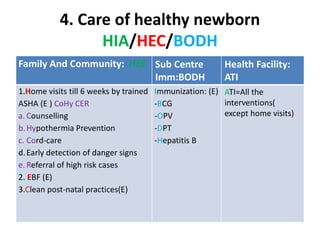
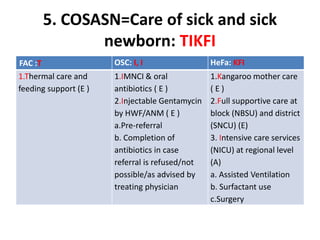
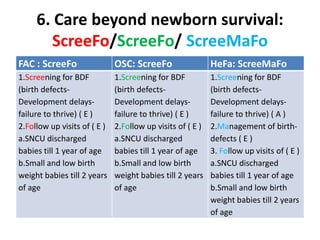
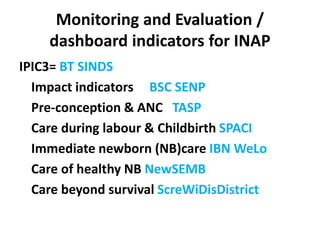
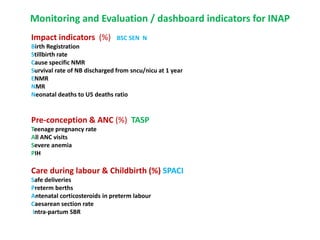
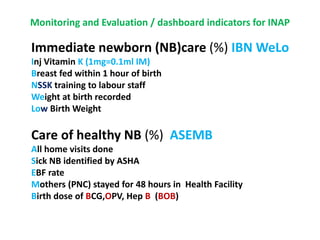
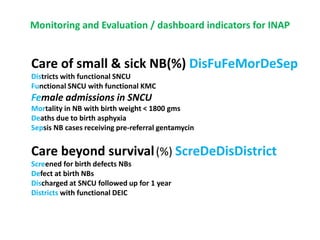
The India Newborn Action Plan (INAP) was launched in 2014 to achieve its goals of single digit neonatal mortality rate and stillbirth rate by 2030. It has 6 components covering pre-conception to post-newborn care delivered through 3 levels - family/community, outreach, and health facilities. Progress is monitored using a dashboard of impact and coverage indicators across the components like institutional deliveries, newborn resuscitation, breastfeeding, and post-discharge follow-up. The plan aims to strengthen newborn care through strategic essential, situational and advanced interventions tailored for different settings.