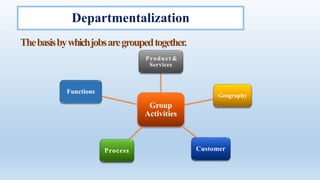
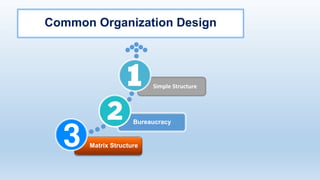
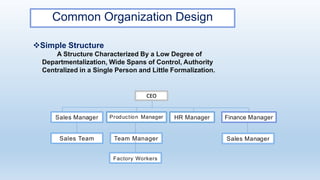
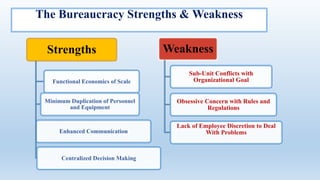
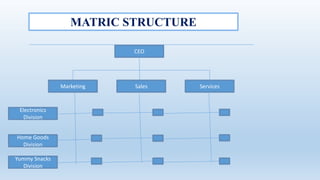
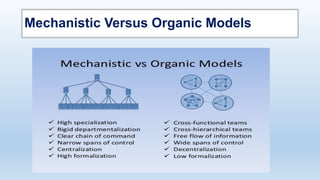
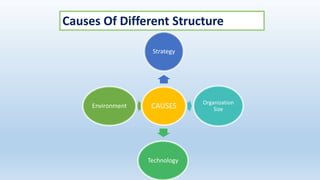
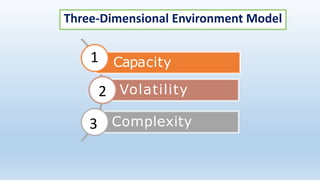
The document outlines the concept of organizational structure, detailing how tasks are divided, grouped, and coordinated within organizations. It discusses different types of structures such as mechanistic and organic models, as well as various designs including bureaucratic, matrix, and team structures. Factors influencing organizational structure, including strategy, size, and technology, are also explored.