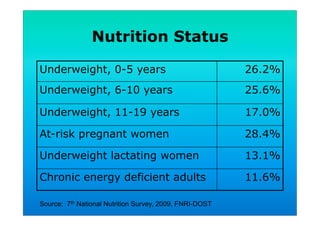
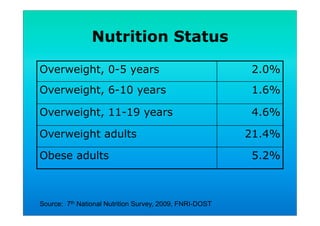
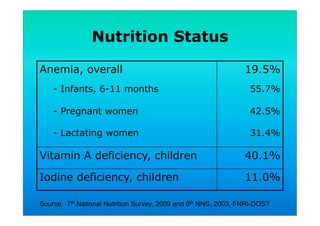
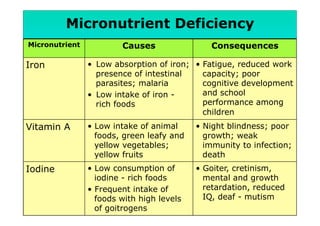
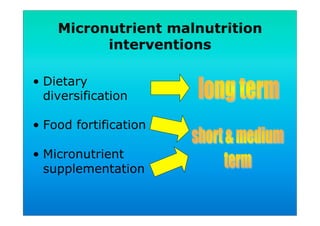
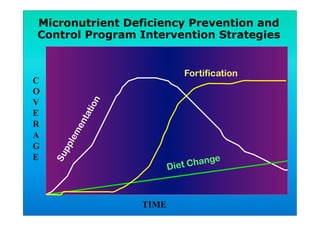
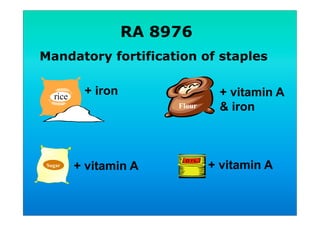
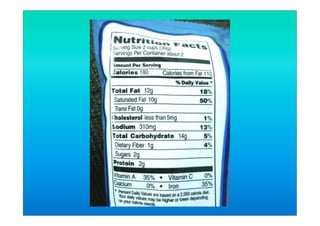
The document discusses fortified snack foods for kids. It provides background on malnutrition issues in the Philippines and food fortification programs and policies mandated by the National Nutrition Council and Republic Act 8976. Fortified foods can help address nutrient deficiencies, but snacks should be chosen carefully and consumed in moderation to avoid issues like obesity. A healthy diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, and whole grains instead of heavily processed foods high in fat, sugar, and salt.