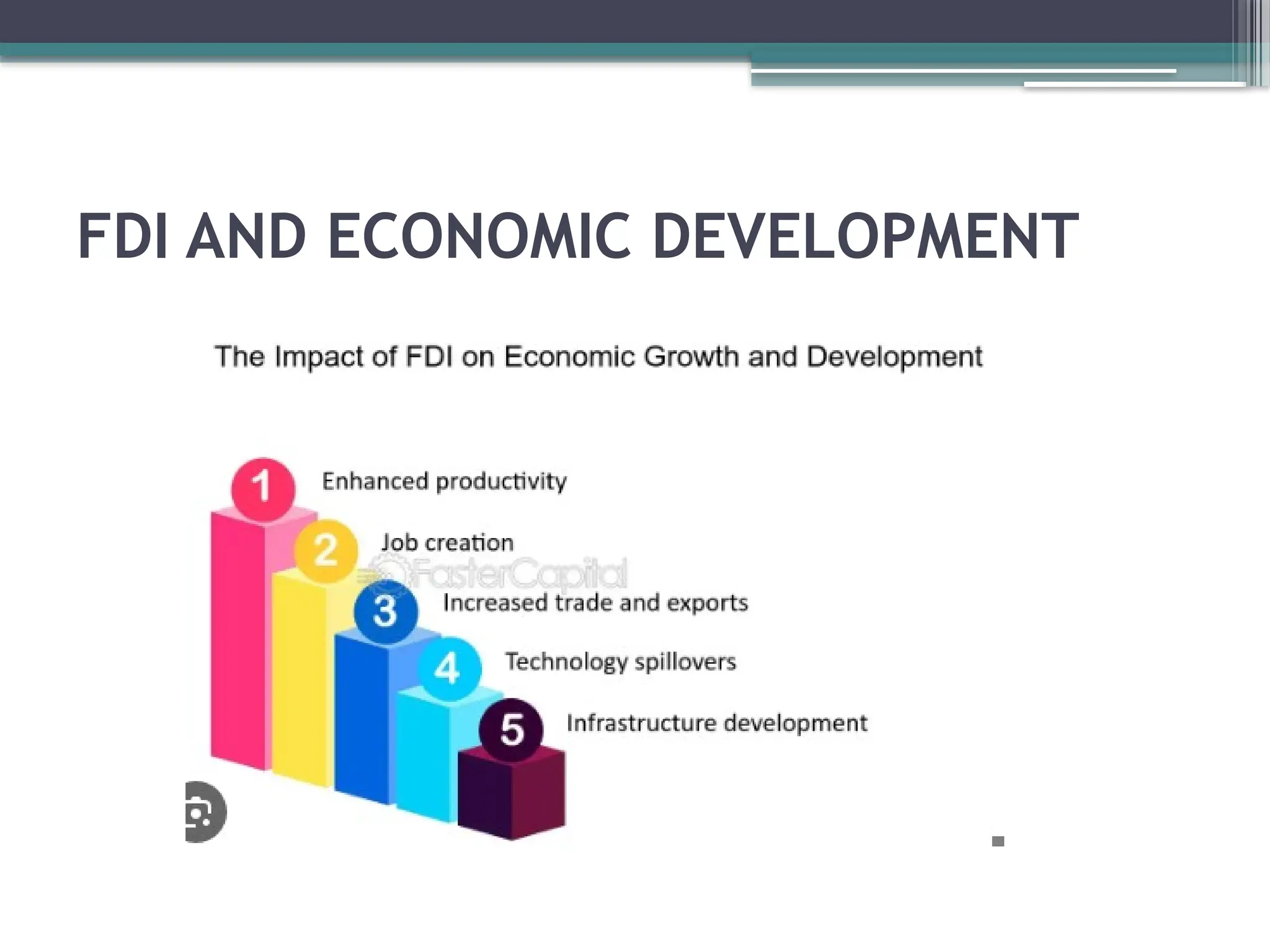
The document provides an overview of foreign direct investment (FDI), its significance in international economic integration, and various theories and approaches related to FDI. It explains different entry modes for FDI, the role of multinational corporations (MNCs), and the impact of foreign institutional investors (FIIs) in host countries, particularly in India. Additionally, it discusses the regulation of foreign trade and the process of disinvestment in public sector units to promote economic development.