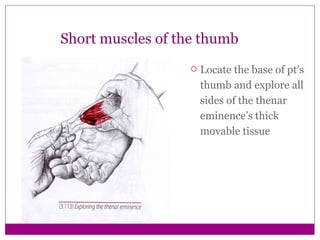
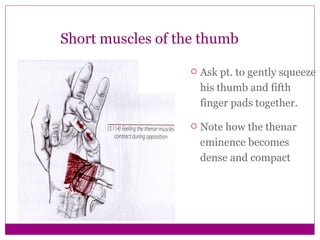
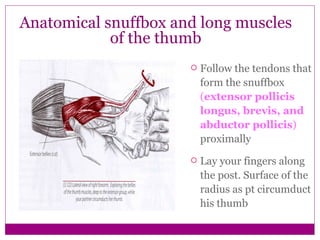
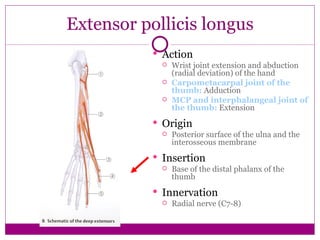
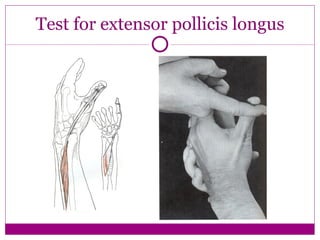
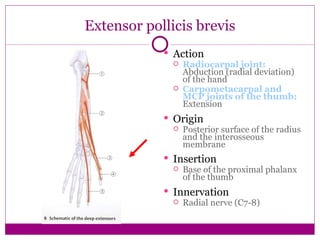
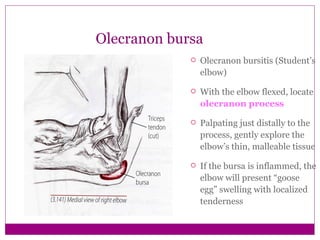
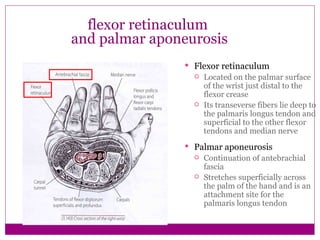
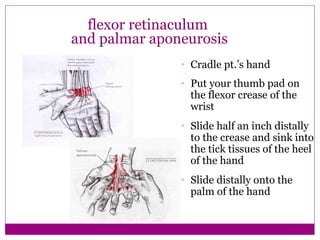
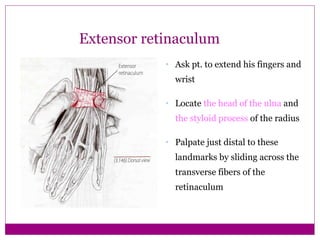
This document provides information about performing physical examinations of various muscles and ligaments in the hand and forearm. It describes how to locate and test the short muscles of the thumb, the extensor pollicis longus and brevis muscles, the abductor pollicis longus and brevis muscles, the anatomical snuffbox, and the radial and ulnar collateral ligaments. It also discusses palpating the radial head, annular ligament, olecranon bursa, flexor and extensor retinacula, and palmar aponeurosis.