Embed presentation
Download to read offline
















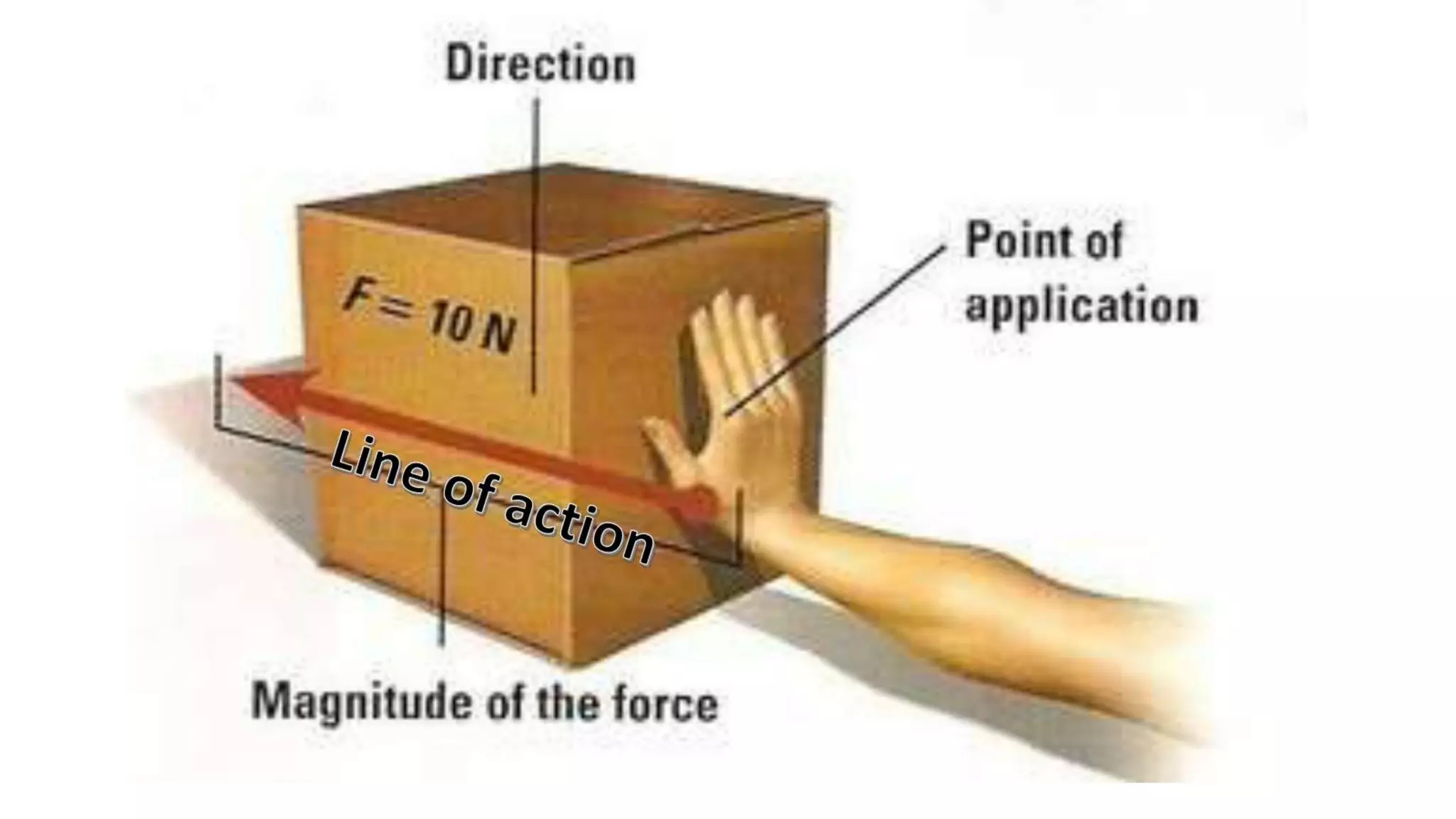













The document outlines a lesson plan on forces for students. It aims to have students define force using examples, describe motion as being caused by a push or pull, and determine how forces affect motion. The lesson includes two hands-on activities - one where students act out forces and others guess the action, and another where students manipulate a ball's motion and discuss the forces involved. It also defines different types of contact forces like applied force, friction, normal force, and tension.






























