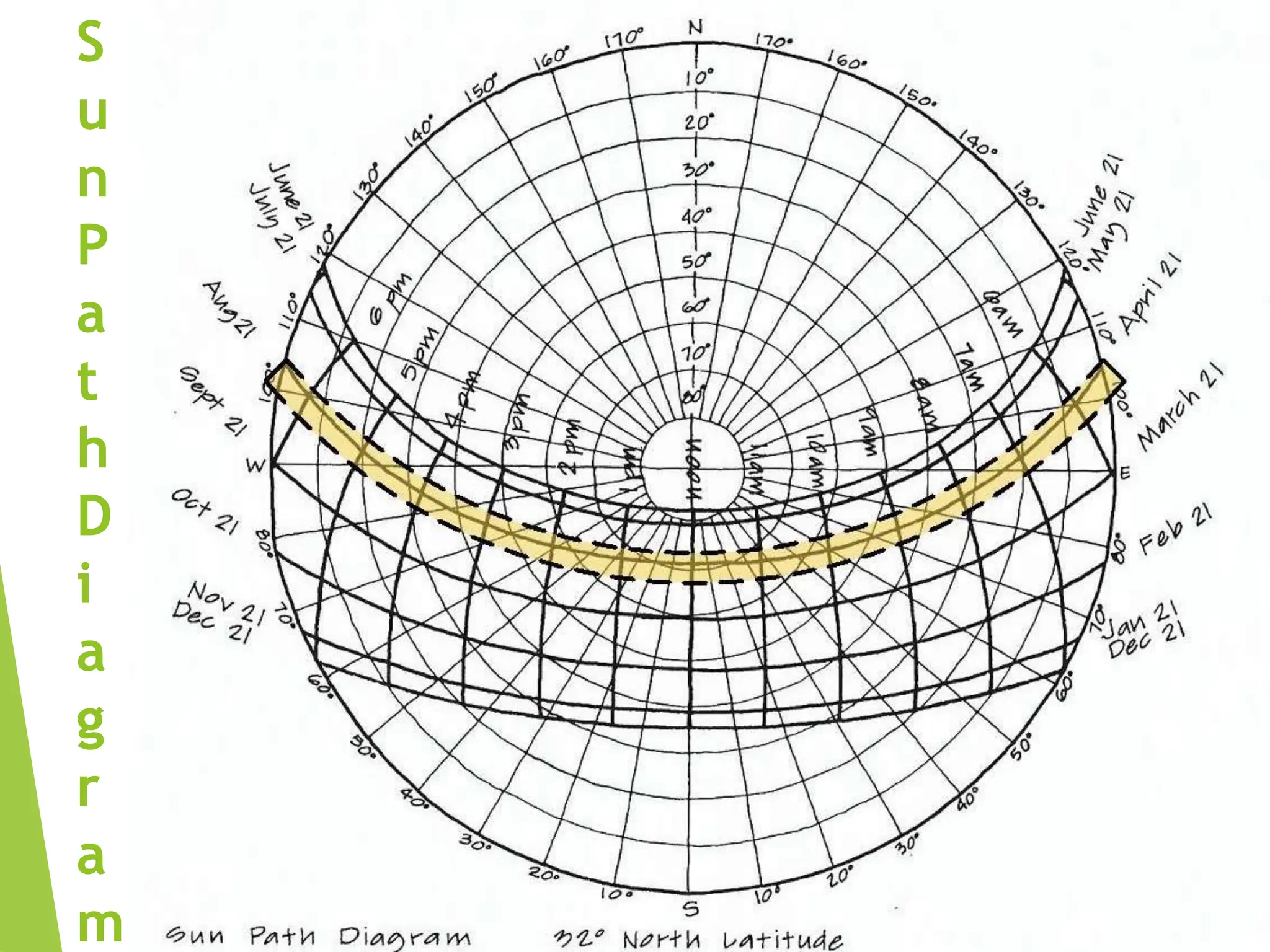
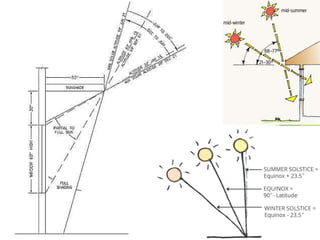
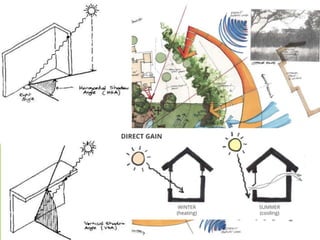
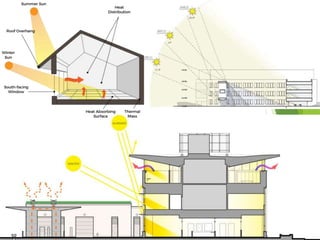
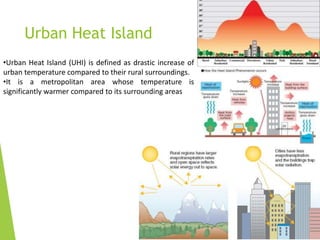
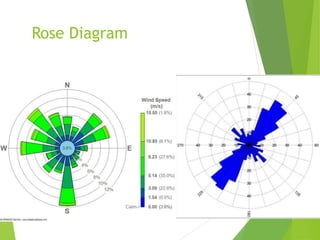
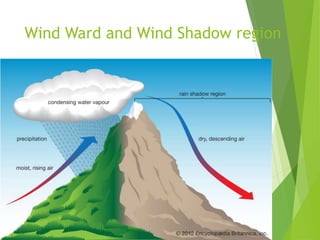
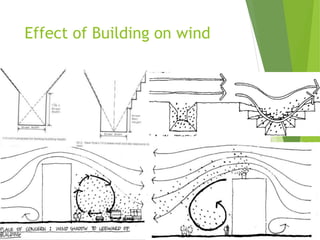
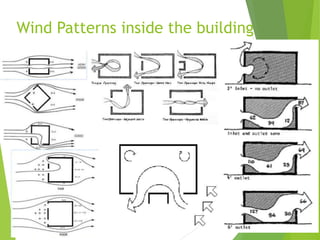
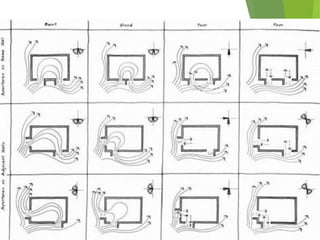
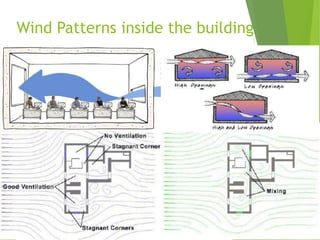
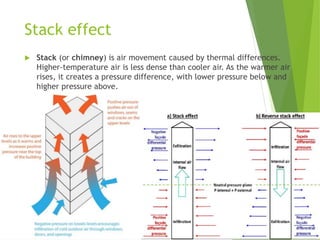
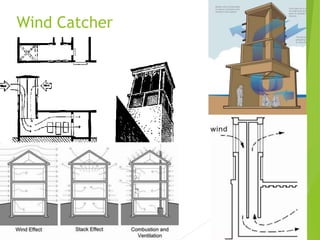
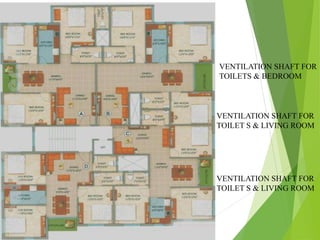
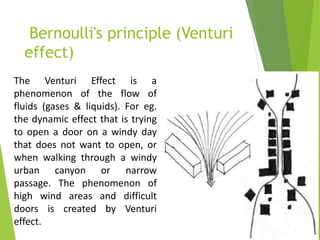
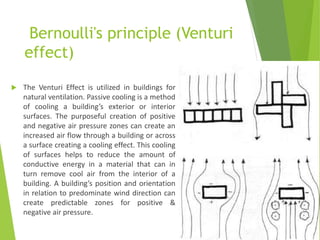
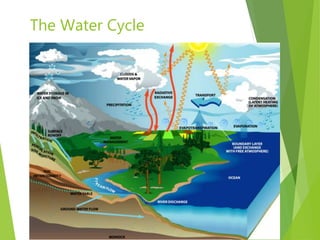
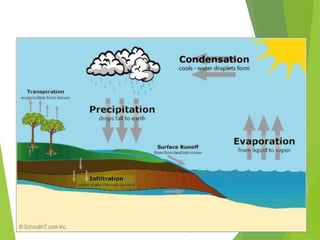
The document discusses urban heat islands, which are metropolitan areas that are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas due to human activities like industry, transportation, and dense development. It notes several factors that contribute to urban heat islands, such as lack of vegetation and presence of heat-absorbing surfaces like asphalt and concrete. The document also outlines some negative health impacts of higher urban temperatures and proposes strategies to decrease urban heat islands, such as increasing green spaces and using lighter-colored surfaces.