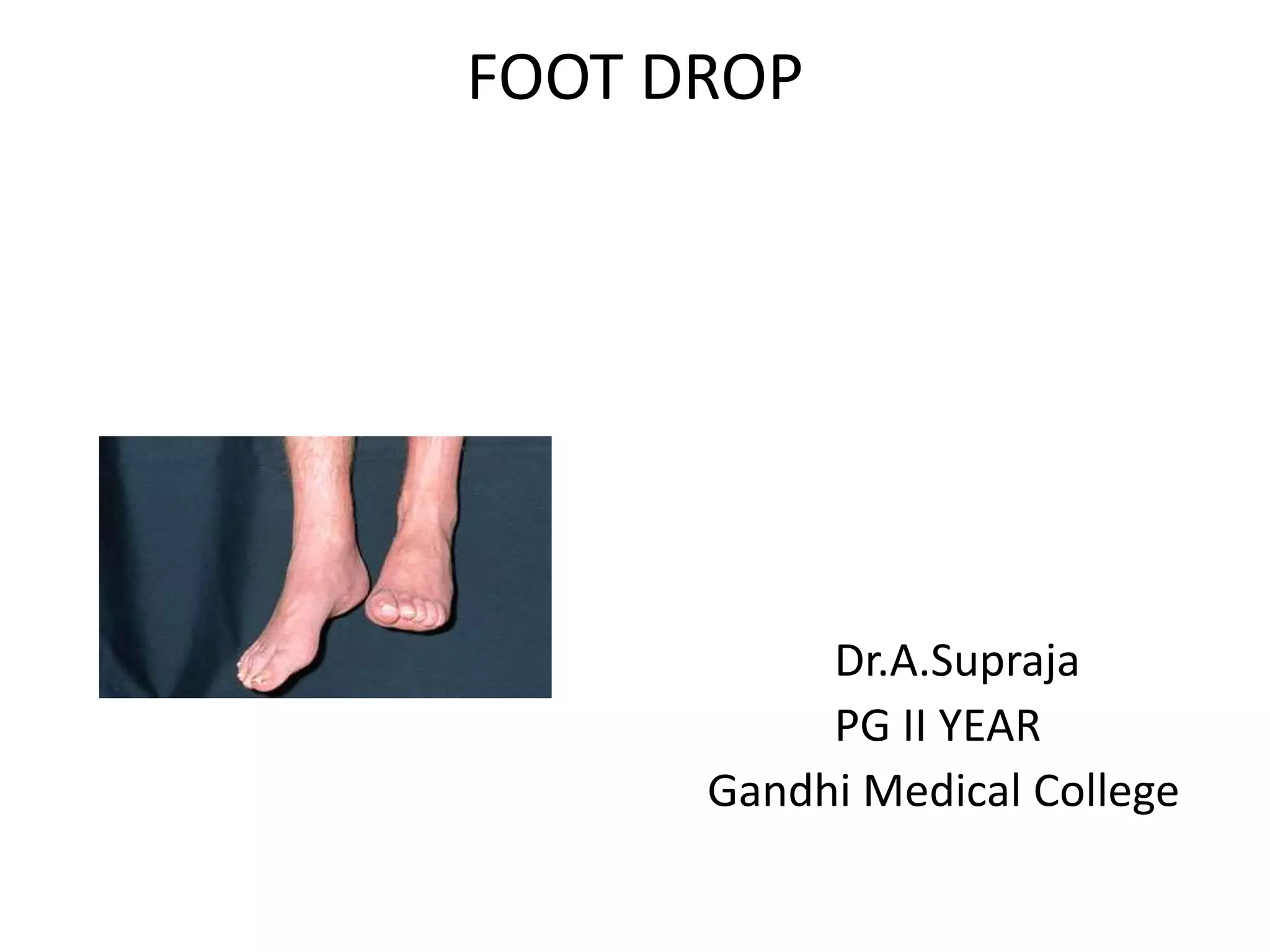
Foot drop is the inability to lift the front part of the foot. It can be caused by injuries or conditions that damage the common peroneal nerve. Symptoms include difficulty lifting the foot and dragging the toes. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but may include bracing, nerve stimulation, tendon transfers, or joint fusions. The goal is to improve mobility and gait.