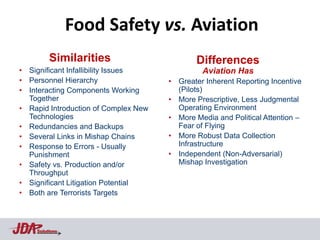
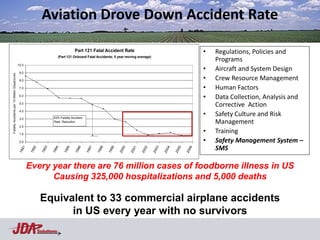
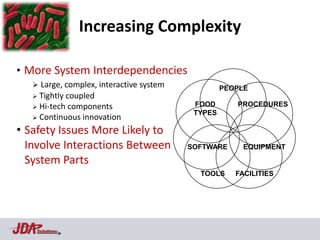
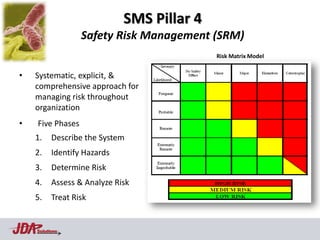
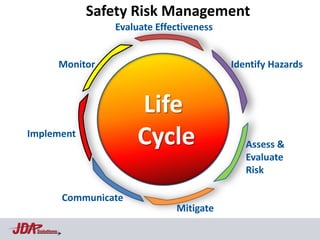
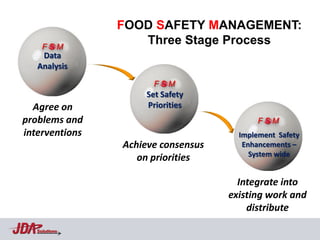
The document discusses using an aviation safety management system (SMS) model to help address food safety issues. It notes similarities between aviation and food safety such as infallibility issues, interacting components, and response to errors usually being punishment. Aviation saw an 83% reduction in fatal accident rates attributed to factors like regulations, safety culture/risk management, data collection/analysis, and SMS. The Heinrich Safety Triangle is presented showing how many incidents lead to accidents and how underlying causal factors need addressed. Areas discouraging voluntary data reporting in food safety are also discussed.