Embed presentation
Downloaded 53 times
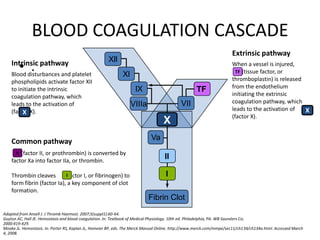










The blood coagulation cascade involves three pathways that ultimately lead to the formation of a fibrin clot. The intrinsic pathway is activated by disturbances in blood and platelet phospholipids and involves multiple coagulation factors leading to the activation of factor X. The extrinsic pathway is initiated when tissue factor is released from injured endothelium, also activating factor X. The common pathway follows, where factor Xa converts prothrombin to thrombin which then cleaves fibrinogen to form fibrin, an essential component of a clot.










