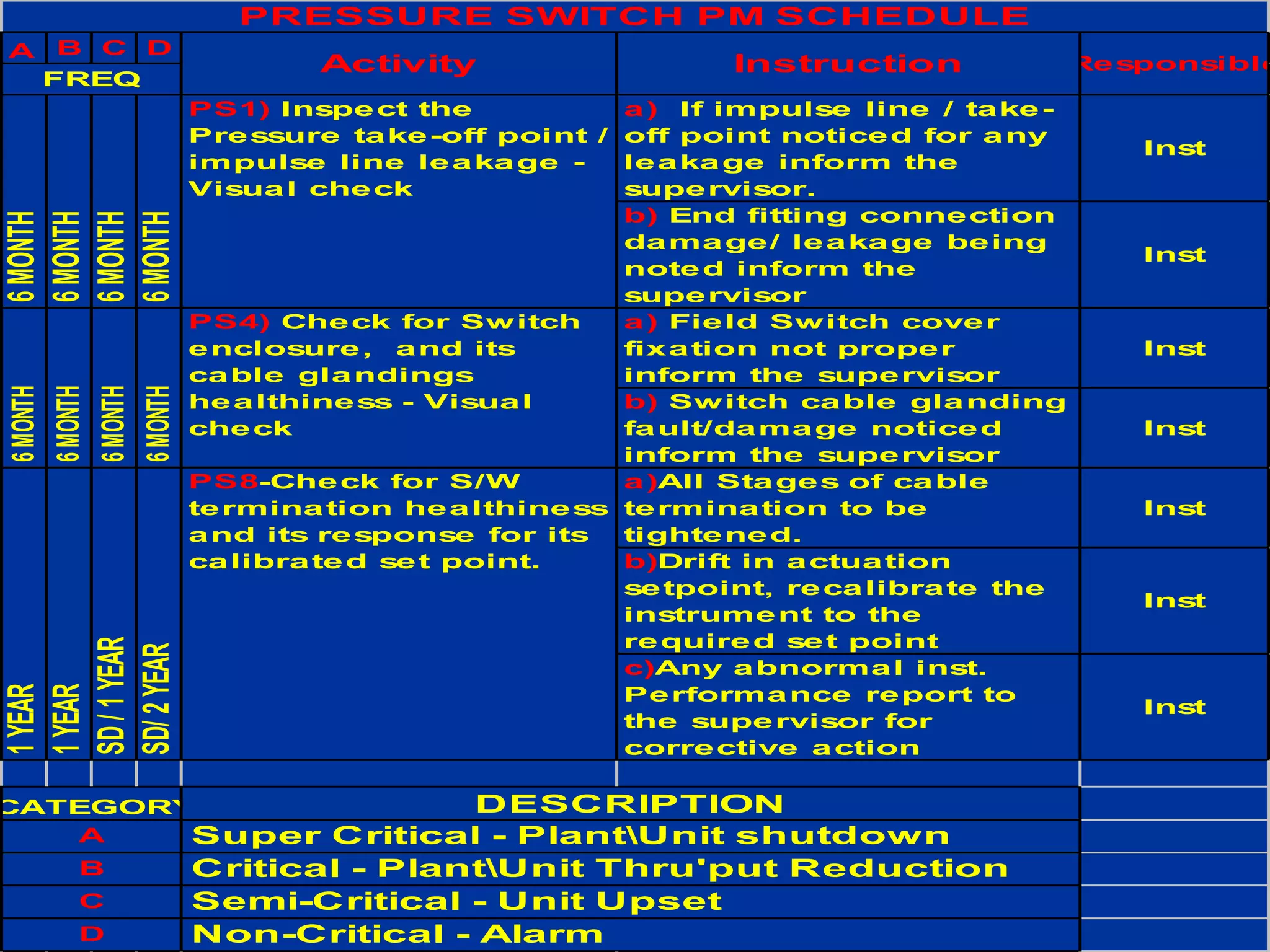
FMEA is a methodology that documents how an asset can fail and the consequences of each failure. It is used to identify critical assets, failure modes, and their effects. The document outlines the FMEA process which includes identifying failure modes and calculating a Risk Priority Number for each. Preventative maintenance tasks are then matched to failure modes to reduce risk. An example FMEA is provided for a pressure switch that lists potential failure modes, likelihood, severity, criticality ranking, and matched preventative maintenance tasks.