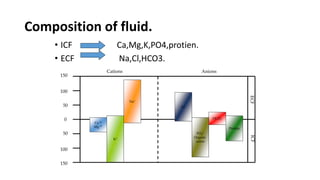
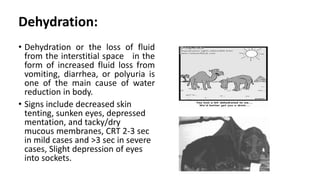
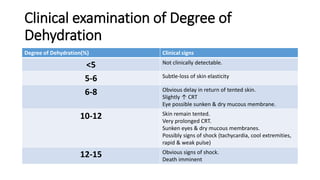
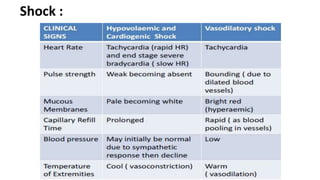
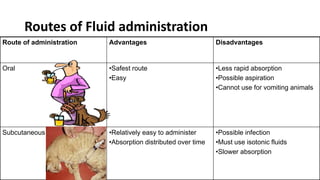
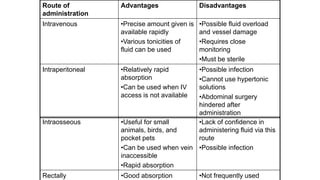
This document discusses fluid therapy, including the basics of body fluids, fluid composition, water balance, and fluid regulation. It covers the types of fluids used in therapy including crystalloids like lactated Ringer's solution and normal saline, as well as colloids. The routes of fluid administration and indications for fluid therapy are described. Signs of dehydration and fluid overload are also summarized. Calculations for fluid resuscitation based on weight and dehydration percentage are demonstrated through examples.