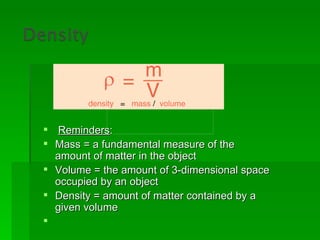
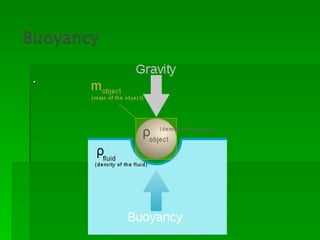
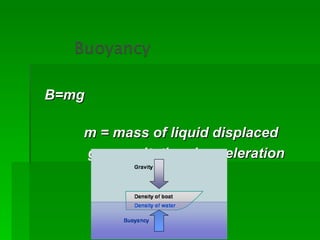
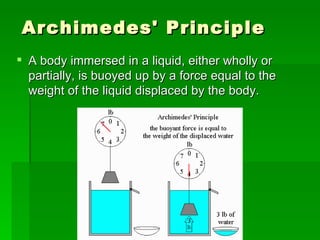
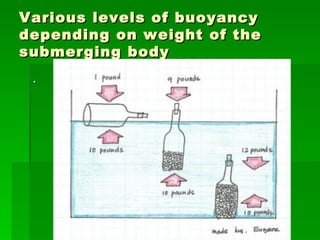
Buoyancy is the ability of an object to float. It is related to an object's density, with less dense objects floating more easily than denser objects. Buoyancy is caused by the upward force of displaced fluid acting on the submerged part of an object, and an object will float if this upward buoyant force is greater than the downward gravitational force on the object.