Embed presentation
Download to read offline





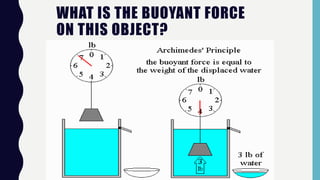



Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an immersed object. This force arises due to the pressure difference of the fluid acting on the submerged and exposed parts of the object. Archimedes' principle states that the buoyant force on an object equals the weight of the fluid it displaces. An object will float if its density is less than the density of the fluid it displaces.








