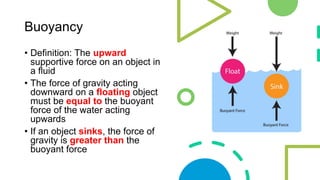
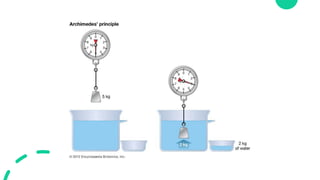
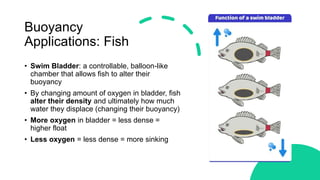
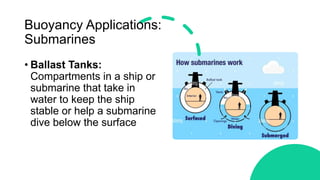
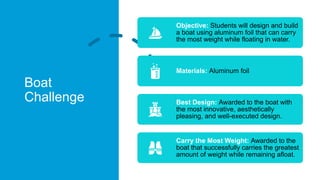
This document discusses Archimedes' principle and buoyancy. It explains that objects float if they displace a weight of fluid equal to their own weight, with the upward buoyant force equaling the weight of fluid displaced. Ships float because their shape displaces more water than a ball of the same weight, creating more upward buoyant force. Submarines and fish control their buoyancy through ballast tanks and swim bladders that alter their density. Oil spills are contained by oil's lower density causing it to float on water.