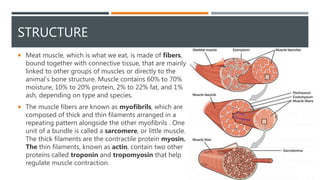
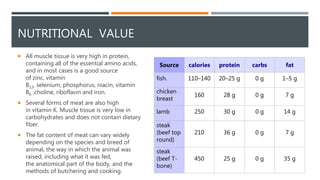
This document provides an overview of meat (flesh food) including its definition, composition, nutritional value, post-mortem changes, aging, curing, and consumption. Meat refers to muscles of warm-blooded animals and is composed primarily of water, protein, and fat. It spoils quickly but can be preserved through methods like aging, curing with salt, nitrates and nitrites, and smoking. Cured meats include products like bacon. Meat consumption varies globally based on culture, religion, economics, and health concerns.